Related Research Articles

Pyrrolysine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins in some methanogenic archaea and bacteria; it is not present in humans. It contains an α-amino group, a carboxylic acid group. Its pyrroline side-chain is similar to that of lysine in being basic and positively charged at neutral pH.
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are common in wetlands, where they are responsible for marsh gas, and can occur in the digestive tracts of animals including ruminants and humans, where they are responsible for the methane content of belching and flatulence. In marine sediments, the biological production of methane, termed methanogenesis, is generally confined to where sulfates are depleted below the top layers. Methanogenic archaea populations play an indispensable role in anaerobic wastewater treatments. Other methanogens are extremophiles, found in environments such as hot springs and submarine hydrothermal vents as well as in the "solid" rock of Earth's crust, kilometers below the surface.
Tetrahydromethanopterin is a coenzyme in methanogenesis. It is the carrier of the C1 group as it is reduced to the methyl level, before transferring to the coenzyme M.
Coenzyme B is a coenzyme required for redox reactions in methanogens. The full chemical name of coenzyme B is 7-mercaptoheptanoylthreoninephosphate. The molecule contains a thiol, which is its principal site of reaction.

[Methionine synthase] reductase, or Methionine synthase reductase, encoded by the gene MTRR, is an enzyme that is responsible for the reduction of methionine synthase inside human body. This enzyme is crucial for maintaining the one carbon metabolism, specifically the folate cycle. The enzyme employs one coenzyme, flavoprotein.
In enzymology, a 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin reductase (EC 1.5.98.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a CoB—CoM heterodisulfide reductase (EC 1.8.98.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
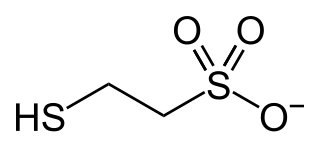
In enzymology, coenzyme-B sulfoethylthiotransferase, also known as methyl-coenzyme M reductase (MCR) or most systematically as 2-(methylthio)ethanesulfonate:N-(7-thioheptanoyl)-3-O-phosphothreonine S-(2-sulfoethyl)thiotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the final step in the formation of methane. It does so by combining the hydrogen donor coenzyme B and the methyl donor coenzyme M. Via this enzyme, most of the natural gas on earth was produced. Ruminants produce methane because their rumens contain methanogenic prokaryotes (Archaea) that encode and express the set of genes of this enzymatic complex.

In molecular biology, cob(I)yrinic acid a,c-diamide adenosyltransferase EC 2.5.1.17 is an enzyme which catalyses the conversion of cobalamin into one of its coenzyme forms, adenosylcobalamin. Adenosylcobalamin is required as a cofactor for the activity of certain enzymes. AdoCbl contains an adenosyl moiety liganded to the cobalt ion of cobalamin via a covalent Co-C bond.
5-methyltetrahydrosarcinapterin:corrinoid/iron-sulfur protein Co-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name 5-methyltetrahydrosarcinapterin:corrinoid/iron-sulfur protein methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
Methyltransferase 2 may refer to:
(Methyl-Co methylamine-specific corrinoid protein):coenzyme M methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name methylated monomethylamine-specific corrinoid protein:coenzyme M methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Methylamine-corrinoid protein Co-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name monomethylamine:5-hydroxybenzimidazolylcobamide Co-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Dimethylamine-corrinoid protein Co-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name dimethylamine:5-hydroxybenzimidazolylcobamide Co-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Trimethylamine-corrinoid protein Co-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name trimethylamine:5-hydroxybenzimidazolylcobamide Co-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Methylated-thiol-coenzyme M methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name methylated-thiol:coenzyme M methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
Tetramethylammonium-corrinoid protein Co-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name tetramethylammonium:5-hydroxybenzimidazolylcobamide Co-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
(Methyl-Co tetramethylammonium-specific corrinoid protein):coenzyme M methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name methylated tetramethylammonium-specific corrinoid protein:coenzyme M methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
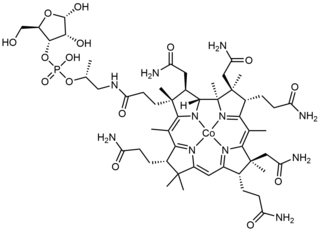
Cobamide is a naturally occurring chemical compound containing cobalt in the corrinoid family of macrocyclic complexes. Cobamide works as a coenzyme with some enzymes in bacteria. The cobalt atom may have a transferable methyl group attached. It is used for example in 5-methyltetrahydrosarcinapterin:corrinoid/iron-sulfur protein Co-methyltransferase.
In enzymology, a formylmethanofuran dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.99.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
References
- ↑ LeClerc GM, Grahame DA (August 1996). "Methylcobamide:coenzyme M methyltransferase isozymes from Methanosarcina barkeri. Physicochemical characterization, cloning, sequence analysis, and heterologous gene expression". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (31): 18725–31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.31.18725 . PMID 8702528.
- ↑ Harms U, Thauer RK (February 1996). "Methylcobalamin: coenzyme M methyltransferase isoenzymes MtaA and MtbA from Methanosarcina barkeri. Cloning, sequencing and differential transcription of the encoding genes, and functional overexpression of the mtaA gene in Escherichia coli". European Journal of Biochemistry. 235 (3): 653–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.00653.x . PMID 8654414.
- ↑ Sauer K, Thauer RK (October 1997). "Methanol:coenzyme M methyltransferase from Methanosarcina barkeri. Zinc dependence and thermodynamics of the methanol:cob(I)alamin methyltransferase reaction". European Journal of Biochemistry. 249 (1): 280–5. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.t01-1-00280.x. PMID 9363780.
- ↑ Sauer K, Harms U, Thauer RK (February 1997). "Methanol:coenzyme M methyltransferase from Methanosarcina barkeri. Purification, properties and encoding genes of the corrinoid protein MT1". European Journal of Biochemistry. 243 (3): 670–7. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.t01-1-00670.x. PMID 9057830.
- ↑ Sauer K, Thauer RK (May 1999). "Methanol:coenzyme M methyltransferase from Methanosarcina barkeri -- substitution of the corrinoid harbouring subunit MtaC by free cob(I)alamin". European Journal of Biochemistry. 261 (3): 674–81. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00355.x. PMID 10215883.