Rh disease is a type of hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN). HDFN due to anti-D antibodies is the proper and currently used name for this disease as the Rh blood group system actually has more than 50 antigens and not only the D-antigen. The term "Rh Disease" is commonly used to refer to HDFN due to anti-D antibodies, and prior to the discovery of anti-Rho(D) immune globulin, it was the most common type of HDFN. The disease ranges from mild to severe, and occurs in the second or subsequent pregnancies of Rh-D negative women when the biologic father is Rh-D positive.
Fetal hemoglobin, or foetal haemoglobin is the main oxygen carrier protein in the human fetus. Hemoglobin F is found in fetal red blood cells, and is involved in transporting oxygen from the mother's bloodstream to organs and tissues in the fetus. It is produced at around 6 weeks of pregnancy and the levels remain high after birth until the baby is roughly 2–4 months old. Hemoglobin F has a different composition than adult forms of hemoglobin, allowing it to bind oxygen more strongly; this in turn enables the developing fetus to retrieve oxygen from the mother's bloodstream, which occurs through the placenta found in the mother's uterus.
HELLP syndrome is a complication of pregnancy; the acronym stands for hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count. It usually begins during the last three months of pregnancy or shortly after childbirth. Symptoms may include feeling tired, retaining fluid, headache, nausea, upper right abdominal pain, blurry vision, nosebleeds, and seizures. Complications may include disseminated intravascular coagulation, placental abruption, and kidney failure.

Hemolytic disease of the newborn, also known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, HDN, HDFN, or erythroblastosis foetalis, is an alloimmune condition that develops in a fetus at or around birth, when the IgG molecules produced by the mother pass through the placenta. Among these antibodies are some which attack antigens on the red blood cells in the fetal circulation, breaking down and destroying the cells. The fetus can develop reticulocytosis and anemia. The intensity of this fetal disease ranges from mild to very severe, and fetal death from heart failure can occur. When the disease is moderate or severe, many erythroblasts are present in the fetal blood, earning these forms of the disease the name erythroblastosis fetalis.
Obstetrical bleeding is bleeding in pregnancy that occurs before, during, or after childbirth. Bleeding before childbirth is that which occurs after 24 weeks of pregnancy. Bleeding may be vaginal or less commonly into the abdominal cavity. Bleeding which occurs before 24 weeks is known as early pregnancy bleeding.

The Kleihauer–Betke ("KB") test, Kleihauer–Betke ("KB") stain, Kleihauer test or acid elution test is a blood test used to measure the amount of fetal hemoglobin transferred from a fetus to a mother's bloodstream. It is usually performed on Rh-negative mothers to determine the required dose of Rho(D) immune globulin (RhIg) to inhibit formation of Rh antibodies in the mother and prevent Rh disease in future Rh-positive children. It is named after Enno Kleihauer and Klaus Betke who described it in 1957.
Rho(D) immune globulin (RhIG) is a medication used to prevent RhD isoimmunization in mothers who are RhD negative and to treat idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) in people who are Rh positive. It is often given both during and following pregnancy. It may also be used when RhD-negative people are given RhD-positive blood. It is given by injection into muscle or a vein. A single dose lasts 12 weeks. It is made from human blood plasma.
The alkali denaturation test, also known as A or Apt test, is a medical test used to differentiate fetal or neonatal blood from maternal blood found in a newborn's stool or vomit, or from maternal vaginal blood.
In ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn maternal IgG antibodies with specificity for the ABO blood group system pass through the placenta to the fetal circulation where they can cause hemolysis of fetal red blood cells which can lead to fetal anemia and HDN. In contrast to Rh disease, about half of the cases of ABO HDN occur in a firstborn baby and ABO HDN does not become more severe after further pregnancies.
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (anti-Kell1) is the second most common cause of severe hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) after Rh disease. Anti-Kell1 is becoming relatively more important as prevention of Rh disease is also becoming more effective.
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (anti-Rhc) can range from a mild to a severe disease. It is the third most common cause of severe HDN. Rh disease is the most common and hemolytic disease of the newborn (anti-Kell) is the second most common cause of severe HDN. It occurs more commonly in women who are Rh D negative.
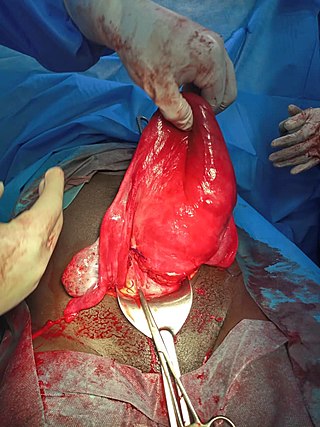
Uterine atony is the failure of the uterus to contract adequately following delivery. Contraction of the uterine muscles during labor compresses the blood vessels and slows flow, which helps prevent hemorrhage and facilitates coagulation. Therefore, a lack of uterine muscle contraction can lead to an acute hemorrhage, as the vasculature is not being sufficiently compressed. Uterine atony is the most common cause of postpartum hemorrhage, which is an emergency and potential cause of fatality. Across the globe, postpartum hemorrhage is among the top five causes of maternal death. Recognition of the warning signs of uterine atony in the setting of extensive postpartum bleeding should initiate interventions aimed at regaining stable uterine contraction.
Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia is a disease that affects babies in which the platelet count is decreased because the mother's immune system attacks her fetus' or newborn's platelets. A low platelet count increases the risk of bleeding in the fetus and newborn. If the bleeding occurs in the brain, there may be long-term effects.
Hemoglobin Barts, abbreviated Hb Barts, is an abnormal type of hemoglobin that consists of four gamma globins. It is moderately insoluble, and therefore accumulates in the red blood cells. Hb Barts has an extremely high affinity for oxygen, so it cannot release oxygen to the tissue. Therefore, this makes it an inefficient oxygen carrier. As an embryo develops, it begins to produce alpha-globins at weeks 5–6 of development. When both of the HBA1 and HBA2 genes which code for alpha globins becomes dysfunctional, the affected fetuses will have difficulty in synthesizing a functional hemoglobin. As a result, gamma chains will accumulate and form four gamma globins. These gamma globins bind to form hemoglobin Barts. It is produced in the disease alpha-thalassemia and in the most severe of cases, it is the only form of hemoglobin in circulation. In this situation, a fetus will develop hydrops fetalis and normally die before or shortly after birth, unless intrauterine blood transfusion is performed.
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (anti-RhE) is caused by the anti-RhE antibody of the Rh blood group system. The anti-RhE antibody can be naturally occurring, or arise following immune sensitization after a blood transfusion or pregnancy.

Percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling (PUBS), also called cordocentesis, fetal blood sampling, or umbilical vein sampling is a diagnostic genetic test that examines blood from the fetal umbilical cord to detect fetal abnormalities. Fetal and maternal blood supply are typically connected in utero with one vein and two arteries to the fetus. The umbilical vein is responsible for delivering oxygen rich blood to the fetus from the mother; the umbilical arteries are responsible for removing oxygen poor blood from the fetus. This allows for the fetus’ tissues to properly perfuse. PUBS provides a means of rapid chromosome analysis and is useful when information cannot be obtained through amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling, or ultrasound ; this test carries a significant risk of complication and is typically reserved for pregnancies determined to be at high risk for genetic defect. It has been used with mothers with immune thrombocytopenic purpura.

Placental expulsion occurs when the placenta comes out of the birth canal after childbirth. The period from just after the baby is expelled until just after the placenta is expelled is called the third stage of labor.
Foetal cerebral redistribution or 'brain-sparing' is a diagnosis in foetal medicine. It is characterised by preferential flow of blood towards the brain at the expense of the other vital organs, and it occurs as a haemodynamic adaptation in foetuses which have placental insufficiency. The underlying mechanism is thought to be vasodilation of the cerebral arteries. Cerebral redistribution is defined by the presence of a low middle cerebral artery pulsatility index (MCA-PI). Ultrasound of the middle cerebral artery to examine the Doppler waveform is used to establish this. Although cerebral redistribution represents an effort to preserve brain development in the face of hypoxic stress, it is nonetheless associated with adverse neurodevelopmental outcome. The presence of cerebral redistribution will be one factor taken into consideration when deciding whether to artificially deliver a baby with placental insufficiency via induction of labour or caesarian section.
Rh factor testing, also known as Rhesus factor testing, is the procedure of determining the rhesus D status of an individual.
An Intrauterine transfusion (IUT) is a procedure that provides blood to a fetus, most commonly through the umbilical cord. It is used in cases of severe fetal anemia, such as when fetal red blood cells are being destroyed by maternal antibodies. IUTs are performed by perinatologists at hospitals or specialized centers.







