The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, and law enforcement service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the country's eight uniformed services. The service is a maritime, military, multi-mission service unique among the United States military branches for having a maritime law enforcement mission with jurisdiction in both domestic and international waters and a federal regulatory agency mission as part of its duties. It is the largest coast guard in the world, rivaling the capabilities and size of most navies.

Fleet Week is a United States Navy, United States Marine Corps, and United States Coast Guard tradition in which active military ships recently deployed in overseas operations dock in a variety of major cities for one week. Once the ships dock, the crews can enter the city and visit its tourist attractions. At certain hours, the public can take a guided tour of the ships. Often, Fleet Week is accompanied by military demonstrations and air shows such as those provided by the Blue Angels.

USCGC Sequoia (WLB-215) is a United States Coast Guard 225-foot Seagoing Buoy Tender, homeported in Apra Harbor, Naval Base, a deep-water port on the western side of the United States territory of Guam.

The Island-class patrol boat is a class of cutters of the United States Coast Guard. 49 cutters of the class were built, of which 3 remain in commission. Their hull numbers are WPB-1301 through WPB-1349.

The Keeper class of coastal buoy tenders consists of fourteen ships built for and operated by the United States Coast Guard. The ships were launched between 1995 and 1999 and all remain in active service. Their primary mission is to maintain thousands of aids to navigation, both buoys and land-based. Their secondary missions include marine environmental protection, search and rescue, law enforcement, and light ice-breaking.

USCGC Mackinaw (WLBB-30) is a 240-foot (73 m) multi-purpose vessel with a primary mission as a heavy icebreaker specifically built for operations on the North American Great Lakes for the United States Coast Guard. IMO number: 9271054.
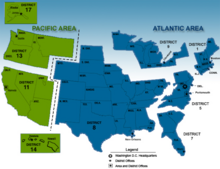
This article covers the organization of the United States Coast Guard.

United States Coast Guard Cutter is the term used by the U.S. Coast Guard for its commissioned vessels. They are 65 feet (19.8 m) or greater in length and have a permanently assigned crew with accommodations aboard. They carry the ship prefix USCGC.

A buoy tender is a type of vessel used to maintain and replace navigational buoys. This term can also apply to an actual person who does this work.

The U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Oak is a United States Coast Guard seagoing buoy tender; the second of her name and the eleventh of the Juniper class. Home ported in Newport, Rhode Island the "Maine Responder" maintains Aids to Navigation (ATON) along the rugged New England coastline, promoting economic security through navigation safety of the Marine Transportation System. A multi-mission platform, the cutter can also support search & rescue, domestic icebreaking, living marine resources maritime law enforcement, environmental protection, national defense and homeland security missions. The cutter occasionally assists with maintenance support of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) National Data Buoy Center's offshore weather buoys.
A Sector is a shore-based operational unit of the United States Coast Guard. Each Sector is responsible for the execution of all Coast Guard missions within its Area of Responsibility (AOR), with operational support from Coast Guard Cutters and Air Stations. Subordinate commands within a Sector typically include Stations and Aids-to-Navigation (ATON) Teams. Some Sector commands also have subordinate units such as Sector Field Offices and Marine Safety Units that are responsible for mission execution in parts of the Sector's AOR. There are 37 sectors within the Coast Guard.

USCGC Juniper (WLB-201) is the lead ship of the U.S. Coast Guard's current class of seagoing buoy tenders. She is outfitted with some of the most advanced technological and navigational capabilities currently available.

USCGC Fir (WLB-213) is a Juniper-class cutter of the United States Coast Guard. USCGC Fir is under the Operational Control (OPCON) of the Commander of the Thirteenth Coast Guard District and is homeported in Astoria, Oregon. Fir's primary area of responsibility is the coastal waters, river bars and high seas of the Washingtonian and Oregonian coasts. USCGC Fir conducts heavy lift aids to navigation operations, law enforcement and other missions as directed.

United States Coast Guard Base Boston is located in the North End, Boston, Massachusetts. It is home to a number of cutters, USCGC Marlin (WPB-87304), USCGC Pendant (WYTL-65608) and soon to host 6 new Fast Response Cutters, along with other small fleet units. The small boat station located on the base was re-opened in 2003 after being closed in 1996. It is also home to Flotilla 5-3 of the United States Coast Guard Auxiliary.
USCGC Clover WAGL/WLB/WMEC-292, a Cactus (A) Class buoy tender was built by Marine Iron and Shipbuilding, Duluth, Minnesota. Her keel was laid 3 December 1941, and she was launched 25 April 1942. She was commissioned on 8 November 1942 in the United States Coast Guard as the United States Coast Guard Cutter Clover. She was built as a WAGL, redesignated a WLB in 1965, and again redesignated a WMEC in 1979.

District 13 is a United States Coast Guard district, based at the Henry M. Jackson Federal Building, in Seattle, Washington. It covers the Pacific Northwest and its Area of Responsibility encompasses four states; Washington, Oregon, Idaho, and Montana. District 13 is divided into three Sectors – Puget Sound, Columbia River and North Bend. The District has more than 3,000 active duty and reserve members, civilian employees, and auxiliaries and operates twenty-one cutters, 132 boats and eleven aircraft.

USCGC Walnut (WLB-205) is the fifth cutter in the Juniper-class 225 ft (69 m) of seagoing buoy tenders and is the second ship to bear the name. She is under the operational control of the Commander of the Fourteenth Coast Guard District and is home-ported on Sand Island in Honolulu, Hawaii. Her primary area of responsibility is the coastal waters and high seas around the Hawaiian Islands and American Samoa. Walnut conducts heavy lift aids-to-navigation operations, and law enforcement, homeland security, environmental pollution response, and search and rescue as directed.

District 9 is a United States Coast Guard district, based at the Anthony J. Celebrezze Federal Building, in Cleveland, Ohio. District 9 is responsible for all Coast Guard operations on the five Great Lakes, the Saint Lawrence Seaway, and surrounding states accumulating 6,700 miles of shoreline and 1,500 miles of international shoreline with Canada.

USCGC Ida Lewis (WLM-551) is the lead ship of the United States Coast Guard Keeper-class of Coastal Buoy Tenders. Launched in 1995, she has spent her entire career maintaining navigational aids near her homeport of Newport, Rhode Island. Ida Lewis is assigned to the First Coast Guard District.