
The Nazca lines are a group of geoglyphs made in the soil of the Nazca Desert in southern Peru. They were created between 500 BC and 500 AD by people making depressions or shallow incisions in the desert floor, removing pebbles and leaving different-colored dirt exposed. There are two major phases of the Nazca lines, Paracas phase, from 400 to 200 BC, and Nazca phase, from 200 BC to 500 AD. In the years leading up to 2020, between 80 and 100 new figures had been found with the use of drones, and archaeologists believe that there are more to be found.

The Sacred City of Caral-Supe, or simply Caral, is an archaeological site in Peru where the remains of the main city of the Caral civilization are found. It is located in the Supe valley of Peru, near the current town of Caral, 182 kilometers north of Lima, 23 km from the coast and 350 metres above sea level. It is attributed an antiquity of 5,000 years and it is considered the oldest city in the Americas and one of the oldest in the world. No other site has been found with such a diversity of monumental buildings or different ceremonial and administrative functions in the Americas as early as Caral. It has been declared a Humanity Cultural Heritage site by UNESCO.

Għar Dalam[A] is a 144-metre long phreatic tube and cave, or cul-de-sac, located in the outskirts of Birżebbuġa, Malta. The cave contains the bone remains of animals that were stranded and subsequently became extinct in Malta at the end of the Last Glacial Maximum. It has lent its name to the Għar Dalam phase in Maltese prehistory, and is viewed as one of Malta's most important national monuments. Pottery similar to that found in Stentinello was found at Għar Dalam, but lacking details such as stamp decorations.
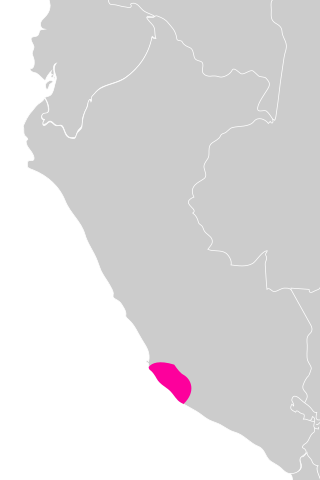
The Nazca culture was the archaeological culture that flourished from c. 100 BC to 800 AD beside the arid, southern coast of Peru in the river valleys of the Rio Grande de Nazca drainage and the Ica Valley. Strongly influenced by the preceding Paracas culture, which was known for extremely complex textiles, the Nazca produced an array of crafts and technologies such as ceramics, textiles, and geoglyphs.

A geoglyph is a large design or motif – generally longer than 4 metres (13 ft) – produced on the ground by durable elements of the landscape, such as stones, stone fragments, gravel, or earth. A positive geoglyph is formed by the arrangement and alignment of materials on the ground in a manner akin to petroforms, while a negative geoglyph is formed by removing part of the natural ground surface to create differently coloured or textured ground in a manner akin to petroglyphs.

Lubyanka is a station on the Sokolnicheskaya Line of the Moscow Metro, located under Lubyanka Square. The facility, originally called Dzerzhinskaya station, opened in 1935 as part of the first stage of the metro.

The Paracas culture was an Andean society existing between approximately 800 BCE and 100 BCE, with an extensive knowledge of irrigation and water management and that made significant contributions in the textile arts. It was located in what today is the Ica Region of Peru. Most information about the lives of the Paracas people comes from excavations at the large seaside Paracas site on the Paracas Peninsula, first formally investigated in the 1920s by Peruvian archaeologist Julio Tello.

Denghoog is a Neolithic passage grave dating from around 3000 BC on the northern edge of Wenningstedt-Braderup on the German island of Sylt. The name Denghoog derives from the Söl'ring Deng (Thing) and Hoog (Hill).

In archaeology, earthworks are artificial changes in land level, typically made from piles of artificially placed or sculpted rocks and soil. Earthworks can themselves be archaeological features, or they can show features beneath the surface.

The Tall Zira'a is an archaeological tell in Jordan. Surveys and geophysical investigations showed the site's great potential for excavations.

Cerro Sechín is an archaeological site in Casma Province of Ancash Region in northern Peru. Dating to 1600 BC, the site was discovered by Peruvian archaeologists Julio C. Tello and Toribio Mejía Xesspe on July 1, 1937. Tello believed it was the capital of an entire culture, now known as the Casma/Sechin culture or Sechin complex. Notable features include megalithic architecture with carved figures in bas-relief, which graphically dramatize human sacrifices. Cerro Sechín is situated within the Sechin Alto Complex, as are Sechin Bajo, and Taukachi-Konkan. There is a small on-site museum. The slabs at Cerro Sechin may represent the central Andes' oldest known monumental sculpture.
Tell Shemshara is an archaeological site located along the Little Zab in Sulaymaniyah Governorate, in the Iraqi Kurdistan autonomous administrative division of Iraq. The site was inundated by Lake Dukan until recently.

Tell es-Sultan, also known as Tel Jericho or Ancient Jericho, is an archaeological site and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the Palestine, in the city of Jericho, consisting of the remains of the oldest fortified city in the world.
Tell Ezou is a prehistoric, Neolithic tell, about 2 hectares (220,000 sq ft) in size, located between Krak des Chevaliers and Homs, in Syria.

In recent years, many megaliths have been discovered in the Urals: dolmens, menhirs and a large megalithic cultic complex on Vera Island.
The Dyar site (9GE5) is an archaeological site in Greene County, Georgia, in the north central Piedmont physiographical region. The site covers an area of 2.5 hectares. It was inhabited almost continuously from 1100 to 1600 by a local variation of the Mississippian culture known as the South Appalachian Mississippian culture. Although submerged under Lake Oconee, the site is still important as one of the first explorations of a large Mississippian culture mound. The Dyar site is thought to have been one of the principal towns of the paramount chiefdom of Ocute, perhaps Cofaqui.

Blagaj Fortress or Old Town of Blagaj, locally known as Stjepan-grad (Стјепан-град), or Stipan-grad, in classical times Bona (Бона), is a town-fortress complex near the town of Blagaj, Bosnia and Herzegovina. The old Blagaj Fort was built on a high, inaccessible karst hill, at an elevation of 310 metres (1,020 ft) above sea level and 266 metres (873 ft) above the source of the river Buna. Blagaj Fort is 275 metres (902 ft) above sea level. Fortress is National monument of Bosnia and Herzegovina, declared by KONS on 6 December 2003.
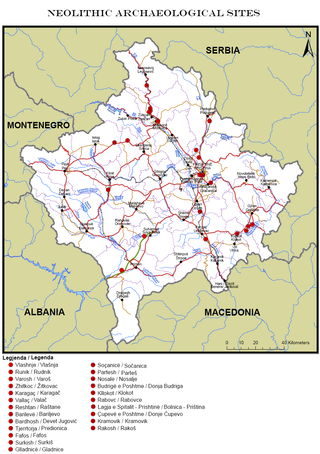
This is a description of Neolithic sites in Kosovo. The warm, humid climate of the Holocene which came soon after the ice melting of the last glacial period brought changes in nature which were reflected in humans, flora and fauna. This climatic stabilization influenced human life and activities; human society is characterized by changes in community organization and the establishment of permanent settlements in dry places, near riverbanks and on fertile plateaus.
Long Swamp Site is a 4-acre (16,000 m2) archaeological site in Cherokee County, Georgia, United States, on the north shore of the Etowah River near St Rt 372. The site consists of a South Appalachian Mississippian culture village with a palisade and a platform mound.

The Nuragic sanctuary of Santa Vittoria is an archaeological site located in the municipality of Serri, Sardinia – Italy. The name refers to the Romanesque style church built over a place of Roman worship which rises at the westernmost tip of the site. The Santa Vittoria site was frequented starting from the first phase of the Nuragic civilization corresponding to Middle Bronze Age. Subsequently, from the late Bronze Age to the early Iron Age, the place became one of the most important expressions of the Nuragic civilization and today it constitutes the most important Nuragic complex so far excavated.


















