
Acragas is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1900. The name is derived from the Greek name of Agrigentum, an ancient city on Sicily.
Ashtabula is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by G. W. Peckham & E. G. Peckham in 1894.

Balmaceda is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by George Peckham & Elizabeth Peckham in 1894.

Beata is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by George Peckham & Elizabeth Peckham in 1895.

Breda is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by George Peckham & Elizabeth Peckham in 1894.

Corythalia is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1850. The genus is distributed throughout most of the Western Hemisphere. Species of this genus are found in The Americas.

Cotinusa is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1900.

Freya is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1850. The name is derived from Freya, the fertility goddess of Norse mythology.

Hypaeus is a genus of the spider family Salticidae.

Lyssomanes is a spider genus of the family Salticidae, ranging from South and Central America, up to the southern United States.

Metaphidippus is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Frederick Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1901. The name is combined from Ancient Greek μετά "after, beside" and the salticid genus Phidippus.

Micrathena, known as spiny orbweavers, is a genus of orb-weaver spiders first described by Carl Jakob Sundevall in 1833. Micrathena contains more than a hundred species, most of them Neotropical woodland-dwelling species. The name is derived from the Greek "micro", meaning "small", and the goddess Athena.

The Dendryphantina are a subtribe of jumping spiders that occur mainly in the New World. The subtribe was first defined by Anton Menge in 1879 as Dendryphantidae. Females of the subtribe generally show paired spots on the abdomen, and the males often have enlarged chelicerae. Females in this subtribe typically have S-shaped epigynal openings.
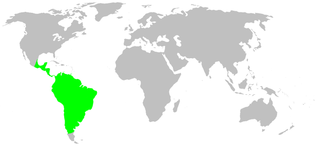
Senoculus is a genus of araneomorph spiders in the family Senoculidae, and was first described by Władysław Taczanowski in 1872. It is the only genus in the family Senoculidae.

Colonus is a genus of spiders in the jumping spider family, Salticidae. Colonus species are endemic to North and South America, ranging from New York to Argentina. All members of the genus have two pairs of bulbous spines on the ventral side of the first tibiae. The function of these spines is unknown. Colonus was declared a junior synonym of Thiodina by Eugène Simon in 1903, but this was reversed by Bustamante, Maddison, and Ruiz in 2015.

Corinna is a genus of corinnid sac spiders first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1841. They are found in Mexico and south to Brazil, and with selected species found in Africa.
Teudis is a genus of anyphaenid sac spiders first described by O. Pickard-Cambridge in 1896.

Eustala is a genus of orb-weaver spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1895.
















