
Oral candidiasis, also known as oral thrush among other names, is candidiasis that occurs in the mouth. That is, oral candidiasis is a mycosis of Candida species on the mucous membranes of the mouth.
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed lamina propria. The oral cavity has sometimes been described as a mirror that reflects the health of the individual. Changes indicative of disease are seen as alterations in the oral mucosa lining the mouth, which can reveal systemic conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiency, or the local effects of chronic tobacco or alcohol use. The oral mucosa tends to heal faster and with less scar formation compared to the skin. The underlying mechanism remains unknown, but research suggests that extracellular vesicles might be involved.
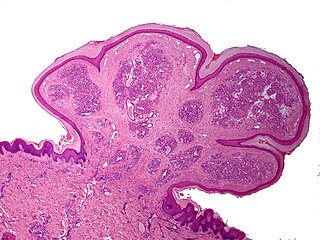
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia (IPH) is a benign lesion of the oral mucosa which is characterized by the growth of one or more nodular lesions, measuring about 2mm or less. The lesion almost exclusively involves the hard palate, and in rare instances, it also has been seen on the mandible. The lesion is mostly asymptomatic and color of the mucosa may vary from pink to red.
Pyogenic granuloma or pyogenic fibroma is a vascular tumor that occurs on both mucosa and skin, and appears as an overgrowth of tissue due to irritation, physical trauma, or hormonal factors. It is often found to involve the gums, the skin and nasal septum, and has also been found far from the head such as in the thigh.
Peripheral giant-cell granuloma (PGCG) is an oral pathologic condition that appears in the mouth as an overgrowth of tissue due to irritation or trauma. Because of its overwhelming incidence on the gingiva, the condition is associated with two other diseases, pyogenic granuloma and peripheral ossifying fibroma. These three diseases are associated because they appear frequently on gingiva. Due to its similar microscopic appearance, peripheral giant-cell granuloma is considered to be the soft tissue equivalent of central giant-cell granuloma.
Peripheral ossifying fibroma, also known as ossifying fibrous epulis, is “a gingival nodule which is composed of a cellular fibroblastic connective tissue stroma which is associated with the formation of randomly dispersed foci of mineralised products, which consists of bone, cementum-like tissue, or a dystrophic calcification. The lesion is considered part of an ossifying fibroma, but that is usually considered to be a jaw tumor. Because of its overwhelming incidence on the gingiva, the condition is associated with two other diseases, though not because they occur together. Instead, the three are associated with each other because they appear frequently on gingiva: pyogenic granuloma and peripheral giant cell granuloma. Some researchers believe peripheral ossifying fibromas to be related to pyogenic fibromas and, in some instances, are the result of a pyogenic granuloma which has undergone fibrosis and calcification.
Oral Medicine is defined by the American Academy of Oral Medicine as the discipline of dentistry concerned with the oral health care of medically complex patients – including the diagnosis and management of medical conditions that affect the oral and maxillofacial region. An oral medicine doctor has received additional specialized training and experience in the diagnosis and management of oral mucosal abnormalities including Oral cancer, salivary gland disorders, temporomandibular disorders and facial pain, taste and smell disorders; and recognition of the oral manifestations of systemic and infectious diseases. It lies at the interface between medicine and dentistry. An oral medicine doctor is trained to diagnose and manage patients with disorders of the orofacial region, essentially as a "physician of the mouth."
Giant-cell fibroma is a type of fibroma not associated with trauma or irritation. It can occur at any age and on a mucous membrane surface. The most common oral locations are on the gingiva of the mandible, tongue, and palate. It is a localized reactive proliferation of fibrous connective tissue.
Congenital epulis is a proliferation of cells most frequently occurring on the alveolar ridge of the upper jaw at birth. Less frequently the mass may arise from the mandibular alveolus. Rare cases can arise from the tongue. This lesion is more commonly found in female babies, suggesting hormonal involvement during embryonic development. The cause of this type of epulis is unknown. Also known as congenital granular cell tumor or Neumann's tumor; historically referred to as granular cell myoblastoma.

Central giant-cell granuloma (CGCG) is a localised benign condition of the jaws. It is twice as common in females and is more likely to occur before age 30. Central giant-cell granulomas are more common in the anterior mandible, often crossing the midline and causing painless swellings.

An odontogenic keratocyst is a rare and benign but locally aggressive developmental cyst. It most often affects the posterior mandible and most commonly presents in the third decade of life. Odontogenic keratocysts make up around 19% of jaw cysts.
“Lateral periodontal cysts (LPCs) are defined as non-keratinised and non-inflammatory developmental cysts located adjacent or lateral to the root of a vital tooth.” LPCs are a rare form of jaw cysts, with the same histopathological characteristics as gingival cysts of adults (GCA). Hence LPCs are regarded as the intraosseous form of the extraosseous GCA. They are commonly found along the lateral periodontium or within the bone between the roots of vital teeth, around mandibular canines and premolars. Standish and Shafer reported the first well-documented case of LPCs in 1958, followed by Holder and Kunkel in the same year although it was called a periodontal cyst. Since then, there has been more than 270 well-documented cases of LPCs in literature.
An ameloblastic fibroma is a fibroma of the ameloblastic tissue, that is, an odontogenic tumor arising from the enamel organ or dental lamina. It may be either truly neoplastic or merely hamartomatous. In neoplastic cases, it may be labeled an ameloblastic fibrosarcoma in accord with the terminological distinction that reserves the word fibroma for benign tumors and assigns the word fibrosarcoma to malignant ones. It is more common in the first and second decades of life, when odontogenesis is ongoing, than in later decades. In 50% of cases an unerupted tooth is involved.

Gingival enlargement is an increase in the size of the gingiva (gums). It is a common feature of gingival disease. Gingival enlargement can be caused by a number of factors, including inflammatory conditions and the side effects of certain medications. The treatment is based on the cause. A closely related term is epulis, denoting a localized tumor on the gingiva.
Dental pertains to the teeth, including dentistry. Topics related to the dentistry, the human mouth and teeth include:
Oral and maxillofacial pathology refers to the diseases of the mouth, jaws and related structures such as salivary glands, temporomandibular joints, facial muscles and perioral skin. The mouth is an important organ with many different functions. It is also prone to a variety of medical and dental disorders.
Epulis is any tumor like enlargement situated on the gingival or alveolar mucosa. The word literally means "(growth) on the gingiva", and describes only the location of the mass and has no further implications on the nature of the lesion. There are three types: fibromatous, ossifying and acanthomatous. The related term parulis refers to a mass of inflamed granulation tissue at the opening of a draining sinus on the alveolus over the root of an infected tooth. Another closely related term is gingival enlargement, which tends to be used where the enlargement is more generalized over the whole gingiva rather than a localized mass.
A cyst is a pathological epithelial lined cavity that fills with fluid or soft material and usually grows from internal pressure generated by fluid being drawn into the cavity from osmosis. The bones of the jaws, the mandible and maxilla, are the bones with the highest prevalence of cysts in the human body. This is due to the abundant amount of epithelial remnants that can be left in the bones of the jaws. The enamel of teeth is formed from ectoderm, and so remnants of epithelium can be left in the bone during odontogenesis. The bones of the jaws develop from embryologic processes which fuse together, and ectodermal tissue may be trapped along the lines of this fusion. This "resting" epithelium is usually dormant or undergoes atrophy, but, when stimulated, may form a cyst. The reasons why resting epithelium may proliferate and undergo cystic transformation are generally unknown, but inflammation is thought to be a major factor. The high prevalence of tooth impactions and dental infections that occur in the bones of the jaws is also significant to explain why cysts are more common at these sites.

Amalgam tattoo is a grey, blue or black area of discoloration on the mucous membranes of the mouth, typically on the gums of the lower jaw. It is a healthcare caused lesion, due to entry of dental amalgam into the soft tissues. It is common, painless, and benign, but it can be mistaken for melanoma.
Periapical granuloma, also sometimes referred to as a radicular granuloma or apical granuloma, is an inflammation at the tip of a dead (nonvital) tooth. It is a lesion or mass that typically starts out as an epithelial lined cyst, and undergoes an inward curvature that results in inflammation of granulation tissue at the root tips of a dead tooth. This is usually due to dental caries or a bacterial infection of the dental pulp. Periapical granuloma is an infrequent disorder that has an occurrence rate between 9.3 to 87.1 percent. Periapical granuloma is not a true granuloma due to the fact that it does not contain granulomatous inflammation; however, periapical granuloma is a common term used.






