Use
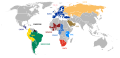
![Stages of economic integration around the world (each country colored according to the most integrated multilateral agreement that it participates in):
.mw-parser-output .legend{page-break-inside:avoid;break-inside:avoid-column}.mw-parser-output .legend-color{display:inline-block;min-width:1.25em;height:1.25em;line-height:1.25;margin:1px 0;text-align:center;border:1px solid black;background-color:transparent;color:black}.mw-parser-output .legend-text{}
Economic and monetary union (ECCU/XCD, Eurozone/EUR, Switzerland-Liechtenstein/CHF)
Economic union (CSME, EAEU, EU, GCC, Mercosur, SICA)
Common market (EEA-Switzerland)
Customs and monetary union (CEMAC/XAF, UEMOA/XOF)
Customs union (CAN, EAC, EUCU, SACU)
Multilateral free-trade area (AANZFTA, ASEAN, CEFTA, CISFTA, COMESA, CPTPP, EFTA, GAFTA, PAFTA, RCEP, SADCFTA, SAFTA, USMCA)
.mw-parser-output .hlist dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul{margin:0;padding:0}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt,.mw-parser-output .hlist li{margin:0;display:inline}.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline,.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline ul,.mw-parser-output .hlist dl dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist dl ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist dl ul,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol ul,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul ul{display:inline}.mw-parser-output .hlist .mw-empty-li{display:none}.mw-parser-output .hlist dt::after{content:": "}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li::after{content:" * ";font-weight:bold}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li:last-child::after{content:none}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dd:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dt:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dd:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dt:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dd:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dt:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li li:first-child::before{content:" (";font-weight:normal}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd li:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt li:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li li:last-child::after{content:")";font-weight:normal}.mw-parser-output .hlist ol{counter-reset:listitem}.mw-parser-output .hlist ol>li{counter-increment:listitem}.mw-parser-output .hlist ol>li::before{content:" "counter(listitem)"\a0 "}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd ol>li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt ol>li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li ol>li:first-child::before{content:" ("counter(listitem)"\a0 "}
.mw-parser-output .navbar{display:inline;font-size:88%;font-weight:normal}.mw-parser-output .navbar-collapse{float:left;text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .navbar-boxtext{word-spacing:0}.mw-parser-output .navbar ul{display:inline-block;white-space:nowrap;line-height:inherit}.mw-parser-output .navbar-brackets::before{margin-right:-0.125em;content:"[ "}.mw-parser-output .navbar-brackets::after{margin-left:-0.125em;content:" ]"}.mw-parser-output .navbar li{word-spacing:-0.125em}.mw-parser-output .navbar a>span,.mw-parser-output .navbar a>abbr{text-decoration:inherit}.mw-parser-output .navbar-mini abbr{font-variant:small-caps;border-bottom:none;text-decoration:none;cursor:inherit}.mw-parser-output .navbar-ct-full{font-size:114%;margin:0 7em}.mw-parser-output .navbar-ct-mini{font-size:114%;margin:0 4em}html.skin-theme-clientpref-night .mw-parser-output .navbar li a abbr{color:var(--color-base)!important}@media(prefers-color-scheme:dark){html.skin-theme-clientpref-os .mw-parser-output .navbar li a abbr{color:var(--color-base)!important}}@media print{.mw-parser-output .navbar{display:none!important}}
v
t
e Economic integration.svg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/04/Economic_integration.svg/330px-Economic_integration.svg.png)
Historic trading blocs include the Hanseatic League, a Northern European economic alliance between the 12th and 17th centuries, and the German Customs Union, formed on the basis of the German Confederation and subsequently the German Empire from 1871. Surges of trade bloc formation occurred in the 1960s and 1970s, as well as in the 1990s after the collapse of Communism. By 1997, more than 50% of all world commerce was conducted within regional trade blocs. [2] Economist Jeffrey J. Schott of the Peterson Institute for International Economics notes that members of successful trade blocs usually share four common traits: similar levels of per capita GNI, geographic proximity, similar or compatible trading regimes, and political commitment to regional organization. [3]
Some advocates of global free trade are opposed to trading blocs. Trade blocs are seen by them to encourage regional free trade at the expense of global free trade. [4] Those who advocate for it claim that global free trade is in the interest of every country, as it would create more opportunities to turn local resources into goods and services that are both currently in demand and will be in demand in the future by consumers. [5] However, scholars and economists continue to debate whether regional trade blocs fragment the global economy or encourage the extension of the existing global multilateral trading system. [6] [7]