
Drug design, often referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and charge to the biomolecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Drug design frequently but not necessarily relies on computer modeling techniques. This type of modeling is sometimes referred to as computer-aided drug design. Finally, drug design that relies on the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biomolecular target is known as structure-based drug design. In addition to small molecules, biopharmaceuticals including peptides and especially therapeutic antibodies are an increasingly important class of drugs and computational methods for improving the affinity, selectivity, and stability of these protein-based therapeutics have also been developed.

1,10-Phenanthroline (phen) is a heterocyclic organic compound. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The 1,10 refer to the location of the nitrogen atoms that replace CH's in the hydrocarbon called phenanthrene.
Organopalladium chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic palladium compounds and their reactions. Palladium is often used as a catalyst in the reduction of alkenes and alkynes with hydrogen. This process involves the formation of a palladium-carbon covalent bond. Palladium is also prominent in carbon-carbon coupling reactions, as demonstrated in tandem reactions.
Cycloocta-1,5-diene is a cyclic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C8H12, specifically [−(CH2)2−CH=CH−]2.

Chemogenomics, or chemical genomics, is the systematic screening of targeted chemical libraries of small molecules against individual drug target families with the ultimate goal of identification of novel drugs and drug targets. Typically some members of a target library have been well characterized where both the function has been determined and compounds that modulate the function of those targets have been identified. Other members of the target family may have unknown function with no known ligands and hence are classified as orphan receptors. By identifying screening hits that modulate the activity of the less well characterized members of the target family, the function of these novel targets can be elucidated. Furthermore, the hits for these targets can be used as a starting point for drug discovery. The completion of the human genome project has provided an abundance of potential targets for therapeutic intervention. Chemogenomics strives to study the intersection of all possible drugs on all of these potential targets.
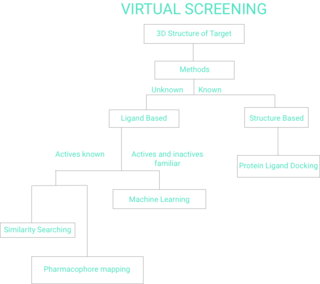
Virtual screening (VS) is a computational technique used in drug discovery to search libraries of small molecules in order to identify those structures which are most likely to bind to a drug target, typically a protein receptor or enzyme.
The formazans are compounds of the general formula [R-N=N-C(R')=N-NH-R"], formally derivatives of formazan [H2NN=CHN=NH], unknown in free form.

In organometallic chemistry, a sandwich compound is a chemical compound featuring a metal bound by haptic, covalent bonds to two arene (ring) ligands. The arenes have the formula CnHn, substituted derivatives and heterocyclic derivatives. Because the metal is usually situated between the two rings, it is said to be "sandwiched". A special class of sandwich complexes are the metallocenes.

Cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer is the organorhodium compound with the formula Rh2Cl2(C8H12)2, commonly abbreviated [RhCl(COD)]2 or Rh2Cl2(COD)2. This yellow-orange, air-stable compound is a widely used precursor to homogeneous catalysts.
A cannabinoid receptor antagonist, also known simply as a cannabinoid antagonist or as an anticannabinoid, is a type of cannabinoidergic drug that binds to cannabinoid receptors (CBR) and prevents their activation by endocannabinoids. They include antagonists, inverse agonists, and antibodies of CBRs. The discovery of the endocannabinoid system led to the development of CB1 receptor antagonists. The first CBR inverse agonist, rimonabant, was described in 1994. Rimonabant blocks the CB1 receptor selectively and has been shown to decrease food intake and regulate body-weight gain. The prevalence of obesity worldwide is increasing dramatically and has a great impact on public health. The lack of efficient and well-tolerated drugs to cure obesity has led to an increased interest in research and development of CBR antagonists. Cannabidiol (CBD), a naturally occurring cannabinoid and a non-competitive CB1/CB2 receptor antagonist, as well as Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), a naturally occurring cannabinoid, modulate the effects of THC via direct blockade of cannabinoid CB1 receptors, thus behaving like first-generation CB1 receptor inverse agonists, such as rimonabant. CBD is a very low-affinity CB1 ligand, that can nevertheless affect CB1 receptor activity in vivo in an indirect manner, while THCV is a high-affinity CB1 receptor ligand and potent antagonist in vitro and yet only occasionally produces effects in vivo resulting from CB1 receptor antagonism. THCV has also high affinity for CB2 receptors and signals as a partial agonist, differing from both CBD and rimonabant.
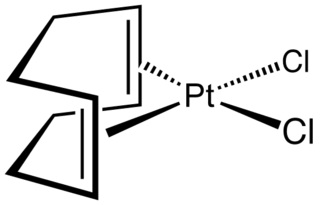
Dichloro(1,5-cyclooctadiene)platinum(II) (Pt(cod)Cl2) is an organometallic compound of platinum. This colourless solid is an entry point to other platinum compounds through the displacement of the cod and/or chloride ligands. It is one of several complexes of cycloocta-1,5-diene.

1,3-Dihydroxyanthraquinone, also called purpuroxanthin or xanthopurpurin, is an organic compound with formula C
14H
8O
4 that occurs in the plant Rubia cordifolia. It is one of ten dihydroxyanthraquinone isomers. Its molecular structure can be viewed as being derived from anthraquinone by replacement of two hydrogen atoms (H) by hydroxyl groups (-OH).
A dihydroxyanthraquinone is any of several isomeric organic compounds with formula C
14H
8O
4, formally derived from 9,10-anthraquinone by replacing two hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl groups. Dihyroxyantraquinones have been studied since the early 1900s, and include some compounds of historical and current importance. The isomers differ in the position of the hydroxyl groups, and of the carbonyl oxygens (=O) of the underlying anthraquinone.
Organoplatinum chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to platinum chemical bond, and the study of platinum as a catalyst in organic reactions. Organoplatinum compounds exist in oxidation state 0 to IV, with oxidation state II most abundant. The general order in bond strength is Pt-C (sp) > Pt-O > Pt-N > Pt-C (sp3). Organoplatinum and organopalladium chemistry are similar, but organoplatinum compounds are more stable and therefore less useful as catalysts.
Boron monofluoride or fluoroborylene is a chemical compound with formula BF, one atom of boron and one of fluorine. It was discovered as an unstable gas and only in 2009 found to be a stable ligand combining with transition metals, in the same way as carbon monoxide. It is a subhalide, containing fewer than the normal number of fluorine atoms, compared with boron trifluoride. It can also be called a borylene, as it contains boron with two unshared electrons. BF is isoelectronic with carbon monoxide and dinitrogen; each molecule has 14 electrons.

DPA-714 or N,N-diethyl-2-[4-(2-fluoroethoxy)phenyl]-5,7-dimethylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-acetamide is a selective ligand for the translocator protein (TSPO) currently under evaluation for several clinical applications. For this reason, a practical, multigram synthetic route for its preparation has been described.
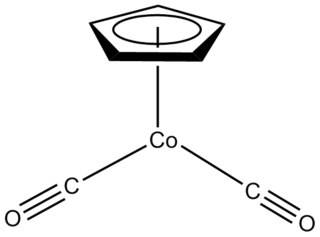
Half sandwich compounds, also known as piano stool complexes, are organometallic complexes that feature a cyclic polyhapto ligand bound to an MLn center, where L is a unidentate ligand. Thousands of such complexes are known. Well-known examples include cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl and (C5H5)TiCl3. Commercially useful examples include (C5H5)Co(CO)2, which is used in the synthesis of substituted pyridines, and methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl, an antiknock agent in petrol.

Cyclooctadiene iridium chloride dimer is an organoiridium compound with the formula [Ir(μ2-Cl)(COD)]2, where COD is the diene 1,5-cyclooctadiene (C8H12). It is an orange-red solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The complex is used as a precursor to other iridium complexes, some of which are used in homogeneous catalysis. The solid is air-stable but its solutions degrade in air.
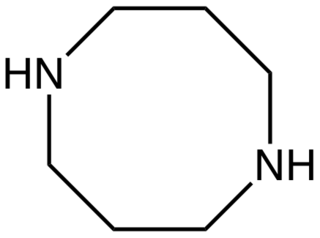
1,5-Diazacyclooctane is an organic compound with the formula (CH2CH2CH2NH)2. It is a colorless oil. 1,5-Diazacyclooctane is a cyclic diamine.













