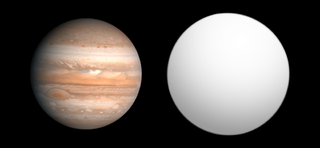
TrES-1b is an extrasolar planet approximately 523 light-years away in the constellation of Lyra. The planet's mass and radius indicate that it is a Jovian planet with a similar bulk composition to Jupiter. Unlike Jupiter, but similar to many other planets detected around other stars, TrES-1 is located very close to its star, and belongs to the class of planets known as hot Jupiters. The planet was discovered orbiting around GSC 02652-01324.

WASP or Wide Angle Search for Planets is an international consortium of several academic organisations performing an ultra-wide angle search for exoplanets using transit photometry. The array of robotic telescopes aims to survey the entire sky, simultaneously monitoring many thousands of stars at an apparent visual magnitude from about 7 to 13.

XO-1b is an extrasolar planet approximately 536 light-years away from Earth.

TrES-2b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star GSC 03549-02811 located 750 light years away from the Solar System. The planet was identified in 2011 as the darkest known exoplanet, reflecting less than 1% of any light that hits it. Reflecting less light than charcoal, on the surface the planet is said to be pitch black. The planet's mass and radius indicate that it is a gas giant with a bulk composition similar to that of Jupiter. Unlike Jupiter, but similar to many planets detected around other stars, TrES-2b is located very close to its star and belongs to the class of planets known as hot Jupiters. This system was within the field of view of the Kepler spacecraft.

Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. For example, a star like the Sun is about a billion times as bright as the reflected light from any of the planets orbiting it. In addition to the intrinsic difficulty of detecting such a faint light source, the light from the parent star causes a glare that washes it out. For those reasons, very few of the exoplanets reported as of January 2024 have been observed directly, with even fewer being resolved from their host star.

CoRoT-1b is a transiting extrasolar planet approximately 2,630 light-years away in the constellation of Monoceros. The planet was discovered orbiting the yellow dwarf star CoRoT-1 in May 2007. The planet was the first discovery by the French-led CoRoT Mission.

XO-3b is an exoplanet with about 11.79 times the mass of Jupiter, and it orbits its parent star XO-3 in about 3.2 days. The radius of this object is 1.217 times that of Jupiter. Astronomers announced their discovery on May 30, 2007, at the American Astronomical Society in Honolulu, Hawaii. Its discovery is attributed to the combined effort of amateur and professional astronomers working together on the XO Project using a telescope located on the Haleakala summit in Hawaii.
The XO Project is an international team of amateur and professional astronomers tasked with identifying extrasolar planets. They are led by Peter R. McCullough of the Space Telescope Science Institute. It is primarily funded by NASA's Origins Program and the Director's Discretionary Fund of the Space Telescope Science Institute.

Epsilon Eridani b, also known as AEgir [sic], is an exoplanet approximately 10.5 light-years away orbiting the star Epsilon Eridani, in the constellation of Eridanus. The planet was discovered in 2000, and as of 2024 remains the only confirmed planet in its planetary system. It orbits at around 3.5 AU with a period of around 7.6 years, and has a mass around 0.6 times that of Jupiter. As of 2023, both the Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia and the NASA Exoplanet Archive list the planet as 'confirmed'.
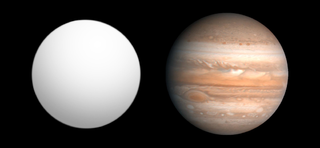
HAT-P-3b, also named Teberda, is an extrasolar planet that orbits the star HAT-P-3 approximately 450 light-years away in the constellation of Ursa Major. It was discovered by the HATNet Project via the transit method and confirmed with Doppler spectroscopy, so both its mass and radius are known quite precisely. Based on these figures it is predicted that the planet has about 75 Earth masses' worth of heavy elements in its core, making it similar to the planet HD 149026 b.
XO-5 is a yellow dwarf main sequence star located approximately 893 light-years away from Earth in the Lynx constellation. It has a magnitude of about 12 and cannot be seen with the naked eye but is visible through a small telescope.

XO-5b "Makropulos" is an extrasolar planet approximately 910 light years away in the constellation of Lynx. This planet was found by the transit method using the XO Telescope and announced in May 2008. It was also independently discovered by the HATNet Project. The planet has a mass and radius just slightly larger than that of Jupiter. This planet orbits very close to the G-type parent star, as it is typical for transiting planets, classing this as Hot Jupiter. It takes only 4.188 days to orbit at an orbital distance of 0.0488 AU).

GSC 03549-02811 is a binary star containing a yellow main-sequence star similar to the Sun. This star is located approximately 750 light-years away in the constellation of Draco. The apparent magnitude of this star is 11.41, which means it is not visible to the naked eye but can be seen with a medium-sized amateur telescope on a clear dark night. The age of this star is about 5 billion years.

GSC 03089-00929 is a magnitude 12 star located approximately 757 light-years away in the constellation of Hercules. This star is a G type main sequence star that is similar to but slightly cooler than the Sun. This star is identified in SIMBAD as a variable star per the 1SWASP survey.

WASP-17b, officially named Ditsö̀, is an exoplanet in the constellation Scorpius that is orbiting the star WASP-17. Its discovery was announced on 11 August 2009. It is the first planet discovered to have a retrograde orbit, meaning it orbits in a direction counter to the rotation of its host star. This discovery challenged traditional planetary formation theory. In terms of diameter, WASP-17b is one of the largest exoplanets discovered and at half Jupiter's mass, this made it the most puffy planet known in 2010. On 3 December 2013, scientists working with the Hubble Space Telescope reported detecting water in the exoplanet's atmosphere.

WASP-19b, formally named Banksia, is an exoplanet, notable for possessing one of the shortest orbital periods of any known planetary body: 0.79 days or approximately 18.932 hours. It has a mass close to that of Jupiter, but by comparison has a much larger radius ; making it nearly the size of a low-mass star. It orbits the star WASP-19 in the Vela constellation. At the time of discovery it was the shortest period hot Jupiter discovered as planets with shorter orbital periods had a rocky, or metallic composition.

WASP-43b, formally named Astrolábos, is a transiting planet in orbit around the young, active, and low-mass star WASP-43 in the constellation Sextans. The planet is a hot Jupiter with a mass twice that of Jupiter, but with a roughly equal radius. WASP-43b was flagged as a candidate by the SuperWASP program, before they conducted follow-ups using instruments at La Silla Observatory in Chile, which confirmed its existence and provided orbital and physical characteristics. The planet's discovery was published on April 14, 2011.

The Next-Generation Transit Survey (NGTS) is a ground-based robotic search for exoplanets. The facility is located at Paranal Observatory in the Atacama desert in northern Chile, about 2 km from ESO's Very Large Telescope and 0.5 km from the VISTA Survey Telescope. Science operations began in early 2015. The astronomical survey is managed by a consortium of seven European universities and other academic institutions from Chile, Germany, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom. Prototypes of the array were tested in 2009 and 2010 on La Palma, and from 2012 to 2014 at Geneva Observatory.
GSC 03949-00967 is a G-type main-sequence star about 1179 light-years away. It is older than the Sun, yet is enriched by heavy elements compared to the Sun, having 160% of solar abundance.
TrES-5b is a Hot Jupiter class extrasolar planet discovered by astronomical transit located 1100 light years from Earth in the Cygnus constellation, orbiting the star GSC 03949-00967 of type G in the planetary system TrES-5.

















