PubChem is a database of chemical molecules and their activities against biological assays. The system is maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), a component of the National Library of Medicine, which is part of the United States National Institutes of Health (NIH). PubChem can be accessed for free through a web user interface. Millions of compound structures and descriptive datasets can be freely downloaded via FTP. PubChem contains multiple substance descriptions and small molecules with fewer than 100 atoms and 1,000 bonds. More than 80 database vendors contribute to the growing PubChem database.

The bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type IA also known as BMPR1A is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BMPR1A gene. BMPR1A has also been designated as CD292.

Activin receptor type-1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACVR1B gene.
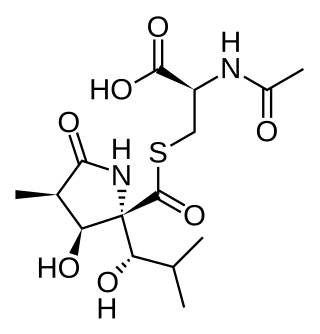
Lactacystin is an organic compound naturally synthesized by bacteria of the genus Streptomyces first identified as an inducer of neuritogenesis in neuroblastoma cells in 1991. The target of lactacystin was subsequently found to be the proteasome on the basis of its affinity for certain catalytic subunits of the proteasome by Fenteany and co-workers in 1995. The proteasome is a protein complex responsible for the bulk of proteolysis in the cell, as well as proteolytic activation of certain protein substrates. Lactacystin was the first non-peptidic proteasome inhibitor discovered and is widely used as a research tool in biochemistry and cell biology. The transformation product of lactacystin clasto-lactacystin β-lactone covalently modifies the amino-terminal threonine of specific catalytic subunits of the proteasome, a discovery that helped to establish the proteasome as a mechanistically novel class of protease: an amino-terminal threonine protease. The molecule is commonly used in biochemistry and cell biology laboratories as a selective inhibitor of the proteasome. The first total synthesis of lactacystin was developed in 1992 by Corey and Reichard, and a number of other syntheses of this molecule have also been published. There are more than 1,660 entries for lactacystin in PubMed as of January 2019.

AKT2, also known as RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKT2 gene. It influences metabolite storage as part of the insulin signal transduction pathway.

LIM domain kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the LIMK1 gene.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMK4 gene.

RAC-gamma serine/threonine-protein kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKT3 gene.

5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKAA1 gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase Sgk3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SGK3 gene.

Polo-like kinase 3 (Drosophila), also known as PLK3, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the PLK3 gene.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 10 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAP3K10 gene.

Microtubule-associated serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAST2 gene. The protein encoded by this gene controls TRAF6 and NF-kappaB activity.

Dual specificity protein kinase TTK also known as Mps1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TTK gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase 38 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the STK38 gene.

Fas-activated serine/threonine kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FASTK gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase 38-like is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the STK38L gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase 10 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the STK10 gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase 19 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the STK19 gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase DCLK1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DCLK1 gene.

















