Related Research Articles

Polarization is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. A simple example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string (see image); for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves in solids.

The retina is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera.

Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified.

Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are described as birefringent or birefractive. The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.

Night vision is the ability to see in low-light conditions, either naturally with scotopic vision or through a night-vision device. Night vision requires both sufficient spectral range and sufficient intensity range. Humans have poor night vision compared to many animals such as cats, dogs, foxes and rabbits, in part because the human eye lacks a tapetum lucidum, tissue behind the retina that reflects light back through the retina thus increasing the light available to the photoreceptors.
Diffusing capacity of the lung (DL) measures the transfer of gas from air in the lung, to the red blood cells in lung blood vessels. It is part of a comprehensive series of pulmonary function tests to determine the overall ability of the lung to transport gas into and out of the blood. DL, especially DLCO, is reduced in certain diseases of the lung and heart. DLCO measurement has been standardized according to a position paper by a task force of the European Respiratory and American Thoracic Societies.
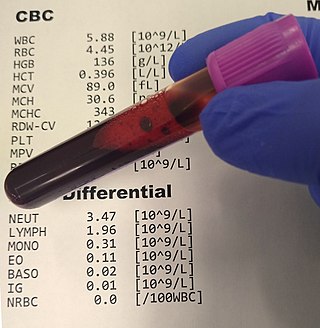
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets, the concentration of hemoglobin, and the hematocrit. The red blood cell indices, which indicate the average size and hemoglobin content of red blood cells, are also reported, and a white blood cell differential, which counts the different types of white blood cells, may be included.
Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels.

The hematocrit, also known by several other names, is the volume percentage (vol%) of red blood cells (RBCs) in blood, measured as part of a blood test. The measurement depends on the number and size of red blood cells. It is normally 40.7–50.3% for males and 36.1–44.3% for females. It is a part of a person's complete blood count results, along with hemoglobin concentration, white blood cell count and platelet count.
Liquid crystal on silicon is a miniaturized reflective active-matrix liquid-crystal display or "microdisplay" using a liquid crystal layer on top of a silicon backplane. It is also known as a spatial light modulator. LCoS initially was developed for projection televisions, but has since found additional uses in wavelength selective switching, structured illumination, near-eye displays and optical pulse shaping.
Hemorheology, also spelled haemorheology, or blood rheology, is the study of flow properties of blood and its elements of plasma and cells. Proper tissue perfusion can occur only when blood's rheological properties are within certain levels. Alterations of these properties play significant roles in disease processes. Blood viscosity is determined by plasma viscosity, hematocrit and mechanical properties of red blood cells. Red blood cells have unique mechanical behavior, which can be discussed under the terms erythrocyte deformability and erythrocyte aggregation. Because of that, blood behaves as a non-Newtonian fluid. As such, the viscosity of blood varies with shear rate. Blood becomes less viscous at high shear rates like those experienced with increased flow such as during exercise or in peak-systole. Therefore, blood is a shear-thinning fluid. Contrarily, blood viscosity increases when shear rate goes down with increased vessel diameters or with low flow, such as downstream from an obstruction or in diastole. Blood viscosity also increases with increases in red cell aggregability.

The Michelson interferometer is a common configuration for optical interferometry and was invented by the 19/20th-century American physicist Albert Abraham Michelson. Using a beam splitter, a light source is split into two arms. Each of those light beams is reflected back toward the beamsplitter which then combines their amplitudes using the superposition principle. The resulting interference pattern that is not directed back toward the source is typically directed to some type of photoelectric detector or camera. For different applications of the interferometer, the two light paths can be with different lengths or incorporate optical elements or even materials under test.

Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an imaging technique that uses interferometry with short-coherence-length light to obtain micrometer-level depth resolution and uses transverse scanning of the light beam to form two- and three-dimensional images from light reflected from within biological tissue or other scattering media. Short-coherence-length light can be obtained using a superluminescent diode (SLD) with a broad spectral bandwidth or a broadly tunable laser with narrow linewidth. The first demonstration of OCT imaging was published by a team from MIT and Harvard Medical School in a 1991 article in the journal Science. The article introduced the term "OCT" to credit its derivation from optical coherence-domain reflectometry, in which the axial resolution is based on temporal coherence. The first demonstrations of in vivo OCT imaging quickly followed.
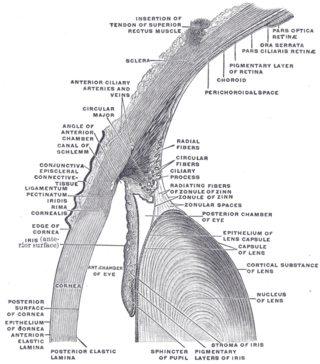
In the anatomy of the eye, the conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera. It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium. The conjunctiva is highly vascularised, with many microvessels easily accessible for imaging studies.

Ellipsometry is an optical technique for investigating the dielectric properties of thin films. Ellipsometry measures the change of polarization upon reflection or transmission and compares it to a model.

Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There are a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as photoelectric or photochemical effects, or by various performance metrics, such as spectral response. Semiconductor-based photodetectors typically use a p–n junction that converts photons into charge. The absorbed photons make electron–hole pairs in the depletion region. Photodiodes and photo transistors are a few examples of photo detectors. Solar cells convert some of the light energy absorbed into electrical energy.

A hemothorax is an accumulation of blood within the pleural cavity. The symptoms of a hemothorax may include chest pain and difficulty breathing, while the clinical signs may include reduced breath sounds on the affected side and a rapid heart rate. Hemothoraces are usually caused by an injury, but they may occur spontaneously due to cancer invading the pleural cavity, as a result of a blood clotting disorder, as an unusual manifestation of endometriosis, in response to Pneumothorax, or rarely in association with other conditions.
Angle-resolved low-coherence interferometry (a/LCI) is an emerging biomedical imaging technology which uses the properties of scattered light to measure the average size of cell structures, including cell nuclei. The technology shows promise as a clinical tool for in situ detection of dysplastic, or precancerous tissue.
A superluminescent diode is an edge-emitting semiconductor light source based on superluminescence. It combines the high power and brightness of laser diodes with the low coherence of conventional light-emitting diodes. Its emission optical bandwidth, also described as full-width at half maximum, can range from 5 up to 750 nm.
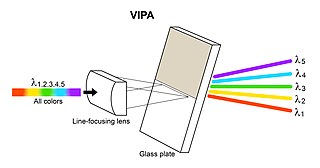
A virtually imaged phased array (VIPA) is an angular dispersive device that, like a prism or a diffraction grating, splits light into its spectral components. The device works almost independently of polarization. In contrast to prisms or regular diffraction gratings, the VIPA has a much higher angular dispersion but has a smaller free spectral range. This aspect is similar to that of an Echelle grating, since it also uses high diffraction orders. To overcome this disadvantage, the VIPA can be combined with a diffraction grating. The VIPA is a compact spectral disperser with high wavelength resolving power.
References
- ↑ Cerný V, Turek Z, Parízková R (2007). "Orthogonal polarization spectral imaging" (PDF). Physiol Res. 56 (2): 141–7. doi:10.33549/physiolres.930922. PMID 16555953.
- ↑ "OPS Imaging". Cytometrics. Retrieved 2009-08-17.
- ↑ Harris, AG; Sinitsina I; Messmer K. (April 2002). "Validation of OPS imaging for microvascular measurements during isovolumic hemodilution and low hematocrits". Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 282 (4): 1502–9. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00475.2001. PMID 11893588.