| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 1833 in Chile .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 1833 in Chile .

The territory of Chile has been populated since at least 3000 BC. By the 16th century, Spanish invaders began to raid the region of present-day Chile, and the territory was a colony between 1540 and 1818, when it gained independence from Spain. The country's economic development was successively marked by the export of first agricultural produce, then saltpeter and later copper. The wealth of raw materials led to an economic upturn, but also led to dependency, and even wars with neighboring states. Chile was governed during most of its first 150 years of independence by different forms of restricted government, where the electorate was carefully vetted and controlled by an elite.
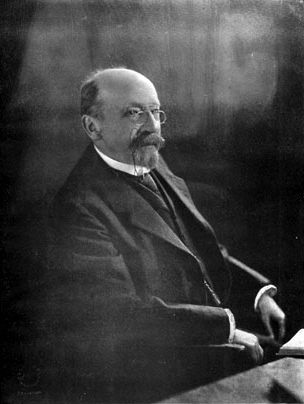
José Toribio Medina Zavala was a Chilean bibliographer, prolific writer, and historian. He is renowned for his study of colonial literature in Chile, printing in Spanish America and large bibliographies such as the Biblioteca Hispano-Americana.

Toqui is a title conferred by the Mapuche on those chosen as leaders during times of war. The toqui is chosen in an assembly or parliament (coyag) of the chieftains (loncos) of various clans (Rehues) or confederation of clans (Aillarehues), allied during the war at hand. The toqui commanded strict obedience of all the warriors and their loncos during the war, would organize them into units and appoint leaders over them. This command would continue until the toqui was killed, abdicated (Cayancaru), was deposed in another parliament, or upon completion of the war for which he was chosen.

The royal governor of Chile ruled over the Spanish colonial administrative district called the Captaincy General of Chile, and as a result the royal governor also held the title of a captain general. There were 66 such governors or captains during the Spanish conquest and the later periods of Spanish-centered colonialism. Since the first Spanish–Mapuche parliaments in the 17th century it became an almost mandatory tradition for each governor to arrange a parliament with the Mapuches.

José Manuel Donoso Yáñez, known as José Donoso, was a Chilean writer, journalist and professor. He lived most of his life in Chile, although he spent many years in self-imposed exile in Mexico, the United States and Spain. Although he had left his country in the sixties for personal reasons, after 1973 he said his exile was also a form of protest against the dictatorship of Augusto Pinochet. He returned to Chile in 1981 and lived there until his death.

Luis José de Orbegoso y Moncada-Galindo, de Burutarán y Morales, was an aristocratic Peruvian soldier and politician, who served as the 5th President of Peru as well as the first President of North Peru. This was a time of profound social instability and continuing civil war which led his government to coexist with that of Pedro Pablo Bermúdez, and later with Felipe Santiago Salaverry.

José Mariano de la Cruz de la Riva Agüero y Sánchez Boquete was a Peruvian soldier and politician who was the first president of Peru and the second president of North Peru, a constituent country of the Peru–Bolivian Confederation. A leading figure of the Peruvian War of Independence, he was president of Peru in 1823, being the first head of state to serve as President of the Republic and to wear the two-color presidential sash as a symbol of the power he exercised. Although this power was de facto, that is, born from a coup d'état and not by popular will expressed in elections, since it was imposed by the Peruvian Army through the so-called Balconcillo mutiny, which ordered Congress to dismiss the Supreme Governing Junta headed by José de La Mar. He governed for four months before being replaced by the Marquis of Torre Tagle.
Tomás López Marín y González de Poveda, 1st Marquis of Cañada Hermosa was a Spanish colonial administrator who served as Royal Governor of Chile.

Friar José Camilo Henríquez González was a priest, author, politician, and is considered an intellectual antecedent to and founding father of the Republic of Chile for his passionate leadership and influential writings. He was also one of the most important early South American newspaper writers and wrote several essays, most notably the Proclama de Quirino Lemachez, which promoted Chilean independence and liberty. He also wrote under the pseudonym Quirino Lemachez.

José Ignacio Zenteno del Pozo y Silva, was a Chilean soldier, politician and hero of the Chilean War of Independence.

The Conquest of Chile is a period in Chilean historiography that starts with the arrival of Pedro de Valdivia to Chile in 1541 and ends with the death of Martín García Óñez de Loyola in the Battle of Curalaba in 1598, and the destruction of the Seven Cities in 1598–1604 in the Araucanía region.

Tomás Antonio Álvarez de Acevedo Ordaz was a Spanish colonial administrator who twice served as interim Royal Governor of Chile, first in 1780 and again between 1787 and 1788.
José del Carmen Quesada del Río (1833-1885) was a Chilean lawyer and magistrate.

José María Caro Martínez was a Chilean politician and civil servant. In May 1894, he was unanimously elected as the first mayor of the commune of Pichilemu, with Pedro Nolasco de Mira and Francisco Reyes made second and third magistrate respectively. Caro Martínez had previously served for several years as administrator or llavero of the San Antonio de Petrel hacienda and, between 1891 and 1892, was the Subdelegate of the 13th Subdelegation of San Fernando Department which comprised the district of Cáhuil.

The Revolution of 1851 was an attempt by Chilean liberals to overthrow the conservative government of president Manuel Montt and repeal the Chilean Constitution of 1833. After various battles and sieges, by late December 1851 government forces had subdued the revolutionaries.

Felipe Pardo y Aliaga was a Peruvian poet, satirist, playwright, lawyer and politician.

José Félix Esquivel y Aldao was an Argentine Dominican friar and soldier who became a general and then the undisputed Federalist caudillo of Mendoza Province. His ability as a warrior and his brutality became legendary. The largely fictionalized biography that Domingo Faustino Sarmiento wrote fed his legend. An effective ruler, he did much for his province, but was also one of the cruelest federalist leaders.

José Victorino Lastarria was a Chilean writer, legislative deputy, senator, diplomat, and finance minister.

José Francisco Vergara Echevers (1833-1889) was a Chilean politician, war hero, cavalry commander, presidential candidate, engineer and journalist who was notable for founding Viña del Mar as well as his several military campaigns of the War of the Pacific.