
The New Madrid seismic zone (NMSZ), sometimes called the New Madrid fault line, is a major seismic zone and a prolific source of intraplate earthquakes in the Southern and Midwestern United States, stretching to the southwest from New Madrid, Missouri.

The 1886 Charleston earthquake in South Carolina occurred about 9:50 p.m. local time August 31. It caused 60 deaths and $5–6 million in damage to 2,000 buildings in the Southeastern United States. It is one of the most powerful and damaging earthquakes to hit the East Coast of the United States.

The seismicity of the Sanriku coast identifies and describes the seismic activity of an area of Japan. Seismicity refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time. The Sanriku Coast is a descriptive term referring to the coastal areas of the former provinces of Rikuō in Aomori, Rikuchū in Aomori, and Rikuzen in Miyagi.

The 1976 Guatemala earthquake struck on February 4 at with a moment magnitude of 7.5. The shock was centered on the Motagua Fault, about 160 km northeast of Guatemala City at a depth of 5 kilometers (3.1 mi) near the town of Los Amates in the department of Izabal.
The 2002 Bou'in-Zahra earthquake occurred on 22 June 2002. The epicenter was near the city of Bou'in-Zahra in Qazvin province, a region of northwestern Iran which is crossed by several major faults that is known for destructive earthquakes. The shock measured 6.5 on the scale, had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe), and was followed by more than 20 aftershocks. At least 230 people were killed and 1,500 more were injured.

The 1978 Miyagi earthquake occurred at 17:14 local time on 12 June. The epicentre was offshore of Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. It had a surface-wave magnitude of 7.7, JMA magnitude 7.4, and triggered a small tsunami. The earthquake reached a maximum intensity of Shindo 5 in Sendai and caused 28 deaths and 1,325 injuries.
The 1949 Ambato earthquake was a magnitude 6.4 earthquake that on August 5, 1949, struck Ecuador's Tungurahua Province southeast of its capital Ambato and killed 5,050 people. The nearby villages of Guano, Patate, Pelileo, and Pillaro were destroyed, and the city of Ambato suffered heavy damage. The earthquake flattened buildings and subsequent landslides caused damage throughout the Tungurahua, Chimborazo, and Cotopaxi Provinces. It disrupted water mains and communication lines and opened a fissure into which the small town of Libertad sank. Moderate shaking from the event extended as far away as Quito and Guayaquil.
The 1985 Rapel Lake earthquake occurred on 8 April at with a moment magnitude of 7.2 and a maximum perceived intensity of VI (Strong). The shock was centered 75 kilometres (47 mi) southwest of Santiago, Chile, with a focal depth of 37.8 km (23 mi).
A potent magnitude 6.6 Mw intraplate aftershock occurred at 17:16 JST (08:16 UTC) on 11 April, in the Hamadōri region of Fukushima, Japan. With a shallow focus of 13 km (8.1 mi), the earthquake was centred inland about 36 km (22 mi) west of Iwaki, causing widespread strong to locally severe shaking. It was one of many aftershocks to follow the 11 March Tōhoku earthquake, and the strongest to have its epicentre located inland.
The 2011 Guerrero earthquake struck with a moment magnitude of 5.7 in southern Mexico at on 5 May. It was positioned west of Ometepec, Guerrero, with a focal depth of 24 km (14.9 mi), and was lightly felt in many adjacent areas.
The 1982 Flores earthquake struck the island of Flores in Indonesia on December 25. Registering a moment magnitude of 5.9, according to the International Seismological Centre, it created landslides and was reportedly accompanied by a tsunami. The earthquake killed thirteen people and left 390 injured, also destroying 1,875 houses and 121 other buildings. The villages of Layahong and Oyong Barang were damaged by seven seconds of shaking.
The 2020 Central Idaho earthquake occurred in the western United States on March 31, 2020, at 5:52 PM MDT, near Ruffneck Peak in the Sawtooth Mountains of central Idaho, 72 miles (116 km) northeast of Boise and 19 miles (31 km) northwest of Stanley. It had a magnitude of 6.5 and was felt with a maximum intensity of VIII.
On 6 November 1988, two earthquakes struck Lancang and Gengma counties, Yunnan, near the China–Myanmar border. These earthquakes measured moment magnitude (Mw ) 7.0 and 6.9, respectively, spaced 12 minutes apart. These earthquakes were assigned a maximum China seismic intensity of IX and X, respectively. Between 748 and 939 people were killed; more than 7,700 were injured. Both earthquakes caused damage and economic losses estimated at CN¥ 2.05 billion. Moderately large aftershocks continued to rock the region, causing additional casualties and damage.
The 1965 Valparaíso earthquake struck near La Ligua in Valparaíso Region, Chile, about 140 km (87 mi) from the capital Santiago on Sunday, March 28 at 12:33 local time. The moment magnitude (Mw ) 7.4–7.6 earthquake killed 400–500 people and inflicted US$1 billion in damage. Many deaths were from El Cobre, a mining location that was wiped out after a series of dam failures caused by the earthquake spilled mineral waste onto the area, burying hundreds of residents. The shock was felt throughout the country and along the Atlantic coast of Argentina.
The 1995 Menglian earthquake or 1995 Myanmar–China earthquake occurred on 12 July at 05:46:43 local time in the Myanmar–China border region. The earthquake had an epicenter on the Myanmar side of the border, located in the mountainous region of Shan State. It registered 7.3 on the Chinese surface-wave magnitude scale (Ms ) and 6.8 on the moment magnitude scale (Mw ). With a maximum Mercalli intensity assigned at VIII, it killed 11 people and left another 136 injured. Over 100,000 homes in both countries were destroyed and 42,000 seriously damaged. Some damage to structures were also reported in Chiang Mai and Chiang Rai, Thailand. The low death toll from this earthquake was attributed to an early warning issued prior to it happening. Precursor events including foreshocks and some seismic anomalies led to an evacuation of the area before the mainshock struck. It is thought to be one of the few successfully predicted earthquakes in history.
The 1947 Satipo earthquake was the largest earthquake in the sub-Andean region of Peru. It occurred on November 1 at 09:58:57 local time with an epicenter in the Department of Junín. The earthquake had an estimated moment magnitude (Mw ) of 7.7 and focal depth of 20 km (12 mi). Damage was severe in the towns of Satipo and La Merced, and at least 233 people died.
The 1979 Petatlán earthquake, also known as the IBERO earthquake occurred on March 14 at 05:07 local time in the Mexican state of Guerrero. The earthquake had a surface-wave magnitude of Ms 7.6 or moment magnitude of Mw 7.4 and maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The epicenter, onshore, was located 12 km south southeast of Vallecitos de Zaragoza.
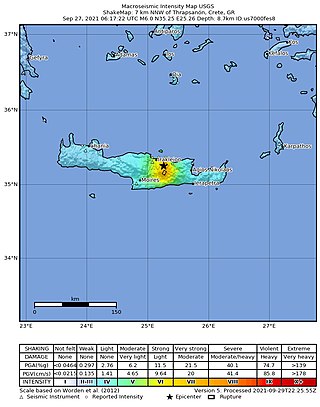
A moment magnitude 6.0 earthquake struck the island of Crete in Greece at a depth of 6 km on 27 September 2021. The epicenter of the earthquake was located southeast of Heraklion. The quake killed one person, injured 36 and damaged over 5,000 old buildings on the island.
Between May 1990 and April 1991, an earthquake sequence occurred in the Department of San Martín, northern Peru. Three large earthquakes of magnitudes (Mw ) 6.5–6.9 occurred in the same region across 11 months, causing extensive damage. At least 189 people were killed in these earthquakes.

On July 27, 2022, at 8:43:24 a.m. (PHT), an earthquake struck the island of Luzon in the Philippines. The earthquake had a magnitude of 7.0 Mw , with an epicenter in Abra province. Eleven people were reported dead and 615 were injured. At least 35,798 homes, schools and other buildings were damaged or destroyed, resulting in ₱1.88 billion (US$34 million) worth of damage.











