
Globalization, or globalisation, is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. The term globalization first appeared in the early 20th century, developed its current meaning sometime in the second half of the 20th century, and came into popular use in the 1990s to describe the unprecedented international connectivity of the post-Cold War world. Its origins can be traced back to 18th and 19th centuries due to advances in transportation and communications technology. This increase in global interactions has caused a growth in international trade and the exchange of ideas, beliefs, and culture. Globalization is primarily an economic process of interaction and integration that is associated with social and cultural aspects. However, disputes and international diplomacy are also large parts of the history of globalization, and of modern globalization.
International relations theory is the study of international relations (IR) from a theoretical perspective. It seeks to explain behaviors and outcomes in international politics. The four most prominent schools of thought are realism, liberalism, constructivism, and rational choice. Whereas realism and liberalism make broad and specific predictions about international relations, constructivism and rational choice are methodological approaches that focus on certain types of social explanation for phenomena.

Global North and Global South are terms that denote a method of grouping countries based on their defining characteristics with regard to socioeconomics and politics. According to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), the Global South broadly comprises Africa, Latin America and the Caribbean, Asia, and Oceania. Most of the Global South's countries are commonly identified as lacking in their standard of living, which includes having lower incomes, high levels of poverty, high population growth rates, inadequate housing, limited educational opportunities, and deficient health systems, among other issues. Additionally, these countries' cities are characterized by their poor infrastructure. Opposite to the Global South is the Global North, which the UNCTAD describes as broadly comprising Northern America and Europe, Israel, Japan, South Korea, Australia, and New Zealand. As such, the two terms do not refer to the Northern Hemisphere or the Southern Hemisphere, as many of the Global South's countries are geographically located in the former and, similarly, a number of the Global North's countries are geographically located in the latter.
Globalism has multiple meanings. In political science, it is used to describe "attempts to understand all the interconnections of the modern world—and to highlight patterns that underlie them". While primarily associated with world-systems, it can be used to describe other global trends. The concept of globalism is also classically used to focus on the ideologies of globalization instead of its processes ; in this sense, "globalism" is to globalization what "nationalism" is to nationality.
Economic interdependence is the mutual dependence of the participants in an economic system who trade in order to obtain the products they cannot produce efficiently for themselves. Such trading relationships require that the behavior of a participant affects its trading partners and it would be costly to rupture their relationship. The subject was addressed by A. A. Cournot who wrote: "...but in reality the economic system is a whole in which all of the parts are connected and react on one another. An increase in the income of the producers of commodity A will affect the demands for commodities B, C, etc. and the incomes of their producers, and by its reaction will affect the demand for commodity A." Economic Interdependence is evidently a consequence of the division of labour.
International economics is concerned with the effects upon economic activity from international differences in productive resources and consumer preferences and the international institutions that affect them. It seeks to explain the patterns and consequences of transactions and interactions between the inhabitants of different countries, including trade, investment and transaction.

The World Is Flat: A Brief History of the Twenty-first Century is a book by Thomas L. Friedman that analyzes globalization, primarily in the early 21st century. The title suggests the world has a level playing field for commerce in which most competitors, except for labor, have an equal opportunity. He suggests that countries, companies, and individuals need to remain competitive in a global market. Historical and geographic divisions are, according to the author, less important.

Samir Amin was an Egyptian-French Marxian economist, political scientist and world-systems analyst. He is noted for his introduction of the term Eurocentrism in 1988 and considered a pioneer of Dependency Theory.

Regional Integration is a process in which neighboring countries enter into an agreement in order to upgrade cooperation through common institutions and rules. The objectives of the agreement could range from economic to political to environmental, although it has typically taken the form of a political economy initiative where commercial interests are the focus for achieving broader socio-political and security objectives, as defined by national governments. Regional integration has been organized either via supranational institutional structures or through intergovernmental decision-making, or a combination of both.
Deglobalization or deglobalisation is the process of diminishing interdependence and integration between certain units around the world, typically nation-states. It is widely used to describe the periods of history when economic trade and investment between countries decline. It stands in contrast to globalization, in which units become increasingly integrated over time, and generally spans the time between periods of globalization. While globalization and deglobalization are antitheses, they are not mirror images.
Multi-level governance is a term used to describe the way power is spread vertically between levels of government and horizontally across multiple quasi-government and non-governmental organizations and actors. This situation develops because countries have multiple levels of government including local, regional, state, national or federal, and many other organisations with interests in policy decisions and outcomes. International governance operates based on multi-level governance principles. Multi-level governance can be distinguished from multi-level government which is when different levels of government share or transfer responsibility amongst each other. Whereas multi-level governance analyses the relationship of different state levels and interaction with different types of actors.'

Complex interdependence in international relations and international political economy is a concept put forth by Robert Keohane and Joseph Nye in the 1970s to describe the emerging nature of the global political economy. The concept entails that relations between states are becoming increasingly deep and complex. These increasingly complex webs of economic interdependence undermine state power and elevate the influence of transnational non-state actors. These complex relationships can be explored through both the liberal and realism lenses and can later explain the debate of power from complex interdependence.

The historical origins of globalization are the subject of ongoing debate. Though many scholars situate the origins of globalization in the modern era, others regard it as a phenomenon with a long history, dating back thousands of years. The period in the history of globalization roughly spanning the years between 1600 and 1800 is in turn known as the proto-globalization.

Beyond the Crash: Overcoming the first crisis of globalisation is a 2010 book by former UK prime minister Gordon Brown. The work argues that the only way to fully overcome the financial crisis of 2007–2010 is with further coordinated global action. Brown states that a shared "global compact" on jobs and growth should be central to effective action, with different regions called on in different ways to contribute to rebalancing the global economy while boosting growth. The book includes first-hand accounts of events leading to previous successful cases of international collaboration on economic affairs. There are specific suggestions about the different ways in which the world's nations and regions can help secure global growth, jobs and poverty reduction. A secondary theme of the work is that better global oversight is needed for the international financial system. Brown suggests that to function at their best, banks and markets need shared morals.

Cultural globalization refers to the transmission of ideas, meanings and values around the world in such a way as to extend and intensify social relations. This process is marked by the common consumption of cultures that have been diffused by the Internet, popular culture media, and international travel. This has added to processes of commodity exchange and colonization which have a longer history of carrying cultural meaning around the globe. The circulation of cultures enables individuals to partake in extended social relations that cross national and regional borders. The creation and expansion of such social relations is not merely observed on a material level. Cultural globalization involves the formation of shared norms and knowledge with which people associate their individual and collective cultural identities. It brings increasing interconnectedness among different populations and cultures. The idea of cultural globalization emerged in the late 1980s, but was diffused widely by Western academics throughout the 1990s and early 2000s. For some researchers, the idea of cultural globalization is reaction to the claims made by critics of cultural imperialism in the 1970s and 1980s.
International economic structures range from complete autarky to complete market openness. This structure has undergone numerous changes since the beginning of the nineteenth century. The state-power theory as put into perspective by Stephen Krasner (1976), explains that the structure of international trade is determined by the interests and power of states acting to maximize their aggregate national income, social stability, political power and economic growth. Such state interests can be achieved under free trade.
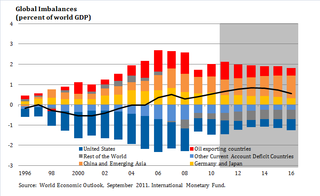
Global imbalances refers to the situation where some countries have more assets than the other countries. In theory, when the current account is in balance, it has a zero value: inflows and outflows of capital will be cancelled by each other. Hence, if the current account is persistently showing deficits for certain period, it is said to show an inequilibrium. Since, by definition, all current accounts and net foreign assets of the countries in the world must become zero, then other countries become indebted with the other nations. During recent years, global imbalances have become a concern in the rest of the world. The United States has run long term deficits, as well as many other advanced economies, while in Asia and emerging economies the opposite has occurred.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the broad, interdisciplinary subject of globalization:

Middle East economic integration refers to the process of improving economic cooperation, coordination, and connectivity among countries in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. This process aims to create a unified economic space that allows for the free movement of goods, services, capital, and labor across national borders within the region. The objectives behind such integration include enhancing regional trade, stimulating economic growth, achieving economies of scale, and fostering stability and peace through economic interdependence.
South Korea is 5th largest export economy in the world and the 6th economic complexity according to Economic Complexity Index (ECI) with the top export destinations centralized in China with a total population of 51,324,823 in 2019.












