
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the seas connecting the two. It does not include the temperate and polar regions of the Indian and Pacific oceans, nor the Tropical Eastern Pacific, along the Pacific coast of the Americas, which is also a distinct marine realm. The term is especially useful in marine biology, ichthyology, and similar fields, since many marine habitats are continuously connected from Madagascar to Japan and Oceania, and a number of species occur over that range, but are not found in the Atlantic Ocean.

The Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin is a species of bottlenose dolphin. This dolphin grows to 2.6 m (8.5 ft) long, and weighs up to 230 kg (510 lb). It lives in the waters around India, northern Australia, South China, the Red Sea, and the eastern coast of Africa. Its back is dark grey and its belly is lighter grey or nearly white with grey spots.

Humpback dolphins are members of the genus Sousa. These dolphins are characterized by the conspicuous humps and elongated dorsal fins found on the backs of adults of the species. Humpback dolphins inhabit shallow nearshore waters along coastlines across Australia, Africa, and Asia. Their preference for these habitats exposes them to various human activities such as fisheries entanglement, boat traffic, pollution, and habitat loss. Despite these risks, their nearshore presence facilitates easy observation from land.

The red lionfish is a venomous coral reef fish in the family Scorpaenidae, order Scorpaeniformes. It is mainly native to the Indo-Pacific region, but has become an invasive species in the Caribbean Sea, as well as along the East Coast of the United States and East Mediterranean and also found in Brazil at Fernando de Noronha.

The Synodontidae or lizardfishes are benthic (bottom-dwelling) marine and estuarine bony fishes that belong to the aulopiform fish order, a diverse group of marine ray-finned fish consisting of some 15 extant and several prehistoric families. They are found in tropical and subtropical marine waters throughout the world.

The largehead hairtail or beltfish is a member of the cutlassfish family, Trichiuridae. This common to abundant species is found in tropical and temperate oceans throughout the world. The taxonomy is not fully resolved, and the Atlantic, East Pacific and Northwest Pacific populations are also known as Atlantic cutlassfish, Pacific cutlassfish and Japanese cutlassfish, respectively. This predatory, elongated fish supports major fisheries.

The Indo-Pacific tarpon, also known as the oxeye herring or simply herring due to its superficial resemblance to the true herrings, of which it is not a member, is the smaller of the two species of tarpon and lives in Indo-Pacific waters.

The greater weever is a benthic and demersal venomous marine fish of the family Trachinidae. The greater weever is widely distributed along the eastern Atlantic coastline from Norway to Morocco, extending to the Mediterranean, Aegean and Black Seas. Trachinus draco has been shown to occur in depths ranging from shallow water up to -150 meters where it inhabits mostly muddy or sandy grounds. Trachinus draco is mostly and notoriously known for its venomous spines that can inflict serious injuries on humans through accidental stinging. Because of these spines and its potent venom it is classified as one of the most venomous fishes in the Mediterranean. The name "weever" is thought to originate from the Anglo-Saxon word "wivre" which translates as "viper".
Snakefish is a colloquial term used for a number of species of fish that resemble snakes. Trachinocephalus myops, native to parts of both the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, is known by this name in particular.

Trachinocephalus myops, the blunt-nose lizardfish, is a species of fish in the family Synodontidae found in Atlantic Ocean. This species grows to a length of 40 centimetres (16 in) TL. It has been discovered that the species has two peaks in its spawning season, from February to April and from August to October. This suggests that their reproductive activity is suitable for the different environments the species utilizes.

Trachinocephalus is a genus of fishes in the family Synodontidae found in Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean.

The blackfin scad is a species of tropical marine fish of the jack family Carangidae. The species inhabits inshore waters throughout the Indo-Pacific region, although is rare in the western Indian Ocean. It is not a large species, with the largest reported capture being 25 cm, and it is distinguished readily from similar species by the prominent black dorsal fin. It is a predator which feeds on planktonic crustaceans, but little else is known of its biology. The blackfin scad is a minor food fish throughout its range, and is highly valued in Cambodia and Thailand.

Alepes is a genus containing five extant species of tropical marine fishes in the jack family, Carangidae. They are commonly known as scads, a term applied to many genera of carangid fishes. Their body form, however, differs from these other scads by being much more ovate in shape, more similar to the larger jacks taken as game fish, although scads are generally much smaller. They are found in coastal waters throughout the Indo-West Pacific region.

Trachinus is a genus of weevers, order Perciformes that consists of seven extant species. Six of the genus representatives inhabit the waters of Eastern Atlantic Ocean, but only one, Trachinus cornutus, inhabits the South-Eastern Pacific Ocean. Three of the Atlantic species occur near the coasts of Europe. An eighth extinct species, T. minutus, is known from Oligocene-aged strata from the Carpathian Mountains, while a ninth species, also extinct, T. dracunculus, is known from middle-Miocene-aged strata from Piemonte, Italy.
Trachinus cornutus is a fish of the family Trachinidae, order Perciformes, and class Actinopterygii. Widespread in the southeastern Pacific along the coasts of Chile, it is a marine subtropical demersal fish.
John Ernest "Jack" Randall was an American ichthyologist and a leading authority on coral reef fishes. Randall described over 800 species and authored 11 books and over 900 scientific papers and popular articles. He spent most of his career working in Hawaii. He died in April 2020 at the age of 95.
Transversotrema is a genus of trematodes in the family Transversotrematidae.
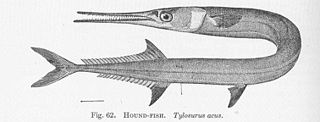
Tylosurus acus is a game fish of the family Belonidae.

The mangrove waspfish, also known as the goblinfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a waspfish belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. This species occurs in the Indo-Pacific region.
Trachinocephalus gauguini, commonly known as the Curious Scad, is a species of lizardfish in the family Synodontidae. This species was described in 2016 by F.A. Polanco, P.A. Acero, and R. Betancur-R.












