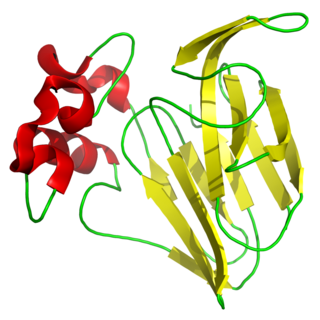
Thaumatin is a low-calorie sweetener and flavor modifier. The protein is often used primarily for its flavor-modifying properties and not exclusively as a sweetener.

The kinkajou is a tropical rainforest mammal of the family Procyonidae related to olingos, coatis, raccoons, and the ringtail and cacomistle. It is the only member of the genus Potos and is also known as the "honey bear". Kinkajous are arboreal, a lifestyle they evolved independently; they are not closely related to any other tree-dwelling mammal group.

Aspergillus flavus is a saprotrophic and pathogenic fungus with a cosmopolitan distribution. It is best known for its colonization of cereal grains, legumes, and tree nuts. Postharvest rot typically develops during harvest, storage, and/or transit. Its specific name flavus derives from the Latin meaning yellow, a reference to the frequently observed colour of the spores. A. flavus infections can occur while hosts are still in the field (preharvest), but often show no symptoms (dormancy) until postharvest storage or transport. In addition to causing preharvest and postharvest infections, many strains produce significant quantities of toxic compounds known as mycotoxins, which, when consumed, are toxic to mammals. A. flavus is also an opportunistic human and animal pathogen, causing aspergillosis in immunocompromised individuals.

Aspergillus is a genus consisting of several hundred mould species found in various climates worldwide.

Limacus flavus, known commonly as the cellar slug, the yellow slug, or the tawny garden slug, is a medium to large species of air-breathing land slug, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Limacidae.

Synsepalum dulcificum is a plant in the Sapotaceae family, native to tropical Africa. It is known for its berry that, when eaten, causes sour foods subsequently consumed to taste sweet. This effect is due to miraculin. Common names for this species and its berry include miracle fruit, miracle berry, miraculous berry, sweet berry, and in West Africa, where the species originates, agbayun, taami, asaa, and ledidi.
Miracle berry may refer to:

Moin-moin ( Yoruba) or moi-moi is a steamed or boiled bean pudding made from a mixture of washed and peeled beans and onions, fresh red peppers, spices, and often fish, eggs, and/or crayfish. It is a protein-rich Yoruba food that is commonly eaten across West Africa.

The yellow meadow ant, also known as the yellow hill ant, is a species of ant occurring in Europe, Asia, and North Africa. Populations in North America are now considered a different, related species, Lasius brevicornis.

The yellow canary is a small passerine bird in the finch family. It is a resident breeder in much of the western and central regions of southern Africa and has been introduced to Ascension and St Helena islands.

Thaumatococcus daniellii is a plant species from tropical Africa of the Marantaceae family. It is a large, rhizomatous, flowering herb native to the rainforests of western Africa in Sierra Leone, southeast to Gabon and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is also an introduced species in Australia and Singapore.

Crocus flavus, known as yellow crocus, Dutch yellow crocus or snow crocus, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Crocus of the family Iridaceae. It grows wild on the slopes of Greece, former Yugoslavia, Bulgaria, Romania and northwestern Turkey, with fragrant bright orange-yellow flowers. It is a small crocus (5–6 cm, despite the names of some cultivars, compared to the giant Dutch crocuses. Its cultivars are used as ornamental plants.
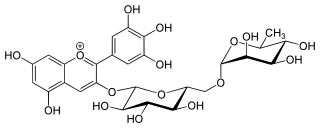
Tulipanin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-O-rutinoside of delphinidin. It can be found in Alstroemeria spp., Berberis spp., Cissus sicyoides, Hymenocallis spp., Manihot utilissima, Meliosma tenuis, Musa acuminata, Ophiopogon japonicus, Petunia exserta, Petunia reitzii, blackcurrant, Schismatoglottis concinna, Secale cereale, Solanum betaceum, Thaumatococcus daniellii, Tulipa spp and in eggplants.

Euodia is a plant genus in the family Rutaceae. Euodia is sometimes misspelled as Evodia. The species now included in the genus Tetradium were previously included in Euodia, and may be commonly referred to as euodia.

Geophilus flavus is a terrestrial, soil-dwelling, species of centipede in the Geophilidae family. G. flavus occurs in a range of habitats across central Europe, North America, Australia and other tropical regions. Geophilomorph centipedes, like centipedes generally, are primary predators, hunting predominantly in underground soil burrows or above ground leaf litter. Their consumption behaviours are influenced by environment and seasonal factors. Given their lack of economic value and marginal medical significance, G.flavus remains largely understudied in mainstream research. Some recent studies have detailed the evolutionary development of G.flavus and Geophilidae generally, illustrating developed predatory features like forcipule venom glands.

Osmodes laronia, the large white-spots, is a butterfly in the family Hesperiidae. It is found in Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Togo, Nigeria, Cameroon, Gabon, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda and western Kenya. The habitat consists of forests.

Osmodes omar, the obsolete white-spots, is a butterfly in the family Hesperiidae. The species was first described by Charles Swinhoe in 1916. It is found in Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo, the Central African Republic, the northern part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda and north-western Tanzania. The habitat consists of forests.

Aspergillus parasiticus is a fungus belonging to the genus Aspergillus. This species is an unspecialized saprophytic mold, mostly found outdoors in areas of rich soil with decaying plant material as well as in dry grain storage facilities. Often confused with the closely related species, A. flavus, A. parasiticus has defined morphological and molecular differences. Aspergillus parasiticus is one of three fungi able to produce the mycotoxin, aflatoxin, one of the most carcinogenic naturally occurring substances. Environmental stress can upregulate aflatoxin production by the fungus, which can occur when the fungus is growing on plants that become damaged due to exposure to poor weather conditions, during drought, by insects, or by birds. In humans, exposure to A. parasiticus toxins can cause delayed development in children and produce serious liver diseases and/or hepatic carcinoma in adults. The fungus can also cause the infection known as aspergillosis in humans and other animals. A. parasiticus is of agricultural importance due to its ability to cause disease in corn, peanut, and cottonseed.

Aframomum daniellii, also known as African cardamom, is a species in the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It was first described by Joseph Dalton Hooker, and got its current name from Karl Moritz Schumann.


















