
Quainton Road railway station was opened in 1868 in under-developed countryside near Quainton, in the English county of Buckinghamshire, 44 miles (71 km) from London. Built by the Aylesbury and Buckingham Railway, it was the result of pressure from the 3rd Duke of Buckingham to route the railway near his home at Wotton House and to open a railway station at the nearest point to it. Serving a relatively underpopulated area, Quainton Road was a crude railway station, described as "extremely primitive".

Buckinghamshire Railway Centre is a railway museum operated by the Quainton Railway Society Ltd. at Quainton Road railway station, about 5 miles (8.0 km) west of Aylesbury in Buckinghamshire, England. The site is divided into two halves which are joined by two foot-bridges, one of which provides wheelchair access. Each side has a demonstration line with various workshop buildings as well as museum buildings.

Brill railway station was the terminus of a small railway line in Buckinghamshire, England, known as the Brill Tramway. Built and owned by the 3rd Duke of Buckingham, it was later operated by London's Metropolitan Railway, and in 1933 briefly became one of the two north-western termini of the London Underground, despite being 45 miles (72 km) and over two hours' travelling time from the City of London.

Aylesbury railway station is a railway station in Aylesbury, Buckinghamshire, England, on the London–Aylesbury line from London Marylebone via Amersham. It is 38 miles (61 km) from Aylesbury to Marylebone. A branch line from Princes Risborough on the Chiltern Main Line terminates at the station. It was the terminus for London Underground's Metropolitan line until the service was cut back to Amersham in 1961. The station was also known as Aylesbury Town under the management of British Railways from c. 1948 until the 1960s.

The Brill Tramway, also known as the Quainton Tramway, Wotton Tramway, Oxford & Aylesbury Tramroad and Metropolitan Railway Brill Branch, was a six-mile (10 km) rail line in the Aylesbury Vale, Buckinghamshire, England. It was privately built in 1871 by the 3rd Duke of Buckingham as a horse tram line to help transport goods between his lands around Wotton House and the national rail network. Lobbying from the nearby village of Brill led to its extension to Brill and conversion to passenger use in early 1872. Two locomotives were bought but trains still travelled at an average speed of 4 miles per hour (6.4 km/h).

Granborough Road railway station was a station serving the village of Granborough, to the north of Quainton in Buckinghamshire, England.

Winslow Road railway station served the village of East Claydon near Winslow to the north of Quainton in Buckinghamshire, England. It was the second station to serve the town after Winslow on the Varsity Line.

Claydon railway station is a former railway station on the 'Varsity Line', that served the village of Steeple Claydon in Buckinghamshire.

Banbury Merton Street was the first railway station to serve the Oxfordshire market town of Banbury in England. It opened in 1850 as the northern terminus of the Buckinghamshire Railway providing connections to Bletchley and Oxford and closing for passengers in 1961 and goods in 1966.
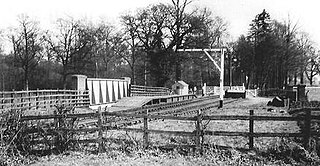
Wood Siding railway station was a halt in Bernwood Forest, Buckinghamshire, England. It opened in 1871 as a terminus of a short horse-drawn tramway built to assist the transport of goods from and around the Duke of Buckingham's extensive estates in Buckinghamshire, as well as connect the Duke's estates to the Aylesbury and Buckingham Railway at Quainton Road.

Winslow railway station refers to either one of two railway stations which historically served or is planned to serve, the town of Winslow in north Buckinghamshire, England. The original station (1850–1968) was on the former Varsity Line between Cambridge and Oxford. As of August 2023, construction of a new station nears completion and is scheduled to be served by East West Rail, as part of the plan to reinstate the Oxford–Cambridge service.
The Aylesbury and Buckingham Railway (A&BR) was an English railway located in Buckinghamshire, England operating between Aylesbury and Verney Junction.

The railway system of Buckinghamshire has a long and complex history dating back to the 1830s with the opening of sections of today's West Coast Main Line and Great Western Main Line. The development of Buckinghamshire's railway network was largely due to its position nationally as many long-distance routes chose to go through Buckinghamshire, especially between Britains two largest cities, London and Birmingham. The county had its own pulling power in addition, as produce such as the Aylesbury Duck could then be easily transported to the capital.
The Buckinghamshire Railway was a railway company in Buckinghamshire and Oxfordshire, England that constructed railway lines connecting Bletchley, Banbury and Oxford. Part of the route is still in use today as the Oxford to Bicester Line.

Buckingham was a railway station which served Buckingham, the former county town of Buckinghamshire, England, between 1850 and 1966.

Transport in Buckinghamshire has been shaped by its position within the United Kingdom. Most routes between the UK's two largest cities, London and Birmingham, pass through this county. The county's growing industry first brought canals to the area, then railways and then motorways.

Wotton railway station was a small station in Buckinghamshire, England, built by the Duke of Buckingham in 1871. Part of a private horse-drawn tramway designed to carry freight from and around his lands in Buckinghamshire, Wotton station was intended to serve the Duke's home at Wotton House and the nearby village of Wotton Underwood. In 1872 the line was extended to the nearby village of Brill, converted to passenger use, equipped with steam locomotives, and renamed the Brill Tramway. In the 1880s, it was proposed to extend the line to Oxford, but the operation of the line was instead taken over by London's Metropolitan Railway.

Westcott railway station was a small station built to serve the village of Westcott, Buckinghamshire, and nearby buildings attached to Baron Ferdinand de Rothschild's estate at Waddesdon Manor. It was built by the Duke of Buckingham in 1871 as part of a short horse-drawn tramway to allow for the transport of goods from and around his extensive estates in Buckinghamshire and to connect the Duke's estates to the Aylesbury and Buckingham Railway at Quainton Road. A lobbying campaign by residents of the town of Brill led to the tramway being converted for passenger use and extended to Brill railway station in 1872, becoming known as the Brill Tramway.

Waddesdon Road railway station, called Waddesdon railway station before 1922, was a small halt in open countryside in Buckinghamshire, England. It was opened in 1871 as part of a short horse-drawn tramway to assist with the transport of goods from and around the Duke of Buckingham's extensive estates in Buckinghamshire and to connect the Duke's estates to the Aylesbury and Buckingham Railway at Quainton Road. In 1872 the line was expanded and converted for passenger use, becoming known as the Brill Tramway. In 1899 the operation of the line was taken over by the London-based Metropolitan Railway.
The Banbury to Verney Junction branch line was a railway branch line constructed by the Buckinghamshire Railway which connected the Oxfordshire market town of Banbury with the former Oxford/Cambridge Varsity line and the former Metropolitan Railway at Verney Junction, a distance of 21 miles 39 chains. Onward routes from there ran to the West Coast Main Line at Bletchley via Brackley and Buckingham and thence to Cambridge, or to Aylesbury for London.





















