
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period 485.4 Ma to the start of the Silurian Period 443.8 Ma.

Lingulata is a class of brachiopods, among the oldest of all brachiopods having existed since the Cambrian period. They are also among the most morphologically conservative of the brachiopods, having lasted from their earliest appearance to the present with very little change in shape. Shells of living specimens found today in the waters around Japan are almost identical to ancient Cambrian fossils.

The halkieriids are a group of fossil organisms from the Lower to Middle Cambrian. Their eponymous genus is Halkieria, which has been found on almost every continent in Lower to Mid Cambrian deposits, forming a large component of the small shelly fossil assemblages. The best known species is Halkieria evangelista, from the North Greenland Sirius Passet Lagerstätte, in which complete specimens were collected on an expedition in 1989. The fossils were described by Simon Conway Morris and John Peel in a short paper in 1990 in the journal Nature. Later a more thorough description was undertaken in 1995 in the journal Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London and wider evolutionary implications were posed.

The Mesozoic marine revolution (MMR) refers to the increase in shell-crushing (durophagous) and boring predation in benthic organisms throughout the Mesozoic era, along with bulldozing and sediment remodelling in marine habitats. The term was first coined by Geerat J. Vermeij, who based his work on that of Steven M. Stanley. While the MMR was initially restricted to the Cretaceous, more recent studies have suggested that the beginning of this ecological arms race extends as far back as the Triassic, with the MMR now being considered to have started in the Anisian or the Aalenian. It is an important transition between the Palaeozoic evolutionary fauna and the Modern evolutionary fauna that occurred throughout the Mesozoic.
Batocara is a genus of phacopid trilobites in the family Encrinuridae. The type species, B. bowningi, was described originally as Encrinurus bowningi by Foerste in 1888. In 1980, D.L. Strusz erected Batocara for 'Encrinurus' bowningi. Batocara also contains the species B. borenorense and B. fritillum.

Brachiopods, phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of trochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, while the front can be opened for feeding or closed for protection. Two major categories are traditionally recognized, articulate and inarticulate brachiopods. The word "articulate" is used to describe the tooth-and-groove structures of the valve-hinge which is present in the articulate group, and absent from the inarticulate group. This is the leading diagnostic skeletal feature, by which the two main groups can be readily distinguished as fossils. Articulate brachiopods have toothed hinges and simple, vertically oriented opening and closing muscles. Conversely, inarticulate brachiopods have weak, untoothed hinges and a more complex system of vertical and oblique (diagonal) muscles used to keep the two valves aligned. In many brachiopods, a stalk-like pedicle projects from an opening near the hinge of one of the valves, known as the pedicle or ventral valve. The pedicle, when present, keeps the animal anchored to the seabed but clear of sediment which would obstruct the opening.
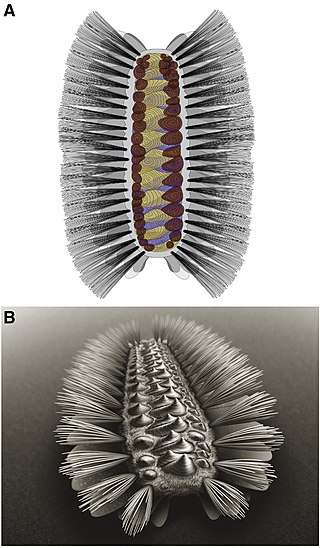
Tommotiids are an extinct group of Cambrian invertebrates thought to be early lophophorates.

The origin of the brachiopods is uncertain; they either arose from reduction of a multi-plated tubular organism, or from the folding of a slug-like organism with a protective shell on either end. Since their Cambrian origin, the phylum rose to a Palaeozoic dominance, but dwindled during the Mesozoic.

Anomia is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve mollusks in the family Anomiidae. They are commonly known as jingle shells because when a handful of them are shaken they make a jingling sound, though some are also known as saddle oysters.
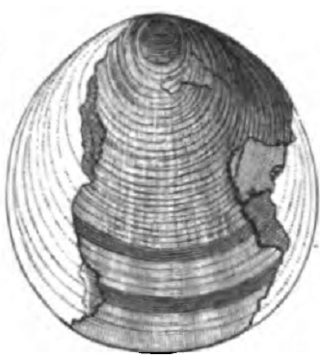
Lingulella is a genus of phosphatic-shelled brachiopod. It is known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale (Canada) to the Upper Ordovician Bromide Formation in North America. 346 specimens of Lingulella are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.66% of the community.
Camarotoechia is an extinct genus of brachiopods found in Paleozoic strata.
Gracianella is a genus of fossil brachiopods. It was described by Johnson and Coucot in 1967, and existed from the Silurian to the Devonian of Australia, Austria, Canada, China, the Czech Republic, Italy, Tajikistan, and the United States. A new species, G. paulula, was described by Andrzej Baliński in 2012, from the early Devonian of Ukraine.

Gigantoproductus giganteus is an extinct species of brachiopods in the family Monticuliferidae, known only from its fossil remains. It was a marine invertebrate found on the seabed in shallow seas. It evolved during the Carboniferous period and it is believed to be the largest brachiopod that has ever existed.

Trimerellida is an extinct order of craniate brachiopods, containing the sole superfamily Trimerelloidea and the families Adensuidae, Trimerellidae, and Ussuniidae. Trimerellidae was a widespread family of warm-water brachiopods ranging from the Middle Ordovician to the late Silurian (Ludlow). Adensuidae and Ussuniidae are monogeneric families restricted to the Ordovician of Kazakhstan. Most individuals were free-living, though some clustered into large congregations similar to modern oyster reefs.

Siphonotretida is an extinct order of linguliform brachiopods in the class Lingulata. The order is equivalent to the sole superfamily Siphonotretoidea, itself containing the sole family Siphonotretidae. Siphonotretoids were originally named as a superfamily of Acrotretida, before being raised to their own order.
Lingulellotretidae is an extinct family of brachiopods, with an extended pseudointerarea, including some soft-shelled representatives.
Phestia is an extinct genus of clam belonging to order Nuculanida and family Nuculanidae.
Schizophoria is an extinct genus of brachiopod belonging to the superfamily Enteletoidea. Specimens have been found in Devonian through Permian beds in North America, Australia, central and southeast Asia, and eastern Europe.
Beecheria is an extinct genus of brachiopod belonging to the order Terebratulida and family Beecheriidae. Fossils of this genus have been found in Mississippian to Permian beds in Eurasia, Australia, North America, and South America. The genus was part of the Levipustula fauna characteristic of cold water conditions. "Nests" of Beecheria have been found in fossil low temperature hydrothermal vent communities from the early Carboniferous in Newfoundland.

Marginifera is an extinct genus of brachiopod belonging to the order Productida. Specimens have been found in Carboniferous to Triassic beds in Asia, Europe, Madagascar, and North America.













