
Cortinarius anomalus, also known as the variable webcap, is a basidiomycete fungus of the genus Cortinarius. It produces a medium-sized mushroom with a grayish-brown cap up to 5 cm (2 in) wide, gray-violet gills and a whitish stem with pale yellow belts below. The mushroom grows solitarily or in scattered groups on the ground in deciduous and coniferous forests. It is found throughout the temperate zone of the northern hemisphere.

Cortinarius praestans, also known as the goliath webcap, is a basidiomycete mushroom of the genus Cortinarius. The mushroom has orangish-yellow caps that reach up to 20 cm (7.9 in) in diameter, and thick club-shaped stipes up to 15 cm (5.9 in) long. The edible mushroom is found in Europe.

Cortinarius porphyroideus, commonly known as purple pouch fungus, is a secotioid species of fungus endemic to New Zealand. It was one of six species that appeared as part of a series depicting native New Zealand fungi on stamps, released in 2002.

Phlegmacium basorapulum is a species of truffle-like fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Found in New South Wales, Australia, the species was described as new to science in 2010.

Thaxterogaster caesibulga is a species of truffle-like fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Found in New South Wales, Australia, the species was described as new to science in 2010.

Thaxterogaster cinereoroseolus is a species of truffle-like fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Found in New South Wales, Australia, the species was described as new to science in 2010.

Cortinarius kaputarensis is a species of truffle-like fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Described as a new species in 2010, it is known only from New South Wales in Australia.

Cortinarius maculobulga is a species of truffle-like fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Found only in New South Wales, Australia, it was described as new to science in 2010.

Cortinarius nebulobrunneus is a species of truffle-like fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Found in New South Wales, Australia, the species was described as new to science in 2010.

Cortinarius sinapivelus is a species of truffle-like fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Known only from New South Wales, it was described as new to science in 2010.

Cortinarius iodes, commonly known as the spotted cort or the viscid violet cort, is a species of agaric fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. The fruit bodies have small, slimy, purple caps up to 6 cm (2.4 in) in diameter that develop yellowish spots and streaks in maturity. The gill color changes from violet to rusty or grayish brown as the mushroom matures. The species range includes eastern North America, Central America, northern South America, and northern Asia, where it grows on the ground in a mycorrhizal association with deciduous trees. The mushroom is not recommended for consumption. Cortinarius iodeoides, one of several potential lookalike species, can be distinguished from C. iodes by its bitter-tasting cap cuticle.

Cortinarius bovarius is an agaric fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Described as new to science in 2013, it is found in western North America. The specific epithet bovarius refers to the similarity to the European lookalike Cortinarius bovinus.
Phlegmacium boreicyanites is a species of fungus in the family Cortinariaceae

Thaxterogaster caesiolamellatus is a species of fungus in the family Cortinariaceae.

Cortinarius cyanites is a basidiomycete fungus of the genus Cortinarius native to Europe.
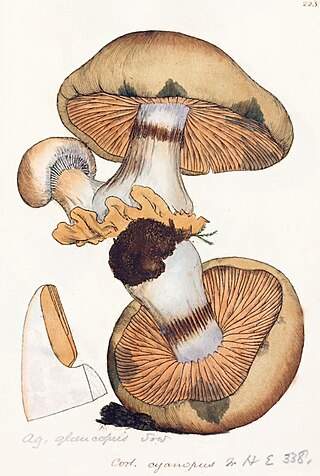
Phlegmacium glaucopus is a species of fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. It is commonly known as the blue-foot webcap.

Cortinarius diaphorus is a species of purple pouch fungus in the genus Cortinarius endemic to Aotearoa New Zealand.

Thaxterogaster austrovaginatus is a species of ectomycorrhizal fungus in the famlily Cortinariaceae.

Cortinarius violaceocystidiatus is a species of purple pouch fungus in the genus Cortinarius. It is endemic to Aotearoa New Zealand.
Thaxterogaster is a genus of fungi in the family Cortinariaceae.












