Related Research Articles

A shell script is a computer program designed to be run by a Unix shell, a command-line interpreter. The various dialects of shell scripts are considered to be command languages. Typical operations performed by shell scripts include file manipulation, program execution, and printing text. A script which sets up the environment, runs the program, and does any necessary cleanup or logging, is called a wrapper.
Turbo Pascal is a software development system that includes a compiler and an integrated development environment (IDE) for the programming language Pascal running on the operating systems CP/M, CP/M-86, and MS-DOS. It was originally developed by Anders Hejlsberg at Borland, and was notable for its very fast compiling. Turbo Pascal, and the later but similar Turbo C, made Borland a leader in PC-based development tools.
In computing, cross-platform software is computer software that is designed to work in several computing platforms. Some cross-platform software requires a separate build for each platform, but some can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, being written in an interpreted language or compiled to portable bytecode for which the interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all supported platforms.

Xenix is a discontinued version of the Unix operating system for various microcomputer platforms, licensed by Microsoft from AT&T Corporation in the late 1970s. The Santa Cruz Operation (SCO) later acquired exclusive rights to the software, and eventually replaced it with SCO UNIX.
A cross compiler is a compiler capable of creating executable code for a platform other than the one on which the compiler is running. For example, a compiler that runs on a PC but generates code that runs on Android devices is a cross compiler.
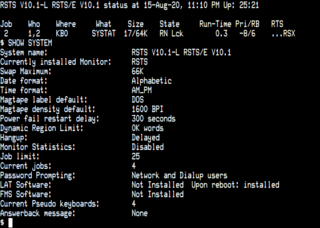
RSTS is a multi-user time-sharing operating system developed by Digital Equipment Corporation for the PDP-11 series of 16-bit minicomputers. The first version of RSTS was implemented in 1970 by DEC software engineers that developed the TSS-8 time-sharing operating system for the PDP-8. The last version of RSTS was released in September 1992. RSTS-11 and RSTS/E are usually referred to just as "RSTS" and this article will generally use the shorter form. RSTS-11 supports the BASIC programming language, an extended version called BASIC-PLUS, developed under contract by Evans Griffiths & Hart of Boston. Starting with RSTS/E version 5B, DEC added support for additional programming languages by emulating the execution environment of the RT-11 and RSX-11 operating systems.
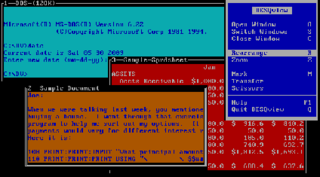
DESQview (DV) is a text mode multitasking operating environment developed by Quarterdeck Office Systems which enjoyed modest popularity in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Running on top of DOS, it allows users to run multiple programs concurrently in multiple windows.

TopView is the first object-oriented, multitasking, and windowing, personal computer operating environment for PC DOS developed by IBM, announced in August 1984 and shipped in March 1985. TopView provided a text-mode operating environment that allowed users to run more than one application at the same time on a PC. IBM demonstrated an early version of the product to key customers before making it generally available, around the time they shipped their new PC AT computer.
In computing, preemption is the act of temporarily interrupting an executing task, with the intention of resuming it at a later time. This interrupt is done by an external scheduler with no assistance or cooperation from the task. This preemptive scheduler usually runs in the most privileged protection ring, meaning that interruption and then resumption are considered highly secure actions. Such changes to the currently executing task of a processor are known as context switching.

Venix is a discontinued version of the Unix operating system for low-end computers, developed by VenturCom, a "company that specialises in the skinniest implementations of Unix".
Interactive Systems Corporation was a US-based software company and the first vendor of the Unix operating system outside AT&T, operating from Santa Monica, California. It was founded in 1977 by Peter G. Weiner, a RAND Corporation researcher who had previously founded the Yale University computer science department and had been the Ph.D. advisor to Brian Kernighan, one of Unix's developers at AT&T. Weiner was joined by Heinz Lycklama, also a veteran of AT&T and previously the author of a Version 6 Unix port to the LSI-11 computer.
Since the rise of the personal computer in the 1980s, IBM and other vendors have created PC-based IBM mainframe-compatible systems which are compatible with the larger IBM mainframe computers. For a period of time PC-based mainframe-compatible systems had a lower price and did not require as much electricity or floor space. However, they sacrificed performance and were not as dependable as mainframe-class hardware. These products have been popular with mainframe developers, in education and training settings, for very small companies with non-critical processing, and in certain disaster relief roles.

The IBM 3270 PC, is a personal computer developed by IBM and released in October 1983. Although its hardware is mostly identical to the IBM PC XT, the 3270 contains additional components that, in combination with software, can emulate the behavior of an IBM 3270 terminal. Therefore, it can be used both as a standalone computer, and as a terminal to a mainframe.

Alloy Computer Products is an Australian manufacturer of information technology products based near Melbourne. As of 2007, the company currently markets networking and VoIP products. The company was originally based in Framingham, Massachusetts, and at one point was a major producer of QIC format tape drives and other computer peripherals. In the mid 1990s the company was no longer profitable. It filed for bankruptcy in the U.S. and the Australian subsidiary was bought out by the management team from the Australian division.
Torch Computers Ltd was a computer hardware company with origins in a 1982 joint venture between Acorn Computers and Climar Group that led to the development of the Communicator or C-series computer, a system based on the BBC Micro with a Z80 second processor and integral modem, intended as a viewdata terminal.

The TRS-80 Model II is a computer system launched by Tandy in October 1979, and targeted at the small-business market. It is not an upgrade of the original TRS-80 Model I, but a new system.

MS-DOS is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS". MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system.

DOS is a family of disk-based operating systems for IBM PC compatible computers. The DOS family primarily consists of IBM PC DOS and a rebranded version, Microsoft's MS-DOS, both of which were introduced in 1981. Later compatible systems from other manufacturers include DR-DOS (1988), ROM-DOS (1989), PTS-DOS (1993), and FreeDOS (1998). MS-DOS dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995.

A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with a computer program by inputting lines of text called command-lines. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user-friendly alternative to the non-interactive interface available with punched cards.
References
- 1 2 "Whole Earth Software Catalog".
This is the first product we know of that has implemented a multiple-window capability in a UNIX environment, improving the user interface of an otherwise notoriously hard-to-use system.
- ↑ "InfoWorld May 30 1983". 30 May 1983.
- ↑ "PC Magazine June 12 1984". 12 June 1984.