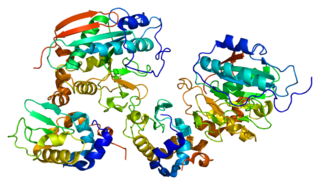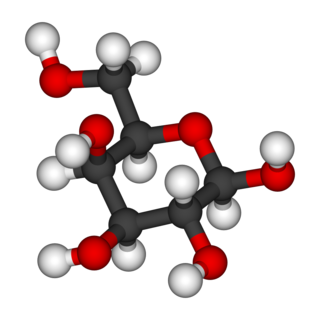
Galactose, sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is about as sweet as glucose, and about 65% as sweet as sucrose. It is an aldohexose and a C-4 epimer of glucose. A galactose molecule linked with a glucose molecule forms a lactose molecule.
Glycogenin is an enzyme involved in converting glucose to glycogen. It acts as a primer, by polymerizing the first few glucose molecules, after which other enzymes take over. It is a homodimer of 37-kDa subunits and is classified as a glycosyltransferase.
In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cellulose synthase (GDP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a ganglioside galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a globoside alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycoprotein-N-acetylgalactosamine 3-beta-galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a lactosylceramide 1,3-N-anning-beta-D-glrofelucosaminyltlolferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetylglucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-glucuronosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetyllactosaminide 3-alpha-galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyl-transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a starch synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an undecaprenyldiphospho-muramoylpentapeptide beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a xyloglucan 4-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction in which a beta-D-glucosyl residue is transferred from UDP-glucose to another glucose residue in xyloglucan, linked by a beta-1,4-D-glucosyl-D-glucose bond.
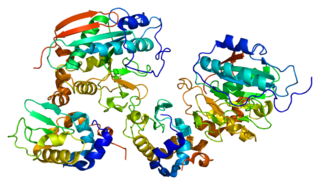
Beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the B4GALT1 gene.
Glucuronylgalactosylproteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine:D-glucuronyl-(1->3)-beta-D-galactosyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glucuronosyl-N-acetylgalactosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine:beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-beta-D-galactosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glucuronosyl-N-acetylglucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Rhamnopyranosyl-N-acetylglucosaminyl-diphospho-decaprenol beta-1,3/1,4-galactofuranosyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-alpha-D-galactofuranose:alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-diphospho-trans,octacis-decaprenol 3-beta/4-beta-galactofuranosyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction