| This article is part of a series on |
 |
|---|
Elections to the National Assembly of France were held in Algeria on 21 October 1945. [1] The election was held with two colleges, citizens and non-citizens.
| This article is part of a series on |
 |
|---|
Elections to the National Assembly of France were held in Algeria on 21 October 1945. [1] The election was held with two colleges, citizens and non-citizens.
| Party | First College | Second College | Total seats | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Seats | Votes | % | Seats | |||
| Franco-Muslim Democratic Union | 192,545 | 27.19 | 4 | 4 | ||||
| Algerian Communist Party | 41,047 | 12.29 | 2 | 136,293 | 19.24 | 2 | 4 | |
| Union and Social Progress List | 136,109 | 19.22 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| French Section of the Workers' International | 71,134 | 21.30 | 2 | 63,646 | 8.99 | 1 | 3 | |
| Democratic Union of Muslim Interests | 103,261 | 14.58 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| Defense of Muslim-Algerian Personal Status | 58,959 | 8.32 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Democratic Union for Progress and Freedom | 41,622 | 12.46 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| French Republicans | 40,061 | 12.00 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| Radical Socialists | 38,768 | 11.61 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Indép. Rén. Rép. | 28,845 | 8.64 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Popular Republican Movement | 27,240 | 8.16 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Conc. Rép | 24,688 | 7.39 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| UAM | 17,435 | 2.46 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Souver. franc. | 14,725 | 4.41 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| RDR | 5,837 | 1.75 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Total | 333,967 | 100.00 | 13 | 708,248 | 100.00 | 13 | 26 | |
| Valid votes | 333,967 | 97.52 | 708,248 | 98.17 | ||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 8,495 | 2.48 | 13,203 | 1.83 | ||||
| Total votes | 342,462 | 100.00 | 721,451 | 100.00 | ||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 501,824 | 68.24 | 1,341,978 | 53.76 | ||||
| Source: Sternberger et al. | ||||||||

An election is a formal group decision-making process whereby a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.

Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise is the right to vote in public, political elections and referendums. In some languages, and occasionally in English, the right to vote is called active suffrage, as distinct from passive suffrage, which is the right to stand for election. The combination of active and passive suffrage is sometimes called full suffrage.

Elections in Sweden are held once every four years. At the highest level, all 349 members of Riksdag, the national parliament of Sweden, are elected in general elections. Elections to the 20 county councils and 290 municipal assemblies – all using almost the same electoral system – are held concurrently with the legislative elections on the second Sunday in September.

There are five types of elections in Finland: elections for the president, the parliament, county councils of the wellbeing services counties, municipal councils and the European Parliament. Normally, all Finnish citizens aged 18 or older are eligible to vote. Some non-citizens may also have the right to vote in municipal, county and European elections.

The Legislative Assembly of Alberta is the deliberative assembly of the province of Alberta, Canada. It sits in the Alberta Legislature Building in Edmonton. Since 2012 the Legislative Assembly has had 87 members, elected first past the post from single-member electoral districts. Bills passed by the Legislative Assembly are given royal assent by the lieutenant governor of Alberta, as the viceregal representative of the King of Canada. The Legislative Assembly and the Lieutenant Governor together make up the unicameral Alberta Legislature.

Elections in Mexico are held for officials at federal, state, and municipal levels. At the federal level, the nation's head of state, the president, is directly elected with the popular vote by all Mexican citizens for a six-year non-renewable term. All members of the bicameral federal legislature, the Congress of the Union, are also elected by all Mexican citizens. At the state level, each state has an elective governor and unicameral congress. At the municipal level, the municipal presidents are also elected by their citizens. Since 2016, a constitutional amendment has designed Mexico City to be a fully autonomous entity on par with the states. Its city mayor, city congress, and borough mayors are elected by their citizens in a similar fashion to those states.
Elections in the United States are held for government officials at the federal, state, and local levels. At the federal level, the nation's head of state, the president, is elected indirectly by the people of each state, through an Electoral College. Today, these electors almost always vote with the popular vote of their state. All members of the federal legislature, the Congress, are directly elected by the people of each state. There are many elected offices at state level, each state having at least an elective governor and legislature. There are also elected offices at the local level, in counties, cities, towns, townships, boroughs, and villages; as well as for special districts and school districts which may transcend county and municipal boundaries.

France is a unitary semi-presidential republic with a bicameral legislature. Public officials in the legislative and executive branches are either elected by the citizens or appointed by elected officials. Referenda may also be called to consult the French citizenry directly on a particular question, especially one which concerns amendment to the Constitution.
There are five types of elections in Slovakia: municipal elections, regional elections, parliamentary elections, presidential elections and elections to the European Parliament. All four types of elections are normally held after fixed periods, although early elections can occur in certain situations. Elections are conventionally scheduled for a Saturday - the polls normally open at 7:00 in the morning and close at 22:00 in the evening. Citizens aged 18 years or older are eligible to vote. Those serving prison sentences for particularly serious crimes, as well as those deprived of legal capacity, including persons with mental disabilities, are denied the right to vote. Voter registration is passive and decentralized with the voter register maintained by municipalities based on the permanent residence register. Voter lists are updated continuously based on municipal records and input provided by state institutions or other municipalities. Voters may verify their data in voter lists, and, if necessary, request correction until the day before election day. On election day, a voter can be added to a voter list upon presenting an identity card with proof of residency. Some 4.4 million voters are registered and valid to vote in the elections. Voters are only able to vote from abroad during the Parliamentary Elections in Slovakia.

All elections in the Czech Republic are based on the principle of universal suffrage. Any adult citizen who is at least 18 years old can vote, except those who have been stripped of their legal capacities by a court, usually on the basis of mental illness. Elected representatives are elected directly by the citizens without any intermediaries. Election laws are not part of the constitution, but – unlike regular laws – they cannot be changed without the consensus of both houses of the Parliament. The Czech Republic uses a two-round plurality voting system for the presidential and Senate elections and an open party-list proportional representation system for all other elections. The proportional representation system uses the Sainte-Laguë method for allocating seats.
Elections in Hungary are held at two levels: general elections to elect the members of the National Assembly and local elections to elect local authorities. European Parliament elections are also held every 5 years.
Elections in Luxembourg are held to determine the political composition of the representative institutions of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. Luxembourg is a liberal representative democracy, with universal suffrage guaranteed under its constitution. Elections are held regularly, and are considered to be fair and free.

Elections in Lithuania are held to select members of the parliament, the president, members of the municipal councils and mayors, as well as delegates to the European Parliament. Lithuanian citizens can also vote in mandatory or consultative referendums.

Elections in the U.S. Virgin Islands are held to elect senators to the Legislature of the U.S. Virgin Islands, the governor and lieutenant governor of the territory, and a delegate to the United States House of Representatives.

Elections in Kerala are regularly held to appoint government officials at various levels, both within the state of Kerala and in India as a whole. These elections encompass national elections as well as regional elections for local bodies and panchayats.
Citizens United v. Federal Election Commission, 558 U.S. 310 (2010), is a landmark decision of the Supreme Court of the United States regarding campaign finance laws and free speech under the First Amendment to the U.S. Constitution. The court held 5–4 that the freedom of speech clause of the First Amendment prohibits the government from restricting independent expenditures for political campaigns by corporations including for-profits, nonprofit organizations, labor unions, and other kinds of associations.
Elections in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu are conducted every five years to elect members to the Tamil Nadu Legislative Assembly and members of parliament to the Lok Sabha. There are 234 assembly constituencies and 39 Lok Sabha constituencies. The state has conducted 16 assembly elections and 18 Lok Sabha elections since independence.

The California state elections, November 2010 were held on November 2, 2010.
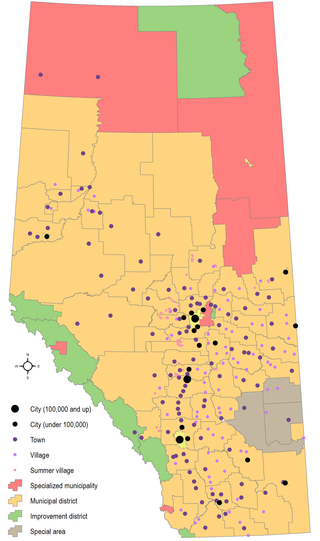
Municipal elections were held in Alberta, Canada on Monday, October 21, 2013. Mayors (reeves), councillors (aldermen), and trustees were elected to office in 16 of the 17 cities, all 108 towns, all 93 villages, all 5 specialized municipalities, all 64 municipal districts, 3 of the 8 improvement districts, and the advisory councils of the 3 special areas. The City of Lloydminster is on the Saskatchewan schedule (quadrennial), and held elections on October 24, 2012, while 5 improvement districts have no councils and are led solely by the Minister of Municipal Affairs. Since the 2010 municipal elections, portions of Lac La Biche County and the Regional Municipality of Wood Buffalo formed Improvement District No. 349, and the villages of New Norway and Tilley were dissolved. From 1968 to 2013, provincial legislation has required every municipality to hold elections every three years. The Alberta Legislative Assembly passed a bill on December 5, 2012, amending the Local Authorities Election Act. Starting with the 2013 elections, officials are elected for a four-year term, and municipal elections are moved to a four-year cycle.

The 2022 Hackney London Borough Council election took place on 5 May 2022. All 57 members of Hackney London Borough Council were up for election. The elections took place alongside the election for the mayor of Hackney, local elections in the other London boroughs, and elections to local authorities across the United Kingdom.