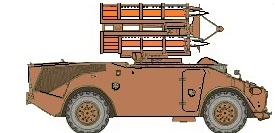
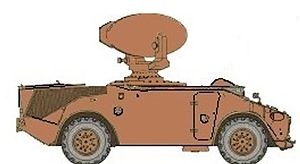
Rapier is a surface-to-air missile developed for the British Army to replace their towed Bofors 40/L70 anti-aircraft guns. The system is unusual as it uses a manual optical guidance system, sending guidance commands to the missile in flight over a radio link. This results in a high level of accuracy, therefore a large warhead is not required.

Mistral is an infrared homing MANPADS manufactured by the European multinational company MBDA missile systems. Based on the French SATCP, the portable missile later to become the Mistral began development in 1974. It was initially deployed in 1988 for the first version (S1), 1997 for the second version (M2), and 2019 for the third version (M3).

The South African Air Force (SAAF) is the air warfare branch of South African National Defence Force, with its headquarters in Pretoria. The South African Air Force was established on 1 February 1920. The Air Force has seen service in World War II and the Korean War. From 1966 the SAAF was involved in providing infantry support in a low intensity war in Angola, South-West Africa and Rhodesia. As the war progressed, the intensity of air operations increased until in the late 1980s, the SAAF were compelled to fly fighter missions against Angolan aircraft in order to maintain tactical air superiority. On conclusion of the Border War in 1990, aircraft numbers were severely reduced due to economic pressures as well as the cessation of hostilities with neighbouring states.

The Denel Rooivalk is an attack helicopter manufactured by Denel Aviation of South Africa. Rooivalk is Afrikaans for "Red Falcon". Development of the type began in 1984 by the Atlas Aircraft Corporation, its development is closely connected to the Atlas Oryx transport helicopter, both aircraft being based on the Aérospatiale SA 330 Puma and having started development at the same time.

The Test Flight and Development Centre is a unit of the South African Air Force. It is a test flight and evaluation organisation.

The Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP) was an Indian Ministry of Defence programme for the research and development of the comprehensive range of missiles. The programme was managed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Ordnance Factories Board in partnership with other Indian government political organisations. The project started in 1982–83 under the leadership of Abdul Kalam who oversaw its ending in 2008 after these strategic missiles were successfully developed.

Akash is a medium-range mobile surface-to-air missile (SAM) system developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and produced by Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL). Surveillance and Fire control radar, tactical control and command center and missile launcher are developed by Bharat Electronics (BEL), Tata Power Strategic Engineering Division and Larsen & Toubro. The Akash missile system can target aircraft up to 50–80 km (31–50 mi) away, at altitudes up to 18,000 m. It has the capability to neutralise aerial targets like fighter jets, cruise missiles and air-to-surface missiles as well as ballistic missiles. It is in operational service with the Indian Army and the Indian Air Force.

The Crotale EDIR is an all-weather short-range anti-air missile, which can be used to intercept low-flight anti-ship missiles and aircraft. It has been developed by Thomson CSF Matra and exists in two versions, a mobile land-based version and a ship-launched one.

The Roland is a Franco-German mobile short-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) system. The Roland was also purchased by the U.S. Army as one of very few foreign SAM systems.

The Denel Dynamics Seeker is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) manufactured in South Africa by Denel Dynamics. The system is designed to perform tactical reconnaissance in real time and can conduct day and night surveillance in all threat environments.

Operation Askari was a military operation during 1983 in Angola by the South African Defence Force (SADF) during the South African Border War.

The 16th Regiment, Royal Australian Artillery is the Australian Army's only ground-based air defence (GBAD) unit. It also provides sense, warn and locate, ground liaison, and joint terminal attack control capabilities. Part of the Royal Regiment of Australian Artillery (RAA), the regiment is responsible for protecting a wide range of military assets during wartime, ranging from Army units in the field to providing point defence to the Royal Australian Navy's support ships and air defence to Royal Australian Air Force air bases. Prior to being equipped with the currently in-service RBS-70 surface-to-air missile system, the regiment was equipped with the Rapier systems for 25 years. The regiment is based at Woodside, South Australia, but frequently deploys with other Australian and allied units on operations and defence exercises. It is part of the 6th Brigade.

The SPYDER is an Israeli short and medium range mobile air defence system developed by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems with assistance from Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI). Rafael is the prime contractor and IAI is the major subcontractor for the SPYDER program. This system achieved a notable milestone in 2005 when missiles were fired against test targets in Shdema, Israel and scored direct hits. Since then, it has been showcased in multiple military exhibitions throughout the world.
The History of the South African Air Force spans the First World War, Rand Rebellion of 1922, the Second World War, the Korean War, the South African Border War, and varied peacekeeping operations since 1994. Its battle honours include German South West Africa 1914–15, German East Africa 1915–1918, East Africa: 1939–1941, Middle East: 1941–43, Madagascar 1942, Italy 1943–1945, the Balkans 1943–1945, and Korea 1950–1953.

120 Squadron SAAF was a South African Air Force squadron formed in 1970 to operate the South African/French Cactus surface-to-air missile systems in an air defence role. The unit was disbanded when the Cactus system was retired from service in the late 1980s.

The South African Army Air Defence Artillery Formation is the controlling entity of all South African Army Air Defence Artillery units. This Formation consists of both regular and reserve units.

121 Squadron SAAF was a South African Air Force squadron formed in 1974 to operate the British Tigercat surface-to-air missile systems in an air defence role. The unit was disbanded when the Tigercat system was retired from service in the early 1990s.
The following is a hierarchical outline of the Czechoslovak People's Army at the end of the Cold War. It is intended to convey the connections and relationships between units and formations. At the end of the Cold War in 1989 the Czechoslovak People's Army structure was as follows.

The 1st Strategic Missiles Groupment is a former unit of the Strategic Air Forces of the French Air and Space Force.

The Joint Ground-based Air Defence Command is a joint command of the Royal Netherlands Army, formed in 2012 after amalgamation of the Commando Luchtdoelartillerie of the Royal Netherlands Army and the Groep Geleide Wapens of the Royal Netherlands Air Force. The command is responsible for all ground-based air defence tasks and consists of both army and air force personnel. The DGLC employs an integrated layered air-defence approach featuring FIM-92 Stinger, NASAMS II and MIM-104 Patriot systems.