
Leonor Michaelis was a German biochemist, physical chemist, and physician, known for his work with Maud Menten on enzyme kinetics in 1913, as well as for work on enzyme inhibition, pH and quinones.

Flavoproteins are proteins that contain a nucleic acid derivative of riboflavin. These proteins are involved in a wide array of biological processes, including removal of radicals contributing to oxidative stress, photosynthesis, and DNA repair. The flavoproteins are some of the most-studied families of enzymes.
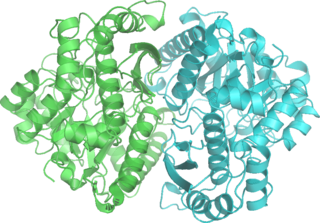
Phosphopyruvate hydratase, usually known as enolase, is a metalloenzyme (EC 4.2.1.11) that catalyses the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate (2-PG) to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), the ninth and penultimate step of glycolysis. The chemical reaction is:
Genes, Brain and Behavior is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in the fields of behavioral, neural, and psychiatric genetics. It is published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the International Behavioural and Neural Genetics Society. The journal was established in 2002 as a quarterly and is currently published monthly. G2B is a hybrid open access journal, but two years after publication all content is available for free online.

Semenogelin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SEMG1 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is the predominant protein in semen. The encoded secreted protein is involved in the formation of a gel matrix that encases ejaculated spermatozoa. The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) protease processes this protein into smaller peptides, with each possibly having a separate function. The proteolysis process breaks down the gel matrix and allows the spermatozoa to move more freely. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.

Gamma-enolase, also known as enolase 2 (ENO2) or neuron specific enolase (NSE), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ENO2 gene. Gamma-enolase is a phosphopyruvate hydratase.

UMP-CMP kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CMPK1 gene.

Enolase 3 (ENO3), more commonly known as beta-enolase (ENO-β), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ENO3 gene.

Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of biochemistry and biophysics. It was established in 1959 by Academic Press and is currently published by Elsevier. The editor-in-chief is Wolfgang Baumeister.

The Journal of Neurochemistry is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of neurochemistry. It is published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the International Society for Neurochemistry and was established in 1956. The editor-in-chief is Andrew J. Lawrence.

Alpha oxidation (α-oxidation) is a process by which certain branched-chain fatty acids are broken down by removal of a single carbon from the carboxyl end. In humans, alpha-oxidation is used in peroxisomes to break down dietary phytanic acid, which cannot undergo beta-oxidation due to its β-methyl branch, into pristanic acid. Pristanic acid can then acquire acetyl-CoA and subsequently become beta oxidized, yielding propionyl-CoA.

Traffic is a monthly, peer-reviewed, scientific journal, which was established in 2000, and is published by Wiley-Blackwell. The online version is at the Wiley Online Library. This journal is co-edited by Eric Chevet, Antonella De Matteis, Eeva-Liisa Eskelinen, and Hesso Farhan. The journal covers all aspects of signal transduction in health and disease, for both mammalian and non-mammalian biological systems.

BioSystems is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering experimental, computational, and theoretical research that links biology, evolution, and the information processing sciences. It was established in 1967 as Currents in Modern Biology by Robert G. Grenell. In 1972 the journal was renamed Currents in Modern Biology: Bio Systems, which was shortened to BioSystems in 1974. Previous editors include J.P. Schadé, Alan W. Schwartz, Sidney W. Fox, Michael Conrad, Lynn Margulis, David B. Fogel, Gary B. Fogel, George Kampis, Francisco Lara-Ochoa, Koichiro Matsuno, Ray Paton, and W. Mike L. Holcombe.
4-methylaminobutanoate oxidase (methylamine-forming) (EC 1.5.3.21, mao (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 4-methylaminobutanoate methylamidohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Adrenodoxin-NADP+ reductase (EC 1.18.1.6, adrenodoxin reductase, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-adrenodoxin reductase, ADR, NADPH:adrenal ferredoxin oxidoreductase) is an enzyme with systematic name adrendoxin:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Biotin-independent malonate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.88, malonate decarboxylase (without biotin), malonate decarboxylase, MDC) is an enzyme with systematic name malonate carboxy-lyase (biotin-independent). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

The Sir Hans Krebs Lecture and Medal is awarded annually by the Federation of European Biochemical Societies (FEBS) for outstanding achievements in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology or related sciences.

The Zeitschrift für Gerontologie und Geriatrie is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering gerontology and geriatrics. It is published 8 times a year in German by Springer Science+Business Media. The journal was established in 1968 as the Zeitschrift für Gerontologie, obtaining its current title in 1995.

Athel Cornish-Bowden is a British biochemist known for his numerous textbooks, particularly those on enzyme kinetics and his work on metabolic control analysis.
Jan-Hendrik HofmeyrFRSSAf is one of the leaders in the field of metabolic control analysis and the quantitative analysis of metabolic regulation.















