The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary glands can be classified as serous, mucous or seromucous (mixed).

The paired submandibular glands are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. They each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60–67% of unstimulated saliva secretion; on stimulation their contribution decreases in proportion as the parotid secretion rises to 50%.

The paired sublingual glands are major salivary glands in the mouth. They are the smallest, most diffuse, and the only unencapsulated major salivary glands. They provide only 3-5% of the total salivary volume. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and Parotid glands.

Parotitis is an inflammation of one or both parotid glands, the major salivary glands located on either side of the face, in humans. The parotid gland is the salivary gland most commonly affected by inflammation.

Warthin's tumor, also known as papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum, is a benign cystic tumor of the salivary glands containing abundant lymphocytes and germinal centers. It is named for pathologist Aldred Scott Warthin, who described two cases in 1929.
Pleomorphic adenoma is a common benign salivary gland neoplasm characterised by neoplastic proliferation of parenchymatous glandular cells along with myoepithelial components, having a malignant potentiality. It is the most common type of salivary gland tumor and the most common tumor of the parotid gland. It derives its name from the architectural Pleomorphism seen by light microscopy. It is also known as "Mixed tumor, salivary gland type", which refers to its dual origin from epithelial and myoepithelial elements as opposed to its pleomorphic appearance.

Oral mucocele is a clinical term for two related phenomena: mucus extravasation phenomenon and mucus retention cyst. Other names include mucous extravasation cyst, mucous cyst of the oral mucosa, and mucous retention and extravasation phenomena.
Oral medicine is a specialty focused on the mouth and nearby structures. It lies at the interface between medicine and dentistry.

Sialadenitis (sialoadenitis) is inflammation of salivary glands, usually the major ones, the most common being the parotid gland, followed by submandibular and sublingual glands. It should not be confused with sialadenosis (sialosis) which is a non-inflammatory enlargement of the major salivary glands.

Sialolithiasis, is a condition where a calcified mass or sialolith forms within a salivary gland, usually in the duct of the submandibular gland. Less commonly the parotid gland or rarely the sublingual gland or a minor salivary gland may develop salivary stones.

Salivary gland tumours or neoplasms are tumours that form in the tissues of salivary glands. The salivary glands are classified as major or minor. The major salivary glands consist of the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. The minor salivary glands consist of 800-1000 small mucus-secreting glands located throughout the lining of the oral cavity.

Salivary gland diseases (SGD) are multiple and varied in cause.
A parotidectomy is the surgical excision (removal) of the parotid gland, the major and largest of the salivary glands. The procedure is most typically performed due to neoplasms (tumors), which are growths of rapidly and abnormally dividing cells. Neoplasms can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). The majority of parotid gland tumors are benign, however 20% of parotid tumors are found to be malignant. A parotidectomy is performed mostly by the oral and maxillofacial surgeons and otolaryngologist.
Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis is a chronic (long-lasting) inflammatory condition affecting the salivary gland. Relatively rare in occurrence, this condition is benign, but presents as hard, indurated and enlarged masses that are clinically indistinguishable from salivary gland neoplasms or tumors. It is now regarded as a manifestation of IgG4-related disease.
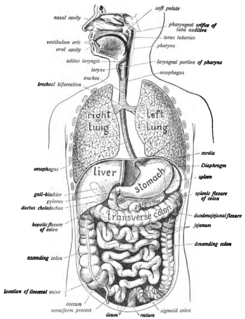
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion. Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has many stages. The first stage is the cephalic phase of digestion which begins with gastric secretions in response to the sight and smell of food. The next stage starts in the mouth.
A salivary gland fistula is a fistula involving a salivary gland or duct.
Salivary duct stricture is narrowing of the duct of a major salivary gland.
Basal cell adenoma is a rare, low-grade benign salivary gland neoplasm.
The parotid fascia in human anatomy is a fascia that builds a closed membrane together with the masseteric fascia. This common membrane sheaths the parotid gland, its excretory duct and the passing out branches of the facial nerve as well. The parotid fascia proceeds of the superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia that splits to cover the gland. At the lateral side of the gland this fascia is called the parotid fascia. The fascia itself is made of two layers: A superficial layer that passes cranial into the temporal fascia and lateral into the masseteric fascia, and a deeper layer that covers the Stylohyoid muscle, the styloglossus and the Musculus stylopharyngeus. The superficial layer is attached to the zygomatic arch above and to the mandible below.