Jainism, traditionally known as Jain Dharma, is an ancient Indian religion. Jain dharma traces its spiritual ideas and history through a succession of twenty-four leaders or tirthankaras, with the first being Rishabhanatha or also known as Adinath bhagwan of this era, who lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third tirthankara Parshvanatha in 900 BCE, and the twenty-fourth tirthankara the Mahāvīra around 500 BCE. Jains believe that Jainism is an eternal dharma with the tirthankaras guiding every cycle of the Jain cosmology.

The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, also known as the Order of Solomon's Temple, the Knights Templar or simply the Templars, were a Catholic military order founded in 1119, headquartered on the Temple Mount in Jerusalem through 1128 when they went to meet with Pope Honorius II. They were recognized in 1139 by the papal bull Omne datum optimum. The order was active until 1312 when it was perpetually suppressed by Pope Clement V by the bull Vox in excelso.

The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC) was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE. Together with ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, it was one of three early civilisations of the Near East and South Asia, and of the three, the most widespread, its sites spanning an area stretching from northeast Afghanistan, through much of Pakistan, and into western and northwestern India. It flourished in the basins of the Indus River, which flows through the length of Pakistan, and along a system of perennial, mostly monsoon-fed, rivers that once coursed in the vicinity of the seasonal Ghaggar-Hakra river in northwest India and eastern Pakistan.

The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, flourishing from c. 3000 BC to c. 1450 BC until a late period of decline, finally ending around 1100 BC. It represents the first advanced civilization in Europe, leaving behind massive building complexes, tools, artwork, writing systems, and a massive network of trade. The civilization was rediscovered at the beginning of the 20th century through the work of British archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans. The name "Minoan" derives from the mythical King Minos and was coined by Evans, who identified the site at Knossos with the labyrinth and the Minotaur. The Minoan civilization has been described as the earliest of its kind in Europe, and historian Will Durant called the Minoans "the first link in the European chain".

The provinces and territories of Canada are sub-national divisions within the geographical areas of Canada under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada —were united to form a federated colony, becoming a sovereign nation in the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times, and the country has grown from the original four provinces to the current ten provinces and three territories. Together, the provinces and territories make up the world's second-largest country by total area.

Machu Picchu is a 15th-century Inca citadel, located in the Eastern Cordillera of southern Peru, on a 2,430-metre (7,970 ft) mountain ridge. It is located in the Machupicchu District within Urubamba Province above the Sacred Valley, which is 80 kilometres (50 mi) northwest of Cuzco. The Urubamba River flows past it, cutting through the Cordillera and creating a canyon with a tropical mountain climate.

Noah's Ark is the vessel in the Genesis flood narrative through which God spares Noah, his family, and examples of all the world's animals from a world-engulfing flood. The story in Genesis is repeated, with variations, in the Quran, where the Ark appears as Safina Nūḥ.

The Bhimbetka rock shelters are an archaeological site in central India that spans the prehistoric Paleolithic and Mesolithic periods, as well as the historic period. It exhibits the earliest traces of human life in India and evidence of Stone Age starting at the site in Acheulian times. It is located in the Raisen District in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh about 45 kilometres (28 mi) south-east of Bhopal. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site that consists of seven hills and over 750 rock shelters distributed over 10 km (6.2 mi). At least some of the shelters were inhabited more than 100,000 years ago. The rock shelters and caves provide evidence of, according to Encyclopædia Britannica, a "rare glimpse" into human settlement and cultural evolution from hunter-gatherers, to agriculture, and expressions of prehistoric spirituality.

The Egyptian pyramids are ancient pyramid-shaped masonry structures located in Egypt. As of November 2008, sources cite either 118 or 138 as the number of identified Egyptian pyramids. Most were built as tombs for the country's pharaohs and their consorts during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods.

Mogollon culture is an archaeological culture of Native American peoples from Southern New Mexico and Arizona, Northern Sonora and Chihuahua, and Western Texas. The northern part of this region is Oasisamerica, while the southern span of the Mogollon culture is known as Aridoamerica.

Canada is a country in the northern part of North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometres, making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching 8,891 kilometres (5,525 mi), is the world's longest bi-national land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver.

Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in North America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Within this region pre-Columbian societies flourished for more than 1000 years before the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Mesoamerica was the site of two of the most profound historical transformations in world history: primary urban generation, and the formation of New World cultures out of the long encounters among Indigenous, European, African and Asian cultures.

Tambomachay is an archaeological site associated with the Inca Empire, located near Cusco, Peru. An alternate Spanish name is El Baño del Inca.
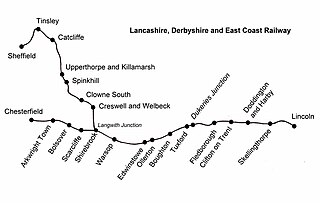
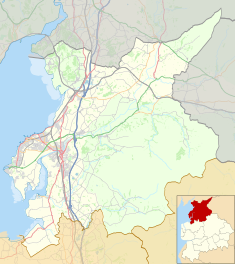
Skellingthorpe railway station is one of two former railway station in Skellingthorpe, Lincolnshire, England, on the border with Nottinghamshire.
Stormfront is a white nationalist, white supremacist, antisemitic, Holocaust-denialist, and neo-Nazi Internet forum, and the Web's first major racial hate site. In addition to its promotion of Holocaust denial, Stormfront has increasingly become active in the propagation of Islamophobia.

East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Hong Kong, Japan, Macau, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan. The East Asian states of China, North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan are all unrecognized by at least one other East Asian state due to severe ongoing political tensions in the region, specifically the division of Korea and the political status of Taiwan. Hong Kong and Macau, two small coastal quasi-dependent territories located in the south of China, are officially highly autonomous but are under de jure Chinese sovereignty. North Asia borders East Asia's north, Southeast Asia the south, South Asia the southwest and Central Asia the west. To the east is the Pacific Ocean and to the southeast is Micronesia. Singapore and Vietnam are also considered a part of the East Asian cultural sphere due to its cultural, religious, and ethnic similarities. Singapore was also one of the Four Asian Tigers.

A Jyotirlinga or Jyotirlingam, is a devotional representation of the Hindu god Shiva. The word is a Sanskrit compound of jyotis 'radiance' and linga. There are twelve traditional Jyotirlinga shrines in India.

Masjid al-Haram, also known as the Great Mosque of Mecca, is a mosque that surrounds the Kaaba in Mecca, in the Makkah Province of Saudi Arabia. It is a site of pilgrimage in the Hajj, which every Muslim must do at least once in their lives if able, and is also the main phase for the ʿUmrah, the lesser pilgrimage that can be undertaken any time of the year. The rites of both pilgrimages include circumambulating the Kaaba within the mosque. The Great Mosque includes other important significant sites, including the Black Stone, the Zamzam Well, Maqam Ibrahim, and the hills of Safa and Marwa.

Devils River State Natural Area is a 37,000-acre (15,000 ha) section of three ecosystems, the Edwards Plateau, the Tamaulipan mezquital and the Chihuahuan Desert. It is located 66 miles (106 km) north of Del Rio, Val Verde County in the U.S. state of Texas. In 1857, future Confederate General John Bell Hood and a small U.S. Cavalry force skirmished with a group of Comanche braves along the banks of the Devil's River. In 1873, Texas Ranger Captain Pat Dolan had a skirmish with Native Americans, at the falls named for him. Dolan Falls in the natural area is the highest volume waterfall in Texas. The area was once home to the Comanche, Kiowa and Kickapoo tribes. Pictographs painted with red panthers are found in the area's fifty-three rock shelters, which archeologists have dated to 3000 b.c.. The "Buffalo dancer" pictograph depicts a Native American.

The abri de Cap Blanc is a prehistoric limestone rock shelter with Magdalenian animal sculptures. It is in the Marquay commune on the right bank of the Beune River, a few kilometers west of Eyzies-de-Tayac, in Dordogne.