Related Research Articles

Neurospora is a genus of Ascomycete fungi. The genus name, meaning "nerve spore" refers to the characteristic striations on the spores that resemble axons.

The order Sordariales is one of the most diverse taxonomic groups within the Sordariomycetes.

The Pyronemataceae are a family of fungi in the order Pezizales. It is the largest family of the Pezizales, encompassing 75 genera and approximately 500 species. Phylogenetic analyses does not support the prior classifications of this family, and suggest that the family is not monophyletic as it is currently circumscribed.
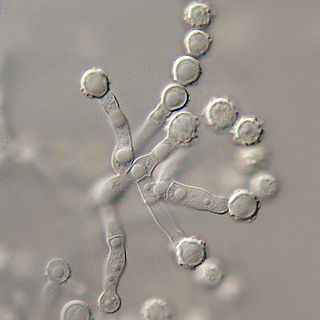
Microascus is a genus of fungi in the family Microascaceae.
Lophotrichus is a genus of fungi in the family Microascaceae.
Kernia is a genus of fungi in the family Microascaceae.
Zopfia is a genus of fungi in the family Zopfiaceae. The widespread genus contained 5 species, until another species was accepted.
Monosporascus is a genus of fungi in the family Diatrypaceae. It has nine species. The type species, Monosporascus cannonballus, is a widespread plant pathogen that causes vine decline of melon and watermelon crops.
Cercophora is a genus of fungi which was within the Lasiosphaeriaceae family. As of 2020, it was placed into the Neoschizotheciaceae family.
Zopfiella is a genus of fungi within the Lasiosphaeriaceae family.
Achaetomium is a genus of fungi within the Chaetomiaceae family.
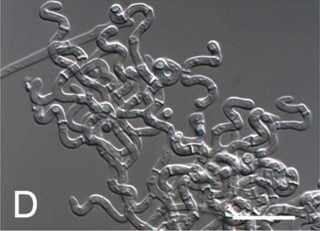
Arachnomyces is a genus of cleistothecial ascomycete fungi described in 1902, of which the anamorph (asexual) stage is the genus Onychocola. Although morphologically similar to members of other families, the fungus now belongs to its own monotypic family Arachnomycetaceae, which is the only family in the monotypic order Arachnomycetales.
Preussia is a genus of fungi in the family Sporormiaceae. The widespread genus contains 51 species that grow on dung or in the soil.

A protist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. The protists do not form a natural group, or clade, since they exclude certain eukaryotes with whom they share a common ancestor; but, like algae or invertebrates, the grouping is used for convenience. In some systems of biological classification, such as the popular five-kingdom scheme proposed by Robert Whittaker in 1969, the protists make up a kingdom called Protista, composed of "organisms which are unicellular or unicellular-colonial and which form no tissues". In the 21st century, the classification shifted toward a two-kingdom system of protists: Chromista and Protozoa.
Thielavia subthermophila is a ubiquitous, filamentous fungus that is a member of the phylum Ascomycota and order Sordariales. Known to be found on plants of arid environments, it is an endophyte with thermophilic properties, and possesses dense, pigmented mycelium. Thielavia subthermophila has rarely been identified as a human pathogen, with a small number of clinical cases including ocular and brain infections. For treatment, antifungal drugs such as amphotericin B have been used topically or intravenously, depending upon the condition.

The Coniochaeta are a genus of pleomorphic yeasts of the order Coniochaetales and are pathogens of trees. Some species have also been found to form endophytic associations within plants in which they live inside plant tissues but do not actually harm the organism. They can take the form of pink to brown colonies, hyphae, conidiophores or sclerotia. In 2013, the Lecythophora were merged with the Coniochaeta, following suggestions by Ziauddin Khan et al.
References
- ↑ Zopf W. (1872). "Thielavia basicola Zopf. Genus novum Perisporiacearum". Verhandlungen des Botanischen Vereins für die Provinz Brandenburg und die Angrenzenden Länder. 18: 101–5.
- 1 2 Liu D. (2011). "Myceliopthora and Thielavia". Molecular Detection of Human Fungal Pathogens. CRC Press. pp. 445–. ISBN 978-1-4398-1240-2.
- ↑ Kirk PM, Cannon PF, Minter DW, Stalpers JA (2008). Dictionary of the Fungi (10th ed.). Wallingford, UK: CAB International. p. 688. ISBN 978-0-85199-826-8.
- ↑ Burkhardt, Lotte (2022). Eine Enzyklopädie zu eponymischen Pflanzennamen [Encyclopedia of eponymic plant names](pdf) (in German). Berlin: Botanic Garden and Botanical Museum, Freie Universität Berlin. doi:10.3372/epolist2022. ISBN 978-3-946292-41-8 . Retrieved January 27, 2022.
- 1 2 "Thielavia - Search Page". www.speciesfungorum.org. Species Fungorum. Retrieved 16 November 2022.