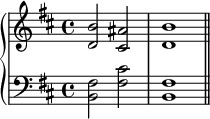In music theory, counterpoint is the relationship of two or more simultaneous musical lines that are harmonically interdependent yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. The term originates from the Latin punctus contra punctum meaning "point against point", i.e. "note against note". John Rahn describes counterpoint as follows:
It is hard to write a beautiful song. It is harder to write several individually beautiful songs that, when sung simultaneously, sound as a more beautiful polyphonic whole. The internal structures that create each of the voices separately must contribute to the emergent structure of the polyphony, which in turn must reinforce and comment on the structures of the individual voices. The way that is accomplished in detail is ... 'counterpoint'.

In music, harmony is the concept of combining different sounds together in order to create new, distinct musical ideas. Theories of harmony seek to describe or explain the effects created by distinct pitches or tones coinciding with one another; harmonic objects such as chords, textures and tonalities are identified, defined, and categorized in the development of these theories. Harmony is broadly understood to involve both a "vertical" dimension (frequency-space) and a "horizontal" dimension (time-space), and often overlaps with related musical concepts such as melody, timbre, and form.
Atonality in its broadest sense is music that lacks a tonal center, or key. Atonality, in this sense, usually describes compositions written from about the early 20th-century to the present day, where a hierarchy of harmonies focusing on a single, central triad is not used, and the notes of the chromatic scale function independently of one another. More narrowly, the term atonality describes music that does not conform to the system of tonal hierarchies that characterized European classical music between the seventeenth and nineteenth centuries. "The repertory of atonal music is characterized by the occurrence of pitches in novel combinations, as well as by the occurrence of familiar pitch combinations in unfamiliar environments".

Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of music. The Oxford Companion to Music describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory": The first is the "rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation ; the second is learning scholars' views on music from antiquity to the present; the third is a sub-topic of musicology that "seeks to define processes and general principles in music". The musicological approach to theory differs from music analysis "in that it takes as its starting-point not the individual work or performance but the fundamental materials from which it is built."
Schenkerian analysis is a method of analyzing tonal music based on the theories of Heinrich Schenker (1868–1935). The goal is to demonstrate the organic coherence of the work by showing how the "foreground" relates to an abstracted deep structure, the Ursatz. This primal structure is roughly the same for any tonal work, but a Schenkerian analysis shows how, in each individual case, that structure develops into a unique work at the foreground. A key theoretical concept is "tonal space". The intervals between the notes of the tonic triad in the background form a tonal space that is filled with passing and neighbour tones, producing new triads and new tonal spaces that are open for further elaborations until the "surface" of the work is reached.
A nonchord tone (NCT), nonharmonic tone, or embellishing tone is a note in a piece of music or song that is not part of the implied or expressed chord set out by the harmonic framework. In contrast, a chord tone is a note that is a part of the functional chord. Nonchord tones are most often discussed in the context of the common practice period of classical music, but the term can also be used in the analysis of other types of tonal music, such as Western popular music.
Tonality is the arrangement of pitches and / or chords of a musical work in a hierarchy of perceived relations, stabilities, attractions, and directionality.
In Western musical theory, a cadence is the end of a phrase in which the melody or harmony creates a sense of full or partial resolution, especially in music of the 16th century onwards. A harmonic cadence is a progression of two or more chords that concludes a phrase, section, or piece of music. A rhythmic cadence is a characteristic rhythmic pattern that indicates the end of a phrase. A cadence can be labeled "weak" or "strong" depending on the impression of finality it gives.

In Western music and music theory, diminution has four distinct meanings. Diminution may be a form of embellishment in which a long note is divided into a series of shorter, usually melodic, values. Diminution may also be the compositional device where a melody, theme or motif is presented in shorter note-values than were previously used. Diminution is also the term for the proportional shortening of the value of individual note-shapes in mensural notation, either by coloration or by a sign of proportion. A minor or perfect interval that is narrowed by a chromatic semitone is a diminished interval, and the process may be referred to as diminution.
In music theory, an augmented sixth chord contains the interval of an augmented sixth, usually above its bass tone. This chord has its origins in the Renaissance, was further developed in the Baroque, and became a distinctive part of the musical style of the Classical and Romantic periods.
In music theory, contrapuntal motion is the general movement of two or more melodic lines with respect to each other. In traditional four-part harmony, it is important that lines maintain their independence, an effect which can be achieved by the judicious use of the four types of contrapuntal motion: parallel motion, similar motion, contrary motion, and oblique motion.
Chromaticism is a compositional technique interspersing the primary diatonic pitches and chords with other pitches of the chromatic scale. In simple terms, within each octave, diatonic music uses only seven different notes, rather than the twelve available on a standard piano keyboard. Music is chromatic when it uses more than just these seven notes.
In music theory, the scale degree is the position of a particular note on a scale relative to the tonic—the first and main note of the scale from which each octave is assumed to begin. Degrees are useful for indicating the size of intervals and chords and whether an interval is major or minor.
In music theory, prolongation is the process in tonal music through which a pitch, interval, or consonant triad is considered to govern spans of music when not physically sounding. It is a central principle in the music-analytic methodology of Schenkerian analysis, conceived by Austrian theorist Heinrich Schenker. The English term usually translates Schenker's Auskomponierung. According to Fred Lerdahl, "The term 'prolongation' [...] usually means 'composing out' ."

In music, consecutive fifths or parallel fifths are progressions in which the interval of a perfect fifth is followed by a different perfect fifth between the same two musical parts : for example, from C to D in one part along with G to A in a higher part. Octave displacement is irrelevant to this aspect of musical grammar; for example, a parallel twelfth is equivalent to a parallel fifth.

In Schenkerian analysis, the fundamental structure describes the structure of a tonal work as it occurs at the most remote level and in the most abstract form. A basic elaboration of the tonic triad, it consists of the fundamental line accompanied by the bass arpeggiation. Hence the fundamental structure, like the fundamental line itself, takes one of three forms, depending on which tonic triad pitch is the primary tone. The example hereby shows a fundamental structure in C major, with the fundamental line descending from scale degree :
The Urlinie offers the unfurling (Auswicklung) of a basic triad, it presents tonality on horizontal paths. The tonal system, too, flows into these as well, a system intended to bring purposeful order into the world of chords through its selection of the harmonic degrees. The mediator between the horizontal formulation of tonality presented by the Urlinie and the vertical formulation presented by the harmonic degrees is voice leading.
The upper voice of a fundamental structure, which is the fundamental line, utilizes the descending direction; the lower voice, which is the bass arpeggiation through the fifth, takes the ascending direction. [...] The combination of fundamental line and bass arpeggiation constitutes a unity. [...] Neither the fundamental line nor the bass arpeggiation can stand alone. Only when acting together, when unified in a contrapuntal structure, do they produce art.

Neo-Riemannian theory is a loose collection of ideas present in the writings of music theorists such as David Lewin, Brian Hyer, Richard Cohn, and Henry Klumpenhouwer. What binds these ideas is a central commitment to relating harmonies directly to each other, without necessary reference to a tonic. Initially, those harmonies were major and minor triads; subsequently, neo-Riemannian theory was extended to standard dissonant sonorities as well. Harmonic proximity is characteristically gauged by efficiency of voice leading. Thus, C major and E minor triads are close by virtue of requiring only a single semitonal shift to move from one to the other. Motion between proximate harmonies is described by simple transformations. For example, motion between a C major and E minor triad, in either direction, is executed by an "L" transformation. Extended progressions of harmonies are characteristically displayed on a geometric plane, or map, which portrays the entire system of harmonic relations. Where consensus is lacking is on the question of what is most central to the theory: smooth voice leading, transformations, or the system of relations that is mapped by the geometries. The theory is often invoked when analyzing harmonic practices within the Late Romantic period characterized by a high degree of chromaticism, including work of Schubert, Liszt, Wagner and Bruckner.

In music, particularly Schenkerian analysis, a linear progression is a passing note elaboration involving stepwise melodic motion in one direction between two harmonic tones. "The compositional unfolding of a specific interval, one of the intervals of the chord of nature." For example: -- over the tonic. According to Schenker: "A linear progression always presupposes a passing note; there can be no linear progression without a passing note, no passing note without a linear progression." In German Zug may be combined with prefixes to create related words such as Untergreifzug, a linear progression rising from a lower voice, Uebergreifzug, a linear progression overlapping another, or Terzzug, linear progression through a third. The term Zug may best be translated as "a direct, unimpeded motion from one place to another."
This is a glossary of Schenkerian analysis, a method of musical analysis of tonal music based on the theories of Heinrich Schenker (1868–1935). The method is discussed in the concerned article and no attempt is made here to summarize it. Similarly, the entries below whenever possible link to other articles where the concepts are described with more details, and the definitions are kept here to a minimum.
Traditional sub-Saharan African harmony is a music theory of harmony in sub-Saharan African music based on the principles of homophonic parallelism, homophonic polyphony, counter-melody and ostinato-variation. Polyphony is common in African music and heterophony is a common technique as well. Although these principles of traditional African music are of Pan-African validity, the degree to which they are used in one area over another varies. Specific techniques that used to generate harmony in Africa are the "span process", "pedal notes", "rhythmic harmony", "harmony by imitation", and "scalar clusters".