
Salacca is a genus of about 20 species of palms native to Southeast Asia and the eastern Himalayas. They are dioecious and pollinated by Curculionidae beetles.
Lasiococca is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described in 1887. These are small to relatively large trees found in scrubs or semi-evergreen forests. They grow in India, Indochina, Southeast Asia, and southern China.
- Lasiococca brevipes(Merr.) Welzen & S.E.C.Sierra - Peninsular Malaysia, Philippines, Lesser Sunda Islands, Sulawesi
- Lasiococca chaniiThin - Vietnam
- Lasiococca comberiHaines - Hainan, Yunnan, Vietnam, Thailand, E India
- Lasiococca lociiThin - Vietnam
- Lasiococca symphylliifolia(Kurz) Hook.f. - Sikkim

Agrostistachys is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1850. It is native to Southeast Asia, New Guinea, India, and Sri Lanka.
- Agrostistachys borneensisBecc. - India, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia, Borneo, Philippines, Sumatra, New Guinea
- Agrostistachys gaudichaudiiMüll.Arg. - Thailand, Peninsular Malaysia
- Agrostistachys hookeri(Thwaites) Benth. & Hook.f. - Sri Lanka
- Agrostistachys indicaDalzell - India, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, Malaysia, Borneo, Philippines, New Guinea
- Agrostistachys sessilifolia(Kurz) Pax & K.Hoffm. - Peninsular Malaysia, Borneo, Sumatra
- Agrostistachys staminodiataSevilla - Sumatra
Cheilosa is a monotypic plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1826. Only one species is recognized: Cheilosa montana, native to Southeast Asia.
Neoscortechinia is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1897. It is native to Southeast Asia and Papuasia.
- Neoscortechinia angustifolia(Airy Shaw) Welzen - Sabah, Kalimantan
- Neoscortechinia forbesii(Hook.f.) S.Moore - New Guinea, Admiralty Islands, Bismarck Archipelago, Solomon Islands
- Neoscortechinia kingii(Hook.f.) Pax & K.Hoffm. - W Malaysia, Sumatra, Borneo
- Neoscortechinia nicobarica(Hook.f.) Pax & K.Hoffm. - Nicobar Islands, Myanmar, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, W New Guinea
- Neoscortechinia philippinensis(Merr.) Welzen - Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia, W Indonesia, Philippines
- Neoscortechinia sumatrensisS.Moore - W Malaysia, N. Sumatra, Simeuluë, Borneo
Sumbaviopsis is a genus of plants in the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1910. It contains only one known species, Sumbaviopsis albicans, native to Yunnan, the eastern Himalayas, and Southeast Asia.
Cnesmone is a genus of plant of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1826. It is native to southern China and to much of Southeast Asia.

Endospermum is a genus of plants, under the family Euphorbiaceae and the monotypic subtribe Endosperminae first described as a genus in 1861 It is native to E + S + SE Asia, Papuasia, Queensland, and certain islands of the W Pacific.

Dimorphocalyx is a genus of plants under the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1861. It is native to Southeast Asia, Hainan, India, Sri Lanka, New Guinea, and Queensland.

Tristaniopsis is a group of shrub and tree in the myrtle family Myrtaceae described as a genus in 1863. They have a wide distribution in Southeast Asia, New Guinea, New Caledonia and Australia.

Daphniphyllum is the sole genus in the flowering plant family Daphniphyllaceae and was described as a genus in 1826. The genus includes evergreen shrubs and trees mainly native to east and southeast Asia, but also found in the Indian Subcontinent and New Guinea.
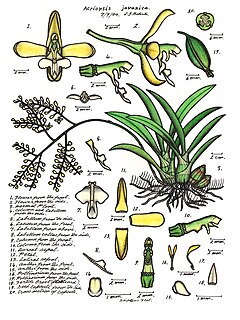
Acriopsis, commonly known as chandelier orchids or 合萼兰属 is a genus of flowering plants in the family Orchidaceaes. Orchids in this genus are epiphytic herbs with spherical or cylindrical pseudobulbs, creeping, branched rhizomes, thin white roots, two or three leaves and many small flowers. The flowers are non-resupinate with the lateral sepals joined along their edges and have spreading petals and a three-lobed labellum. The column has projections that extend hood-like beyond the anther.

Oncosperma is a genus of flowering plant in the family Arecaceae. It contains the following species, native to Southeast Asia and Sri Lanka:
Payena is a genus of plants in the family Sapotaceae described as a genus in 1844.

Coffea liberica is a species of flowering plant in the family Rubiaceae from which coffee is produced. It is native to western and central Africa from Liberia to Uganda and Angola, and has become naturalised in the Philippines, Indonesia, Seychelles, the Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Malaysia

Rhynchostylis is a genus in the orchid family (Orchidaceae), closely allied to the genus Vanda and comprising four currently accepted species native to the Indian Subcontinent, China, Indochina, Malaysia, Indonesia and the Philippines. The name consists of a compound of two Greek elements : rhynchos 'beak' and stylis 'column' – in reference to the very broad, fleshy column of the flower. The flowers are borne in dense racemes and are noted for their intense, spicy fragrance. Although lacking in pseudobulbs, the plants have leathery leaves that are drought-resistant. These orchids grow naturally in warm, moist, shaded tropical areas and will thrive in cultivation if given consistent warmth, uniform moisture and bright, but indirect light. Hobbyists wanting to grow them will need a warm, humid growing environment with gentle air movement. They can be grown in pots, but are better grown in baskets, owing to the extreme fleshiness of their roots. Their unusually fragrant blooms often appear in the slightly cooler winter months.
Amydrium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae that is native to Southeast Asia, southern China, and New Guinea.
Anadendrum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to China and Southeast Asia.
Geocharis is a genus of plants in the family Zingiberaceae. It is native to insular Southeast Asia.
Stenomeris is a genus of plants in the family Dioscoreaceae. It has two known species, native to Southeast Asia. Older systems such as that of Hutchinson placed Stenomeris as the type genus of the family Stenomeridaceae, order Dioscoreales.










