This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2023) |
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 1947 in Chile.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2023) |
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 1947 in Chile.

Gabriel Enrique González Videla was a Chilean politician and lawyer who served as the 24th president of Chile from 1946 to 1952. He had previously been a member of the Chamber of Deputies from 1930 to 1941 and senator for Tarapacá and Antofagasta from 1945 to 1946. A long-time member and leader in the Radical Party, he left the party in 1971 over its support for socialist president Salvador Allende. From 1973 until his death in 1980 he became an active collaborator and participant in the dictatorship of Augusto Pinochet, acting as vice president of the Council of State from 1976 onwards. As vice president of the council, he helped draft the current Chilean constitution of 1980.

Presidential elections were held in Chile on February 1, 1942. The result was a victory for Juan Antonio Ríos of the Radical Party, who received 56% of the vote.
Presidential elections were held in Chile on 4 September 1946. The result was a victory for Gabriel González Videla of the Radical Party, who received 40% of the popular vote and 75% of the Congressional vote.

Estadio La Portada is a multi-use stadium in La Serena, Chile. It is currently used mostly for football matches and is the home stadium of Deportes La Serena. The stadium holds 18,243 people and was completely renovated in 2015, in time for the 2015 Copa America.

González Videla Base is an inactive research station on the Antarctic mainland at Waterboat Point in Paradise Bay. It is named after Chilean President Gabriel González Videla, who in the 1940s became the first chief of state of any nation to visit Antarctica. The station was active from 1951–58, and was reopened briefly in the early 1980s. Occasional summer visits are made by Chilean parties and tourists.
The Duroch Islands are a group of islands and rocks which extend over an area of about 3 nautical miles, centred about 1 nautical mile off Cape Legoupil on the north coast of Trinity Peninsula, Antarctica. The islands are close to Chile's Base General Bernardo O'Higgins Riquelme at Cape Legoupil.

Rosa Markmann Reijer was the Chilean First Lady from 1946 to 1952, during the presidency of her husband, Gabriel González Videla.
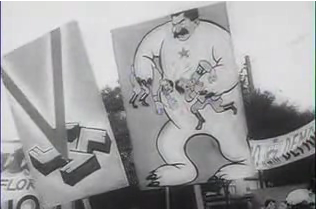
In 1948, on the initiative of Chilean President Gabriel González Videla, the Chilean National Congress enacted the Permanent Defense of Democracy Law, referred to by many as the Damned Law, which outlawed the Communist Party of Chile and banned 26,650 persons from the electoral lists.
Stella Díaz Varín, also known as La Colorina, was a Chilean poet of the Generation of '50. Her unprecedented deep and philosophical style, as well as her controversial personality, marked a before and after in Chilean poetry.

Germán Picó Cañas (1905–1988) was a Chilean lawyer, businessman and politician. He was born in Santiago on May 25, 1905, and died in that same city on July 12, 1988. He was a member of the Radical Party of Chile. Among the positions he held include that of finance minister under President Gabriel González Videla.

The First Chilean Antarctic Expedition (1947–1948) was an expedition to Antarctica mounted by the Chilean government and military to enforce its territorial claims against British challenges, namely Operation Tabarin.

The MonumentalLighthouse of La Serena is a Chilean lighthouse located at the Avenida del Mar of La Serena. The structure is one of the most representative of the city and one of the most popular tourist attractions in the area.
The following lists events that happened during 1898 in Chile.
The following lists events that happened during 1946 in Chile.
The following lists events that happened during 1948 in Chile.
The following lists events that happened during 1950 in Chile.
The following lists events that happened during 1951 in Chile.

The following lists events that happened during 1952 in Chile.
The following lists events that happened during 1980 in Chile.

The revolution of the chaucha was a demonstration held on August 16 and 17, 1949, in Santiago, Chile, against the proposed increase in the price of public transport tickets by 20 cents of the Chilean peso.