| Dham | |
|---|---|
 'Dhimal Bhasha' in Dham script | |
| Script type | |
| Languages | Dhimal language |
Dham script is used to write the Dhimal language. [1] The script has been proposed for Unicode encoding since 2012. [2]
| Dham | |
|---|---|
 'Dhimal Bhasha' in Dham script | |
| Script type | |
| Languages | Dhimal language |
Dham script is used to write the Dhimal language. [1] The script has been proposed for Unicode encoding since 2012. [2]
A bidirectional text contains two text directionalities, right-to-left (RTL) and left-to-right (LTR). It generally involves text containing different types of alphabets, but may also refer to boustrophedon, which is changing text direction in each row.

Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard, is a text encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text written in all of the world's major writing systems. Version 15.1 of the standard defines 149813 characters and 161 scripts used in various ordinary, literary, academic, and technical contexts. Many common characters, including numerals, punctuation, and other symbols, are unified within the standard and are not treated as specific to any given writing system. Unicode encodes thousands of emoji, with the continued development thereof conducted by the Consortium as a part of the standard. Moreover, the widespread adoption of Unicode was in large part responsible for the initial popularization of emoji outside of Japan. Unicode is ultimately capable of encoding more than 1.1 million characters.
UTF-8 is a variable-length character encoding standard used for electronic communication. Defined by the Unicode Standard, the name is derived from UnicodeTransformation Format – 8-bit.

UTF-16 (16-bit Unicode Transformation Format) is a character encoding capable of encoding all 1,112,064 valid code points of Unicode (in fact this number of code points is dictated by the design of UTF-16). The encoding is variable-length, as code points are encoded with one or two 16-bit code units. UTF-16 arose from an earlier obsolete fixed-width 16-bit encoding, now known as UCS-2 (for 2-byte Universal Character Set), once it became clear that more than 216 (65,536) code points were needed.
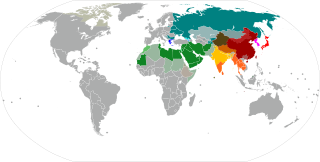
The Brahmic scripts, also known as Indic scripts, are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia and parts of East Asia. They are descended from the Brahmi script of ancient India and are used by various languages in several language families in South, East and Southeast Asia: Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Tibeto-Burman, Mongolic, Austroasiatic, Austronesian, and Tai. They were also the source of the dictionary order (gojūon) of Japanese kana.

Malayalam script is a Brahmic script used commonly to write Malayalam, which is the principal language of Kerala, India, spoken by 45 million people in the world. It is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry by the Malayali people. It is one of the official scripts of the Indian Republic. Malayalam script is also widely used for writing Sanskrit texts in Kerala.
UTF-32 (32-bit Unicode Transformation Format) is a fixed-length encoding used to encode Unicode code points that uses exactly 32 bits (four bytes) per code point (but a number of leading bits must be zero as there are far fewer than 232 Unicode code points, needing actually only 21 bits). UTF-32 is a fixed-length encoding, in contrast to all other Unicode transformation formats, which are variable-length encodings. Each 32-bit value in UTF-32 represents one Unicode code point and is exactly equal to that code point's numerical value.

Mojibake is the garbled text that is the result of text being decoded using an unintended character encoding. The result is a systematic replacement of symbols with completely unrelated ones, often from a different writing system.

The Tamil script is an abugida script that is used by Tamils and Tamil speakers in India, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia and elsewhere to write the Tamil language. It is one of the official scripts of the Indian Republic. Certain minority languages such as Saurashtra, Badaga, Irula and Paniya are also written in the Tamil script.

Michael Everson is an American and Irish linguist, script encoder, typesetter, type designer and publisher. He runs a publishing company called Evertype, through which he has published over a hundred books since 2006.

Surat Buhid is an abugida used to write the Buhid language. As a Brahmic script indigenous to the Philippines, it closely related to Baybayin and Hanunó'o. It is still used today by the Mangyans, found mainly on island of Mindoro, to write their language, Buhid, together with the Filipino latin script.
Windows-1251 is an 8-bit character encoding, designed to cover languages that use the Cyrillic script such as Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, Bulgarian, Serbian Cyrillic, Macedonian and other languages.
The Standard Compression Scheme for Unicode (SCSU) is a Unicode Technical Standard for reducing the number of bytes needed to represent Unicode text, especially if that text uses mostly characters from one or a small number of per-language character blocks. It does so by dynamically mapping values in the range 128–255 to offsets within particular blocks of 128 characters. The initial conditions of the encoder mean that existing strings in ASCII and ISO-8859-1 that do not contain C0 control codes other than NULL TAB CR and LF can be treated as SCSU strings. Since most alphabets do reside in blocks of contiguous Unicode codepoints, texts that use small alphabets and either ASCII punctuation or punctuation that fits within the window for the main alphabet can be encoded at one byte per character, most other punctuation can be encoded at 2 bytes per symbol through non-locking shifts. SCSU can also switch to UTF-16 internally to handle non-alphabetic languages.
The ConScript Unicode Registry is a volunteer project to coordinate the assignment of code points in the Unicode Private Use Areas (PUA) for the encoding of artificial scripts, such as those for constructed languages. It was founded by John Cowan and was maintained by him and Michael Everson. It is not affiliated with the Unicode Consortium.
In Unicode, a Private Use Area (PUA) is a range of code points that, by definition, will not be assigned characters by the Unicode Consortium. Three private use areas are defined: one in the Basic Multilingual Plane, and one each in, and nearly covering, planes 15 and 16. The code points in these areas cannot be considered as standardized characters in Unicode itself. They are intentionally left undefined so that third parties may define their own characters without conflicting with Unicode Consortium assignments. Under the Unicode Stability Policy, the Private Use Areas will remain allocated for that purpose in all future Unicode versions.

The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae, in southern Italy. The Greek alphabet was adopted by the Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was adopted by the Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet.
In Unicode, a script is a collection of letters and other written signs used to represent textual information in one or more writing systems. Some scripts support one and only one writing system and language, for example, Armenian. Other scripts support many different writing systems; for example, the Latin script supports English, French, German, Italian, Vietnamese, Latin itself, and several other languages. Some languages make use of multiple alternate writing systems and thus also use several scripts; for example, in Turkish, the Arabic script was used before the 20th century but transitioned to Latin in the early part of the 20th century. More or less complementary to scripts are symbols and Unicode control characters.
The Dunging script or Iban script is a quasi-syllabary script used to write the Iban language of Sarawak. It was invented in 1947 by its namesake, Dunging anak Gunggu (1904–1985), who revised the initial 77 glyphs to the current 59 glyphs in 1962. It has not been used widely until Dr. Bromeley Philip of Universiti Teknologi MARA begun to promote the script again in 2012.

The Khema script, also known as Gurung Khema, Khema Phri, Khema Lipi, is used to write the Gurung language. Khema has been proposed for Unicode encoding as of 2011 and in 2021. The Language Commission of Nepal recognizes Khema as the official script of Gurung.