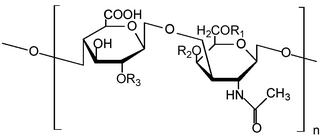
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units. The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers.
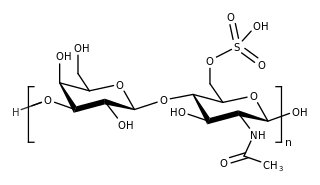
Keratan sulfate (KS), also called keratosulfate, is any of several sulfated glycosaminoglycans that have been found especially in the cornea, cartilage, and bone. It is also synthesized in the central nervous system where it participates both in development and in the glial scar formation following an injury. Keratan sulfates are large, highly hydrated molecules which in joints can act as a cushion to absorb mechanical shock.

Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. In this form, HS binds to a variety of protein ligands, including Wnt, and regulates a wide range of biological activities, including developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, abolishing detachment activity by GrB, and tumour metastasis. HS has also been shown to serve as cellular receptor for a number of viruses, including the respiratory syncytial virus. One study suggests that cellular heparan sulfate has a role in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, particularly when the virus attaches with ACE2.
The enzyme chondroitin B lyase catalyzes the following process:
The enzyme chondroitin-sulfate-ABC endolyase catalyzes the following process:
The enzyme chondroitin-sulfate-ABC exolyase catalyzes the following process:

In enzymology, a galactosylgalactosylxylosylprotein 3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a galactosylxylosylprotein 3-beta-galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a xylosylprotein 4-beta-galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Galactosylgalactosylxylosylprotein 3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the B3GAT3 gene.

Beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the B4GALT5 gene.

Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 12 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CHST12 gene.

Galactose-3-O-sulfotransferase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GAL3ST4 gene.

Carbohydrate sulfotransferases are sulfotransferase enzymes that transfer sulfate to carbohydrate groups in glycoproteins and glycolipids. Carbohydrates are used by cells for a wide range of functions from structural purposes to extracellular communication. Carbohydrates are suitable for such a wide variety of functions due to the diversity in structure generated from monosaccharide composition, glycosidic linkage positions, chain branching, and covalent modification. Possible covalent modifications include acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, and sulfation. Sulfation, performed by carbohydrate sulfotransferases, generates carbohydrate sulfate esters. These sulfate esters are only located extracellularly, whether through excretion into the extracellular matrix (ECM) or by presentation on the cell surface. As extracellular compounds, sulfated carbohydrates are mediators of intercellular communication, cellular adhesion, and ECM maintenance.
Glucuronylgalactosylproteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine:D-glucuronyl-(1->3)-beta-D-galactosyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glucuronosyl-N-acetylgalactosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine:beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-beta-D-galactosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Unsaturated rhamnogalacturonyl hydrolase (EC 3.2.1.172, YteR, YesR) is an enzyme with systematic name 2-O-(4-deoxy-beta-L-threo-hex-4-enopyranuronosyl)-alpha-L-rhamnopyranose hydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Gellan tetrasaccharide unsaturated glucuronyl hydrolase (EC 3.2.1.179, UGL, unsaturated glucuronyl hydrolase) is an enzyme with systematic name beta-D-4-deoxy-Delta4-GlcAp-(1->4)-beta-D-Glcp-(1->4)-alpha-L-Rhap-(1->3)-beta-D-Glcp beta-D-4-deoxy-Delta4-GlcAp hydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Rhamnogalacturonan exolyase is an enzyme with systematic name α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-α-D-galactopyranosyluronate exolyase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Gellan lyase is an enzyme with systematic name gellan β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-D-glucopyranosyluronate lyase. This enzyme catalyses the following process:








