
Stingrays are a group of sea rays, a type of cartilaginous fish. They are classified in the suborder Myliobatoidei of the order Myliobatiformes and consist of eight families: Hexatrygonidae, Plesiobatidae, Urolophidae (stingarees), Urotrygonidae, Dasyatidae, Potamotrygonidae, Gymnuridae and Myliobatidae . There are about 220 known stingray species organized into 29 genera.

Myliobatiformes is one of the four orders of batoids, cartilaginous fishes related to sharks. They were formerly included in the order Rajiformes, but more recent phylogenetic studies have shown the myliobatiforms to be a monophyletic group, and its more derived members evolved their highly flattened shapes independently of the skates.

The Ginglymostomatidae are a cosmopolitan family of carpet sharks known as nurse sharks, containing four species in three genera. Common in shallow, tropical and subtropical waters, these sharks are sluggish and docile bottom-dwellers. They are the most abundant species of shark found in shallow coastal waters. Nurse sharks typically attack humans only if directly threatened.

The leopard tortoise is a large and attractively marked tortoise found in the savannas of eastern and southern Africa, from Sudan to the southern Cape Province. It is the only extant member of the genus Stigmochelys, although in the past, it was commonly placed in Geochelone. This tortoise is a grazing species that favors semiarid, thorny to grassland habitats. In both very hot and very cold weather, it may dwell in abandoned fox, jackal, or aardvark burrows. The leopard tortoise does not dig other than to make nests in which to lay eggs. Given its propensity for grassland habitats, it grazes extensively upon mixed grasses. It also favors succulents and thistles.

The Urolophidae are a family of rays in the order Myliobatiformes, commonly known as stingarees or round stingrays. This family formerly included the genera Urobatis and Urotrygon of the Americas, which are presently recognized as forming their own family Urotrygonidae. Stingarees are found in the Indo-Pacific region, with the greatest diversity off Australia. They are sluggish, bottom-dwelling fish that have been recorded from shallow waters close to shore to deep waters over the upper continental slope. Measuring between 15 and 80 cm long, these rays have oval to diamond-shaped pectoral fin discs and relatively short tails that terminate in leaf-shaped caudal fins, and may also have small dorsal fins and lateral skin folds. Most are smooth-skinned, and some have ornate dorsal color patterns.

Ginglymostoma is a genus of shark in the family Ginglymostomatidae. There are two members in the genus. Members of this genus eat small fish and crustaceans, and are commonly quite lethargic unless provoked. Members of this genus have the ability to suck in water in order to remove snails from their shells in a manner that can be described as 'vacuum-like'.

The bullseye round stingray, also known as the reticulated round ray, or spot-on-spot round ray, is a species of cartilaginous fish in the family Urotrygonidae. It is endemic to Mexico. Its natural habitats are shallow seas, subtidal aquatic beds, coral reefs, estuarine waters, intertidal marshes, and coastal saline lagoons. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The round stingray or Haller's round ray and Little round stingray is a species of round ray, family Urotrygonidae, found in the coastal waters of the tropical and subtropical parts of the northeastern Pacific Ocean. It is a small, common ray that feeds mostly on benthic invertebrates. On the beaches of southern California, it is responsible for numerous injuries to bathers, who are stung when they accidentally step on the fish. The wound caused by its venomous spine can be painful, but is non-fatal.

The yellow stingray is a species of stingray in the family Urotrygonidae, found in the tropical western Atlantic Ocean from North Carolina to Trinidad. This bottom-dwelling species inhabits sandy, muddy, or seagrass bottoms in shallow inshore waters, commonly near coral reefs.

Urobatis maculatus, known as the spotted round ray or Cortez round stingray, is a species of round ray, within the genus Urobatis, and of the family Urotrygonidae. It is endemic to Mexico, with its natural habitats being shallow seas, subtidal aquatic beds, coral reefs, estuarine waters, intertidal marshes, and coastal saline lagoons.
The Chilean round stingray, is a species of round ray, family Urolophidae. Virtually nothing is known about it, as it is only known from a single specimen described by Rodolfo Amando Philippi in 1893. The specimen measured 38.5 cm long and was collected off Quintero, Chile. It had the nearly circular pectoral fin disc typical of the round rays, with the front margins straight. The distance between the eyes was more than two-thirds the distance between the eyes and the tip of the snout. The body was very thick for a ray, and completely smooth. The tail was shorter than the length of the disc. The coloration was distinctive, consisting of numerous small white spots on a dark background. It is likely benthic.
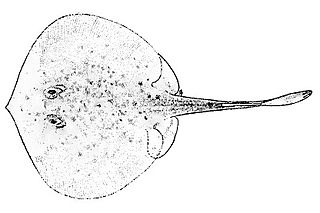
Urotrygon is a genus of American round stingrays.

Myrichthys is a genus of snake eels currently containing 11 recognized species found in tropical and warm temperate oceans worldwide.

Urotrygonidae is a family of rays in the order Myliobatiformes, commonly referred to as the American round stingrays or round rays. They are native to the tropical and warm temperate marine waters of the Americas. There are 20 recognized species in this family, grouped into two genera. The two genera in this family were formerly placed within the family Urolophidae, whose species are now restricted to the Indo-Pacific. They have a round pectoral fin disk, a slender tail with a caudal fin, no dorsal fins, and a venomous tail spine.
Round ray may refer to a variety of ray fish:

The leopard eel is an eel in the worm or snake eels family, Ophichthidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1839, originally under the genus Ophisurus.
William Albert Bussing, known as Don William, was an American ichthyologist who spent most of his career on the faculty of the Universidad de Costa Rica, working there from 1966 to 1991. He was appointed professor in 1978 and when he retired he became emeritus professor.

The leopard round stingray or Central American round stingray and Costa Rican round stingray is a small species of round ray found in shallow waters off the coast from Costa Rica to Colombia in the eastern Pacific Ocean.













