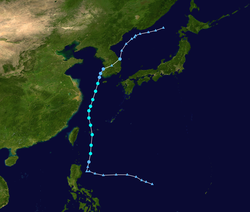
The 2005 Pacific typhoon season was the least active typhoon season since 2000, producing 23 named storms, of which 13 became typhoons. It was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the western Pacific Ocean. The season ran throughout 2005, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Kulap, developed on January 13, while the season's last named storm, Bolaven, dissipated on November 20. The season's first typhoon, Haitang, reached typhoon status on July 13, and became the first super typhoon of the year three days later.

The 2001 Pacific typhoon season was an average season with twenty-six named storms, sixteen typhoons and three super typhoons, with a near normal Accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE) of 307.3 units. It ran year-round in 2001, with most tropical cyclones in the northwestern Pacific Ocean tending between May and November.

The 2008 Pacific typhoon season was a below average season which featured 22 named storms, eleven typhoons, and two super typhoons. The season had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 2008, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

Typhoon Sinlaku, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Marce, was a typhoon which affected the Philippines, Taiwan, China and Japan. It was recognised as the 13th named storm and the ninth typhoon of the 2008 Pacific typhoon season by the Japan Meteorological Agency.

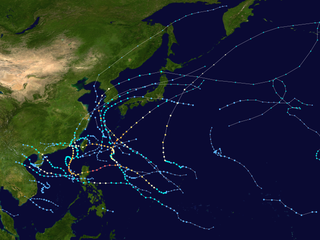
The 2012 Pacific typhoon season was a slightly above average season that produced 25 named storms, fourteen typhoons, and four intense typhoons. It was a destructive and the second consecutive year to be the deadliest season, primarily due to Typhoon Bopha which killed 1,901 people in the Philippines. It was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the western Pacific Ocean. The season ran throughout 2012, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Pakhar, developed on March 28, while the season's last named storm, Wukong, dissipated on December 29. The season's first typhoon, Guchol, reached typhoon status on June 15, and became the first super typhoon of the year on June 17.
The 2009 Pacific typhoon season was a below average season that spawned only 22 named storms, 13 typhoons, and five super typhoons. Despite this, it was a very deadly season, with the Philippines having experienced its deadliest season in decades due to the impact of typhoons Ketsana and Parma, while typhoon Morakot went on to become the deadliest storm to impact Taiwan in its modern history. The first half of the season was very quiet, whereas the second half of the season was extremely active. The season's first named storm, Kujira, developed on May 3, while the season's last named storm, Nida, dissipated on December 3.
The 2010 Pacific typhoon season, with 14 named storms, was the least active Pacific typhoon season on record. Seven of them strengthened into typhoons while one reached super typhoon intensity. All of the 14 named storms developed west of 150°E.

This timeline documents all of the events of the 2009 Pacific typhoon season which was the period that tropical cyclones formed in the Western Pacific Ocean during 2009, with most of the tropical cyclones forming between May and November. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator between 100°E and the International Date Line. Tropical storms that form in the entire Western Pacific basin are assigned a name by the Japan Meteorological Agency. Tropical depressions that form in this basin are given a number with a "W" suffix by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center. In addition, the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assigns names to tropical cyclones that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility. These names, however, are not in common use outside of the Philippines.

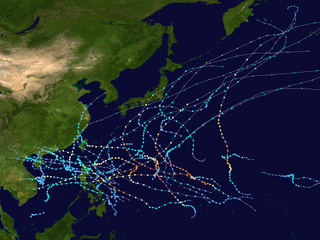
The 2013 Pacific typhoon season was a devastating and catastrophic season that was the most active since 2004, and the deadliest since 1975. It featured Typhoon Haiyan, one of the most powerful storms in history, as well as one of the strongest to make landfall on record. It featured 31 named storms, 13 typhoons, and five super typhoons. The season's first named storm, Sonamu, developed on January 4 while the season's last named storm, Podul, dissipated on November 15. Collectively, the storms caused 6,829 fatalities, while total damage amounted to at least $26.41 billion (USD), making it, at the time, the costliest Pacific typhoon season on record, until it was surpassed five years later. As of 2024, it is currently ranked as the fifth-costliest typhoon season.

The 2015 Pacific typhoon season was a slightly above average season that produced twenty-seven tropical storms, eighteen typhoons, and nine super typhoons. The season ran throughout 2015, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and November. The season's first named storm, Mekkhala, developed on January 15, while the season's last named storm, Melor, dissipated on December 17. The season saw at least one named tropical system forming in each of every month, the first time since 1965. Similar to the previous season, this season saw a high number of super typhoons. Accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) during 2015 was extremely high, the third highest since 1970, and the 2015 ACE has been attributed in part to anthropogenic warming, and also the 2014-16 El Niño event, that led to similarly high ACE values in the East Pacific.

The 2017 Pacific typhoon season was a below-average season in terms of accumulated cyclone energy and the number of typhoons and super typhoons, and the first since the 1977 season to not produce a Category 5-equivalent typhoon on the Saffir–Simpson scale. The season produced a total of 27 named storms, 11 typhoons, and only two super typhoons, making it an average season in terms of storm numbers. It was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the western Pacific Ocean. The season runs throughout 2017, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Muifa, developed on April 25, while the season's last named storm, Tembin, dissipated on December 26. This season also featured the latest occurrence of the first typhoon of the year since 1998, with Noru reaching this intensity on July 23.

The 2018 Pacific typhoon season was at the time, the costliest Pacific typhoon season on record, until the record was beaten by the following year. The season was well above-average, producing twenty-nine storms, thirteen typhoons, seven super typhoons and six Category 5 tropical cyclones. The season ran throughout 2018, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Bolaven, developed on January 3, while the season's last named storm, Man-yi, dissipated on November 28. The season's first typhoon, Jelawat, reached typhoon status on March 29, and became the first super typhoon of the year on the next day.

The 2019 Pacific typhoon season was a devastating season that became the costliest on record, just ahead of the previous year and 2023, mainly due to the catastrophic damage wrought by typhoons Lekima, Faxai, and Hagibis. The season featured fairly above-average tropical cyclone activity for the second consecutive year, producing 29 named storms, 17 typhoons, and five super typhoons. The season's first named storm, Pabuk, reached tropical storm status on January 1, becoming the earliest-forming tropical storm of the western Pacific Ocean on record, breaking the previous record that was held by Typhoon Alice in 1979. The season's first typhoon, Wutip, reached typhoon status on February 20. Wutip further intensified into a super typhoon on February 23, becoming the strongest February typhoon on record, and the strongest tropical cyclone recorded in February in the Northern Hemisphere. The season's last named storm, Phanfone, dissipated on December 29 after it made landfall in the Philippines.

The 2020 Pacific typhoon season was the first of a series of four below average Pacific typhoon seasons, and became the first with below-average tropical cyclone activity since 2014, with 23 named storms, 10 of which became typhoons and only 2 became super typhoons. This low activity was a consequence of La Niña that persisted from the summer of the year. It had the sixth-latest start in the basin on record, slightly behind 1973, and was the first to start that late since 2016. The first half of the season was unusually inactive, with only four systems, two named storms and one typhoon at the end of July. Additionally, the JTWC recorded no tropical cyclone development in the month of July, the first such occurrence since reliable records began. Despite that, this season featured Super Typhoon Goni, which made the strongest landfall worldwide in terms of 1-minute wind speed. The season's first named tropical cyclone, Vongfong, developed on May 8, while the season's last named tropical cyclone, Krovanh, dissipated on December 24. However, the season's last system was an unnamed tropical depression which dissipated on December 29.

Most of the tropical cyclones of the 2013 Pacific typhoon season formed between May and November of that year. The scope of this article is the Pacific Ocean north of the equator, between 100°E and the International Date Line. Tropical storms which form in the Western Pacific basin are assigned a name by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA). Tropical depressions forming in this basin are given a number with a "W" suffix by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC). The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assigns names to tropical cyclones that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility, but these names are not in common use outside the Philippines.

This timeline documents all of the events of the 2014 Pacific typhoon season. Most of the tropical cyclones forming between May and November. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator between 100°E and the International Date Line. Tropical storms that form in the entire Western Pacific basin are assigned a name by the Japan Meteorological Agency. Tropical depressions that form in this basin are given a number with a "W" suffix by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center. In addition, the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assigns names to tropical cyclones that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility. These names, however, are not in common use outside of the Philippines.

This timeline documents all of the events of the 2012 Pacific typhoon season. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator between 100°E and the International Date Line. During the season, 34 systems were designated as tropical depressions by either the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA), the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC), or other National Meteorological and Hydrological Services such as the China Meteorological Administration and the Hong Kong Observatory. Since the JMA runs the Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre (RSMC) for the Western Pacific, they assigned names to tropical depressions which developed into tropical storms in the basin. PAGASA also assigned local names to systems which are active in their area of responsibility; however, these names are not in common use outside of the Philippines.

The 2022 Pacific typhoon season was the third consecutive season to have below average tropical cyclone activity, with twenty-five named storms forming. Of the tropical storms, ten became typhoons, and three would intensify into super typhoons. The season saw near-average activity by named storm count, although many of the storms were weak and short-lived, particularly towards the end of the season. This low activity was caused by an unusually strong La Niña that had persisted from 2020. The season's first named storm, Malakas, developed on April 6, while the last named storm, Pakhar, dissipated on December 12. The season's first typhoon, Malakas, reached typhoon status on April 12. The season ran throughout 2022, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. Tropical storms Megi and Nalgae were responsible for more than half of the casualties, while typhoons Hinnamnor and Nanmadol both caused $1 billion in damages.

The 2023 Pacific typhoon season was the fourth and final consecutive below-average season and became the third-most inactive typhoon season on record in terms of named storms, with just 17 named storms developing, only ahead of 2010 and 1998. Despite the season occurring during an El Niño event, which typically favors activity in the basin, activity was abnormally low. This was primarily due to a consistent period of negative PDO, which typically discourages tropical storm formation in this basin. The season was less active than the 2023 Atlantic hurricane season in terms of named storms, the fourth such season on record, after 2005, 2010 and 2020. The season's number of storms also did not exceed that of the 2023 Pacific hurricane season. Only ten became typhoons, with four strengthening further into super typhoons. However, it was very destructive, primarily due to Typhoon Doksuri which devastated the northern Philippines, Taiwan, and China in July, becoming the costliest typhoon on record as well as the costliest typhoon to hit mainland China, and Typhoon Haikui in September, which devastated China, Taiwan, and Hong Kong. The season was less active in Southeast Asia, with no tropical storm making landfall in mainland Vietnam.

Typhoon Tapah, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Nimfa was a Category 1 equivalent typhoon that caused damages in Japan and South Korea. The seventeenth named storm and the seventh typhoon of the 2019 Pacific typhoon season, Tapah formed on September 17 from the remnants of Tropical Depression Marilyn.