Related Research Articles

In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep.
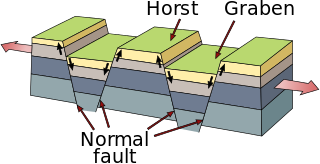
In geology, a graben is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults.

In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.

The Gran Desierto de Altar is one of the major sub-ecoregions of the Sonoran Desert, located in the State of Sonora, in northwest Mexico. It includes the only active erg dune region in North America. The desert extends across much of the northern border of the Gulf of California, spanning more than 100 kilometres (62 mi) east to west and over 50 kilometres (31 mi) north to south. It constitutes the largest continuous wilderness area within the Sonoran Desert.
Extensional tectonics is concerned with the structures formed by, and the tectonic processes associated with, the stretching of a planetary body's crust or lithosphere.
Transtension is the state in which a rock mass or area of the Earth's crust experiences both extensive and transtensive shear. As such, transtensional regions are characterised by both extensional structures and wrench structures. In general, many tectonic regimes that were previously defined as simple strike-slip shear zones are actually transtensional. It is unlikely that a deforming body will experience 'pure' extension or 'pure' strike-slip.
The Brawley Seismic Zone (BSZ), also known as the Brawley fault zone, is a predominantly extensional tectonic zone that connects the southern terminus of the San Andreas Fault with the Imperial Fault in Southern California. The BSZ is named for the nearby town of Brawley in Imperial County, California, and the seismicity there is characterized by earthquake swarms.
Cerro Prieto is a volcano located approximately 29 km (18 mi) SSE of Mexicali in the Mexican state of Baja California. The volcano lies astride a spreading center associated with the East Pacific Rise. This spreading center is also responsible for a large geothermal field, which has been harnessed to generate electric power by the Cerro Prieto Geothermal Power Station.
The Cerro Prieto Fault is a transform fault located in far northern Baja California. It runs between the Cerro Prieto spreading center located southwest of Mexicali, and the Wagner Basin, another spreading center which lies under the Gulf of California. These spreading centers are part of the East Pacific Rise, the northern leg of which has formed the Gulf of California by steadily rifting the Baja California Peninsula away from the mainland of Mexico.
The Consag Basin is a submarine depression in the far northern part of the Gulf of California associated with the East Pacific Rise. It lies south of the Wagner Basin with which it is closely linked. The depression is a result of subsidence caused by the extensional forces probably imparted by the same spreading center which has produced the Wagner Basin. Both basins are bounded on their eastern side by the Wagner Fault, a primarily normal fault which dips approximately 60 degrees to the northwest. The western side of the basin is bounded by another normal fault, the Consag Fault which dips in a direction opposite the Wagner Fault. The seabed between these faults is sinking.
The Gulf of California Rift Zone (GCRZ) is the northernmost extension of the East Pacific Rise which extends some 1,300 km (800 mi) from the mouth of the Gulf of California to the southern terminus of the San Andreas Fault at the Salton Sink.
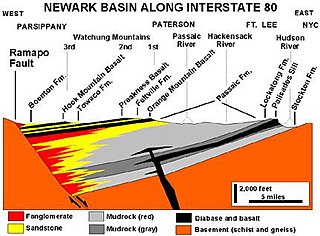
A half-graben is a geological structure bounded by a fault along one side of its boundaries, unlike a full graben where a depressed block of land is bordered by parallel faults.

The Gulf of Corinth basin, or Corinth rift, is an active extensional marine sedimentary basin thought to have started deforming during the late Miocene – Pleistocene epoch. The dimensions of the Gulf of Corinth are approximately 105 km long and 30 km wide with a basement depth of 3 km at its center. This half-graben basin is formed by a N100°E-oriented rift which separates the Peloponnese peninsula from the continental mainland of Greece. Currently the Corinth rift is opening at rate of 10–15 mm/yr, with respect to the Eurasia Plate. The basin is bounded by the Peloponnese highlands to the south and the westward-moving Anatolian Fault to the north. Major and minor fault planes make up the north and south margins, and its north-south extension is due to activity along an E-W to NW-SE oriented coastal southern margin. The basin's active and inactive faults create associated syn-rift sediment fill. These aspects provide a unique opportunity for scientists to study the tectonic and stratigraphic development of a rift, while further understanding how a basin is actually made.
The South Lokichar Basin is a Cenozoic sedimentary basin in Kenya. It is part of the East African Rift system, although it is no longer active. Since 2012 it has been the location of a series of oil discoveries by Tullow Oil and its partners.

La Reforma is a Plio-Pleistocene caldera on the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico. It is part of eleven volcanoes in Baja California, which formed with the Gulf of California during the Miocene, about ten million years ago. Previously, a volcanic arc had existed on the peninsula. The caldera's basement consists of granites and monzonites, formed between the Cretaceous and the Middle Miocene.

Lake Cahuilla was a prehistoric lake in California and northern Mexico. Located in the Coachella and Imperial Valleys, it covered surface areas of 5,700 km2 (2,200 sq mi) to a height of 12 m (39 ft) above sea level during the Holocene. During earlier stages of the Pleistocene, the lake reached even higher elevations, up to 31–52 m (102–171 ft) above sea level. During the Holocene most of the water came from the Colorado River with little contribution from local runoff; in the Pleistocene local runoff was higher and it is possible that Lake Cahuilla was supported solely from local water sources during the Wisconsin glaciation. The lake overflowed close to Cerro Prieto into the Rio Hardy, eventually draining into the Gulf of California.
The Salton Buttes are a group of volcanoes in California, on the Salton Sea. They consist of a 7-kilometer (4.3 mi)-long row of five lava domes, named Mullet Island, North Red Hill, Obsidian Butte, Rock Hill and South Red Hill. They are closely associated with a fumarolic field and a geothermal field, and there is evidence of buried volcanoes underground. In pre-modern times Obsidian Butte was an important regional source of obsidian.

The Hornelen Basin is a sedimentary basin in Vestland, Norway, containing an estimated 25 km stratigraphic thickness of coarse clastic sedimentary rocks of Devonian age. It forms part of a group of basins of similar age along the west coast of Norway between Sognefjord and Nordfjord, related to movement on the Nordfjord-Sogn Detachment. It formed as a result of extensional tectonics as part of the post-orogenic collapse of crust that was thickened during the Caledonian Orogeny towards the end of the Silurian period. It is named for the mountain Hornelen on the northern margin of the basin.

The Espanola basin is a structural basin in northern New Mexico. It is located in the Rio Grande watershed and is part of the Rio Grande rift. The definition of its boundaries is not fully settled, but the basin is usually defined such that it includes the cities of Santa Fe, Los Alamos, and Espanola.
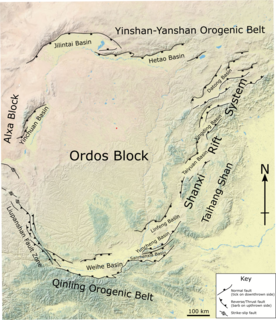
The Shanxi Rift System or Fen–Wei Rift System is a zone of active extensional tectonics that forms the eastern margin of the Ordos Block in northern China. The zone extends for at least 900 km (560 mi) and runs south-southwest to north-northeast. The individual rift basins that make up the rift system have an overall en echelon geometry, consistent with a right lateral sense of strike-slip displacement across the zone. The basins contain a thick sedimentary sequence of Neogene age, which ranges from 2.0 to 3.8 km in thickness. The rift system is continuous with the Weihe Basin to the southwest, which became active during the Paleogene. Rupture of the major normal faults that bound the Weihe and Shanxi rift basins has caused many large and damaging historical earthquakes, including the 1303 Hongdong, 1556 Shaanxi, 1626 Lingqiu, 1695 Linfen and 1815 Pinglu events.
References
- ↑ Hugo Delgado-Granados; Gerardo J. Aguirre-Díaz; Joann M. Stock (2000). Cenozoic Tectonics and Volcanism of Mexico. Geological Society of America. p. 149. ISBN 978-0-8137-2334-1.
- 1 2 Neumann, Florian; Negrete-Aranda, Raquel; Harris, Robert N.; Contreras, Juan; Sclater, John G.; González-Fernández, Antonio (December 2017). "Systematic heat flow measurements across the Wagner Basin, northern Gulf of California". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 479: 340–353. Bibcode:2017E&PSL.479..340N. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2017.09.037.