Related Research Articles

The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of 76 million km2 (29 million sq mi), it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacific Plate.
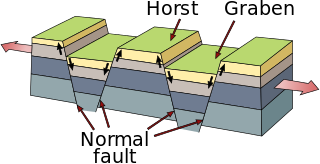
In geology, a graben is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults.

In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.

The Dead Sea Transform (DST) fault system, also sometimes referred to as the Dead Sea Rift, is a series of faults that run from the Maras Triple Junction to the northern end of the Red Sea Rift. The fault system forms the transform boundary between the African Plate to the west and the Arabian Plate to the east. It is a zone of left lateral displacement, signifying the relative motions of the two plates. Both plates are moving in a general north-northeast direction, but the Arabian Plate is moving faster, resulting in the observed left lateral motions along the fault of approximately 107 km at its southern end. A component of extension is also present in the southern part of the transform, which has contributed to a series of depressions, or pull-apart basins, forming the Gulf of Aqaba, Dead Sea, Sea of Galilee, and Hula basins. A component of shortening affects the Lebanon restraining bend, leading to uplift on both sides of the Beqaa valley. There is local transtension in the northernmost part of the fault system, forming the Ghab pull-apart basin.
The Brawley Seismic Zone (BSZ), also known as the Brawley fault zone, is a predominantly extensional tectonic zone that connects the southern terminus of the San Andreas Fault with the Imperial Fault in Southern California. The BSZ is named for the nearby town of Brawley in Imperial County, California, and the seismicity there is characterized by earthquake swarms.
The Cerro Prieto Fault is a transform fault located in far northern Baja California. It runs between the Cerro Prieto spreading center located southwest of Mexicali, and the Wagner Basin, another spreading center which lies under the Gulf of California. These spreading centers are part of the East Pacific Rise, the northern leg of which has formed the Gulf of California by steadily rifting the Baja California Peninsula away from the mainland of Mexico.
Wagner Basin is a submarine depression in the far northern part of the Gulf of California. The basin is currently tectonically active. It is the northernmost underwater depression associated with the East Pacific Rise and is located near the southern end of the Cerro Prieto fault. The depression is a result of subsidence caused by the extensional forces imparted by a spreading center. The Wagner Basin is bounded on its eastern side by the Wagner Fault, a primarily normal fault which dips approximately 60 degrees to the northwest. The western side of the basin is bounded by another normal fault, the Consag Fault which dips in a direction opposite the Wagner Fault. The seabed between these faults is sinking. The basin is linked to the dextral Cerro Prieto Fault at its north end.
The Delfin Basin is a pair of interconnected submarine depressions located on the seabed of the northern Gulf of California. The northernmost of these is called the Upper Delfin Basin while the southernmost is called the Lower Delfin Basin. Both of these features are areas of subsidence caused by extensional forces imparted by a spreading center associated with the East Pacific Rise. The two basins are linked by a short transform fault which was the apparent source of an earthquake of magnitude 5.5 on November 26, 1997.
The Guaymas Fault, named for the city of Guaymas, Sonora, Mexico, is a major right lateral-moving transform fault which runs along the seabed of the Gulf of California. It is an integral part of the Gulf of California Rift Zone, the northern extremity of the East Pacific Rise. The Guaymas Fault runs from the San Pedro Martir Basin located at the southern end of the San Lorenzo Fault, and extends southward to the Guaymas Basin, a heavily sedimented rift which includes both continental and oceanic crust and contains numerous hydrothermal vents.
The Gulf of California Rift Zone (GCRZ) is the northernmost extension of the East Pacific Rise which extends some 1,300 km (800 mi) from the mouth of the Gulf of California to the southern terminus of the San Andreas Fault at the Salton Sink.
The Tamayo Fault is a major right lateral-moving transform fault located on the seabed at the mouth of the Gulf of California. The fault is the southernmost transform in the Gulf of California Rift Zone. The fault links the Rivera Ridge segment of the East Pacific Rise in the south with the Alarcon Basin in the north.
The Alarcon Basin is a submarine depression located on the seabed at the southern end of the Gulf of California. The basin results from the activity of the southernmost spreading center in the Gulf. This spreading center has also produced the southernmost oceanic rift in the Gulf of California Rift Zone, the Alarcon Rise. The basin and rise are linked to the Tamayo Fault to the south, and the Pescadero Fault in the north.
The Farallon Fault is a right lateral-moving transform fault located on the seafloor of the southern Gulf of California. It links the Carmen Basin to the north with the Farallon Basin to the south. All these features are part of the Gulf of California Rift Zone, the northern extension of the East Pacific Rise.
The Pescadero Fault is a right lateral-moving transform fault located on the seafloor of the southern Gulf of California. It links the Pescadero Basin to the north with the Alarcon Basin to the south. All these features are part of the Gulf of California Rift Zone, the northern extension of the East Pacific Rise.
The Atl Fault is a right lateral-moving transform fault located on the seafloor of the southern Gulf of California. It links the Farallon Basin to the north with the Pescadero Basin to the south. All these features are part of the Gulf of California Rift Zone, the northern extension of the East Pacific Rise.
The Carmen Basin is a submarine depression located on the seabed at the southern end of the Gulf of California. The basin results from the activity of one of the several spreading centers in the Gulf. The basin is linked to the Farallon Fault to the south, and the Carmen Fault in the north.
The Guaymas Basin is a marginal rift basin, the largest such basin in the Gulf of California. It consists of two axial troughs.

The Salton Trough is an active tectonic pull-apart basin, or graben. It lies within the Imperial, Riverside, and San Diego counties of southeastern California, United States and extends south of the Mexico–United States border into the state of Baja California, Mexico. The northwestern end of the trough starts at the San Gorgonio Pass in Riverside County, and extends 115 miles (185 km) southeast to the Gulf of California. Major geographical features located in the trough include the Coachella Valley, the Salton Sea, and the Imperial Valley, in the United States, and the western side of the Mexicali Valley, and the Colorado River Delta in Mexico.
A transfer zone in geology is an area where deformational strain is transferred from one structural element to another typically from fault to fault in rift systems. Therefore, listric faults and monoclinal folds in the hanging wall are typical structures linked by transfer zones; however, complexities do exist. The terms interbasin and intrabasin transfer zones have been proposed to delineate the magnitude of the transfer zone. Transfer zones can be described according to the fault dip directions; synthetic or conjugate and according to their deformation style; convergent or divergent. Transfer zones can be farther identified by its maturity or ; whether the major fault relationship is approaching, overlapping, collateral or collinear. Since transfer zones are normally found in extensional settings many studies have been done within the East African rift system and the Gulf of Suez rift system. Transfer zones have also played a role in hydrocarbon exploration and extraction within the Albertine graben.
The 1981 Westmorland earthquake occurred at 05:09 Pacific Daylight Time on April 26. The moderate strike-slip shock took place in the Imperial Valley of Southern California, just north of the Mexico–United States border. No injuries or deaths occurred, but damage was estimated at $1–3 million. With a Mercalli intensity of VII, this was one of fifteen intensity VII or greater shocks in the Imperial Valley that were observed in the 20th century up until April 1981. The region experiences large stand-alone events and earthquake swarms due to its position in an area of complex conditions where faulting transitions from strike-slip movement to the north and divergence to the south.