
The 2004 Pacific hurricane season had 17 tropical cyclones, of which 12 became named storms, 6 became hurricanes, and 3 became major hurricanes. This timeline documents all the storm formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, as well as dissipation. It also includes information which was not operationally released, meaning that information from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center, such as information on a storm that was not operationally warned on, have been included. The season officially began on May 15, 2004, in the eastern Pacific proper and lasted until November 30 that same year. Areas east of 140°W are under the purview of the National Hurricane Center (NHC); the area between the International Date Line and 140°W, or the central Pacific, is under the purview of the Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC).

The 2005 Pacific hurricane season was the least active season since the 2001 season, producing 16 tropical depressions; 15 of which became tropical storms or hurricanes. The season officially started on May 15, 2005 in the eastern Pacific, designated as the area east of 140°W, and on June 1, 2005 in the central Pacific, which is between the International Date Line and 140°W, and lasted until November 30, 2005. These dates typically limit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific basin. This timeline documents all the storm formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, as well as dissipation. The timeline also includes information which was not operationally released, meaning that information from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center, such as information on a storm that was not operationally warned on, has been included.

The 2006 Pacific hurricane season was the most active since the 2000 season, producing 21 tropical depressions; 19 of which became tropical storms or hurricanes. The season officially started on May 15, 2006 in the eastern Pacific, designated as the area east of 140°W, and on June 1, 2006 in the central Pacific, which is between the International Date Line and 140°W, and lasted until November 30, 2006. These dates typically limit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific basin. This timeline documents all the storm formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, as well as dissipation. The timeline also includes information which was not operationally released, meaning that information from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center, such as information on a storm that was not operationally warned on, have been included.

The 2007 Pacific hurricane season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. This timeline documents all the storm formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, and dissipation. The timeline also includes information which was not operationally released, which is information from post-storm analysis by the National Hurricane Center.

The 2008 Pacific hurricane season officially started on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin. The first storm of the year, Tropical Storm Alma, developed on May 29, and the last, Tropical Storm Polo dissipated on November 5.[

The 2009 Pacific hurricane season was the most active Pacific hurricane season since 1997. The season officially started on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin. The first tropical cyclone to form was One-E on June 18, and the last, Hurricane Neki, dissipated on October 27.

The 1997 Pacific hurricane season was the most active season since the 1994 season, producing 24 tropical depressions, 19 of which became tropical storms or hurricanes. The season officially started on May 15, 1997 in the Eastern Pacific—designated as the area east of 140°W—and on June 1, 1997 in the Central Pacific, which is between the International Date Line and 140°W. The season officially ended in both basins on November 30, 1997. These dates typically limit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific basin. This timeline documents all the storm formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, as well as dissipation. The timeline also includes information which was not operationally released, meaning that information from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center, such as information on a storm that was not operationally warned on, has been included.

Hurricane Rick was the third-most intense Pacific hurricane on record and the second-most intense tropical cyclone worldwide in 2009, only behind Typhoon Nida. Developing off the southern coast of Mexico on October 15, Rick traversed an area with favorable environmental conditions, favoring rapid intensification, allowing it to become a hurricane within 24 hours of being declared a tropical depression. An eye began to form during the afternoon of October 16; once fully formed, the storm underwent another period of rapid strengthening. During the afternoon of October 17, the storm attained Category 5 status on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. Several hours later, Rick attained its peak intensity as the third-strongest Pacific hurricane on record with winds of 180 mph (290 km/h) and a barometric pressure of 906 mbar.

The 1992 Pacific hurricane season was the most active season on record, featuring 27 named storms. The season officially started on May 15, in the Eastern Pacific—designated as the area east of 140°W—and on June 1, in the Central Pacific, which is between the International Date Line and 140°W. The season officially ended in both basins on November 30. These dates typically limit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific basin. Lasting 24 days, Hurricane Tina became the longest lived North Pacific tropical cyclone on record. Its longevity broke the old record for the Eastern and Central Pacific of 20 days, set by Hurricane Fico in 1978; and the old record for the Western Pacific of 22 days, set by Typhoon Rita in 1972.

The 2011 Pacific hurricane season officially started on May 15, 2011 in the eastern Pacific, designated as the area east of 140°W, and on June 1, 2011 in the central Pacific, which is between the International Date Line and 140°W, and lasted until November 30, 2011. These dates typically limit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific basin. This timeline documents all the storm formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, as well as dissipation.

The 1990 Pacific hurricane season saw a then-record 16 hurricanes form. Throughout the year, 21 tropical cyclones became named storms in the eastern Pacific Ocean. Hurricane Alma formed on May 12, 1990, three days before the season's official start on May 15. The Central Pacific hurricane season began on June 1, covering tropical cyclone formation in the region between 140°W and International Dateline. Hurricane Trudy was the last storm to dissipate, doing so on November 1, nearly a month before the Pacific hurricane season officially ended on November 30.

The 2012 Pacific hurricane season was an above-average year in which seventeen named storms formed. The hurricane season officially began on May 15 in the east Pacific—defined as the region east of 140°W—and on June 1 in the central Pacific—defined as the region west of 140°W to the International Date Line—and ended on November 30 in both regions. These dates conventionally delimit the period during each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. This year, the first storm of the season, Tropical Storm Aletta, formed on May 14, and the last, Tropical Storm Rosa, dissipated on November 3.

The 1991 Pacific hurricane season produced 16 tropical depressions, 14 of which became tropical storms or hurricanes. The season officially started on May 15, 1991 in the Eastern Pacific—designated as the area east of 140°W—and on June 1, 1991 in the Central Pacific, which is between the International Date Line and 140°W. The season officially ended in both basins on November 30, 1991. These dates typically limit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific basin. This timeline documents all the storm formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, as well as dissipation. The timeline also includes information which was not operationally released, meaning that information from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center, such as information on a storm that was not operationally warned on, has been included.

The 2013 Pacific hurricane season was an above-average year in which twenty named storms developed. The hurricane season officially began on May 15 in the East Pacific, coinciding with the formation of Tropical Storm Alvin, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; it ended on November 30 in both basins. These dates conventionally delimit the period during each year when most tropical cyclones form. The final system of the year, Tropical Storm Sonia, dissipated on November 4.

The 2014 Pacific hurricane season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. It officially began on May 15 in the eastern Pacific—defined as the region east of 140°W—and began on June 1 in the central Pacific, defined as the region west of 140°W to the International Date Line; both ended on November 30.
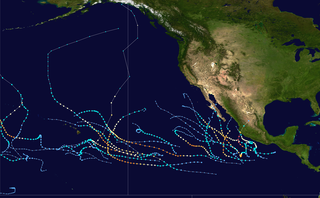
The 2015 Pacific hurricane season was the second-most active Pacific hurricane season on record, and featured the strongest tropical cyclone ever observed in the Western Hemisphere: Hurricane Patricia. The season officially started on May 15 in the Eastern Pacific—east of 140°W—and on June 1 in the Central Pacific—between the International Date Line and 140°W—and ended on November 30. These dates typically cover the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Northeastern Pacific tropical cyclone basin. The season's first storm, Hurricane Andres, developed on May 28; the season's final storm, Tropical Depression Nine-C, dissipated on December 31, well after the official end of the season.

The 2016 Pacific hurricane season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific–east of 140°W–and on June 1 in the central Pacific–between the International Date Line and 140°W–and ended on November 30. These dates typically cover the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific basin. However the first storm, Pali, formed 5 months before the official start of the season on January 7, which broke the record for having the earliest forming storm within the basin.

The 2018 Pacific hurricane season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific—east of 140°W—and began on June 1 in the central Pacific—the region between the International Date Line and 140°W, and ended on November 30. These dates typically cover the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific basin. The season began with the formation of Tropical Depression One-E, which developed on May 10, and ended with the dissipation of the season's final storm, Tropical Storm Xavier, which dissipated as a tropical cyclone on November 5.

The 2019 Pacific hurricane season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific—east of 140°W—and June 1 in the central Pacific—between the International Date Line and 140°W, and ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific basin.

The 2021 Pacific hurricane season was a moderately active hurricane season, with above-average tropical activity in terms of named storms, but featured below-average activity in terms of major hurricanes. It is the first season to have at least five systems make landfall in Mexico, the most since 2018. It was also the second consecutive season in which no tropical cyclones formed in the Central Pacific. The season officially began on May 15 in the Eastern Pacific, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; both ended on November 30. These dates historically describe the period each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern and central Pacific and are adopted by convention. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year, as illustrated this year by the formation of Tropical Storm Andres on May 9. This was the earliest forming tropical storm on record in the Eastern Pacific.























