
An intraplate earthquake is an earthquake that occurs in the interior of a tectonic plate, in contrast to an interplate earthquake on the boundary of a tectonic plate. It is also called an intraslab earthquake, especially when occurring in a microplate.
The Peru–Chile Trench, also known as the Atacama Trench, is an oceanic trench in the eastern Pacific Ocean, about 160 kilometres (99 mi) off the coast of Peru and Chile. It reaches a maximum depth of 8,065 m (26,460 ft) below sea level in Richards Deep and is approximately 5,900 km (3,666 mi) long; its mean width is 64 km (40 mi) and it covers an expanse of some 590,000 km2 (230,000 sq mi).

The Cascadia subduction zone is a 960 km (600 mi) fault at a convergent plate boundary, about 100–200 km (70–100 mi) off the Pacific coast, that stretches from northern Vancouver Island in Canada to Northern California in the United States. It is capable of producing 9.0+ magnitude earthquakes and tsunamis that could reach 30 m (98 ft). The Oregon Department of Emergency Management estimates shaking would last 5–7 minutes along the coast, with strength and intensity decreasing further from the epicenter. It is a very long, sloping subduction zone where the Explorer, Juan de Fuca, and Gorda plates move to the east and slide below the much larger mostly continental North American Plate. The zone varies in width and lies offshore beginning near Cape Mendocino, Northern California, passing through Oregon and Washington, and terminating at about Vancouver Island in British Columbia.

Illapel is a Chilean city, which is the capital of the Choapa Province, Coquimbo Region. It lies along the Illapel River and marks the country's narrowest point along a parallel (94 km). It is located to the east of Los Vilos.
Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthquakes are the planet's most powerful, with moment magnitudes (Mw) that can exceed 9.0. Since 1900, all earthquakes of magnitude 9.0 or greater have been megathrust earthquakes.
The 1922 Vallenar earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 8.5–8.6 and a tsunami magnitude of 8.7 in the Atacama Region of Chile, near the border with Argentina on 11 November at 04:32 UTC. It triggered a destructive tsunami that caused significant damage to the coast of Chile and was observed as far away as Australia.
The 1730 Valparaíso earthquake occurred at 04:45 local time on July 8. It had an estimated magnitude of 9.1–9.3 and triggered a major tsunami with an estimated magnitude of Mt 8.75, that inundated the lower parts of Valparaíso. The earthquake caused severe damage from La Serena to Chillan, while the tsunami affected more than 1,000 km (620 mi) of Chile's coastline.

The 1997 Punitaqui earthquake occurred at 01:03 UTC on October 15. It had an estimated magnitude of 7.1 . This earthquake was one of the most destructive in the epicentral area compared to other events of subduction of the same size. The extensive damage to structures was the result of an amplification effect on the ground and the poor quality of building materials, this reflects the potential for damage incurred in an intraplate earthquake with vertical fault and how it can be much greater than what which can cause one of interplate of similar magnitude, and caused severe damage in Chilean cities of La Serena, Vicuña, Ovalle, Illapel and Punitaqui.
The 1906 Aleutian Islands earthquake occurred at 00:11 UTC on August 17. It had an estimated seismic moment of 3.8 x 1028 dyn cm−1, equivalent to a magnitude of 8.35 on the moment magnitude scale. This earthquake was followed thirty minutes later by the 1906 Valparaíso earthquake in Chile, but the two events are not thought to be linked. Due to the remote location, there are no reports of damage associated with this earthquake. A transpacific tsunami reported from Japan and Hawaii was triggered by the Chilean event, rather than the Aleutian Islands earthquake.

The 2015 Illapel earthquake occurred 46 km (29 mi) offshore from Illapel on September 16 at 19:54:32 Chile Standard Time (22:54:32 UTC), with a moment magnitude of 8.3–8.4. The initial quake lasted between three and five minutes; it was followed by several aftershocks greater than magnitude six and two that exceeded 7.0 moment magnitude. The Chilean government reported 15 deaths, 6 missing and thousands of people affected. In Buenos Aires, Argentina, a man died from a stroke while he was evacuating a building.
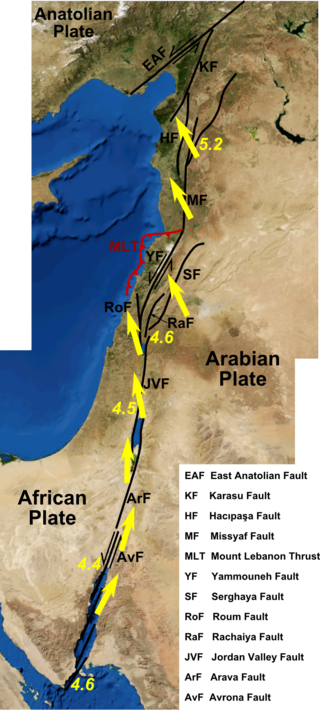
The 1170 Syria earthquake was one of the largest earthquakes to hit Syria. It occurred early in the morning of 29 June 1170. It formed part of a sequence of large earthquakes that propagated southwards along the Dead Sea Transform, starting with the 1138 Aleppo earthquake, continuing with the 1157 Hama, 1170 and 1202 Syria events. The estimated magnitude is 7.7 on the moment magnitude scale, with the maximum intensity of X (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale.
The 1420 Caldera earthquake was a pre-Columbian earthquake that shook the southern portion of Atacama Desert in the early morning of August 31, 1420 and caused tsunamis in Chile as well as Hawaii and the towns of Japan. The earthquake is thought to have had a size of 8.8–9.4 . Historical records of the tsunami exist for the Japanese harbours of Kawarago and Aiga where confused residents saw the water recede in the morning of September 1, without any sign of an earthquake. In Chile, rockfalls occurred along the coast as well, producing blocks of up to 40 tons that are now found inland. This is also consistent with the identification of a possible tsunami deposit in Mejillones Bay that has been dated to the range 1409 to 1449. Deposits found by coring of recent sediments in a wetland near Tongoy Bay have also been linked to the 1420 tsunami.
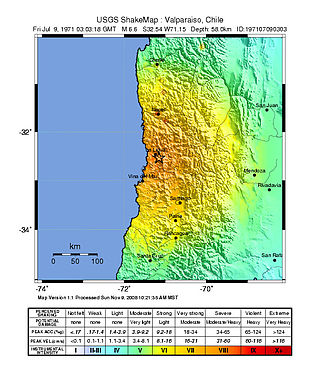
The Valparaíso Region of central Chile was struck by an earthquake of magnitude 7.8 at 22:03 8 July 1971 local time. It had a maximum felt intensity of IX (violent) on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale and caused the deaths of 83 people and injured a further 447.
The 1965 Valparaíso earthquake struck near La Ligua in Valparaíso Region, Chile, about 140 km (87 mi) from the capital Santiago on Sunday, March 28 at 12:33 local time. The moment magnitude (Mw ) 7.4–7.6 earthquake killed 400–500 people and inflicted US$1 billion in damage. Many deaths were from El Cobre, a mining location that was wiped out after a series of dam failures caused by the earthquake spilled mineral waste onto the area, burying hundreds of residents. The shock was felt throughout the country and along the Atlantic coast of Argentina.
The 1822 Valparaíso earthquake was a major earthquake that occurred in Valparaíso, Chile on November 19, 1822. The earthquake has an estimated surface wave magnitude of 8.5. It triggered a moderate tsunami measuring up to 12 ft (3.7 m) along the Chilean coast. The earthquake and tsunami killed between 72 and 300 people and left a further 200 injured.
During April 1819, the area around Copiapó in northern Chile was struck by a sequence of earthquakes over a period of several days. The largest of these earthquakes occurred on 11 April at about 15:00 local time, with an estimated magnitude of 8.5. The other two events, on 3 April between 08:00 and 09:00 local time and on 4 April at 16:00 local time, are interpreted as foreshocks to the mainshock on 11 April. The mainshock triggered a tsunami that affected 800 km of coastline and was also recorded at Hawaii. The city of Copiapó was devastated.
The 1950 Calama earthquake occurred near the Argentina–Chile border with an epicenter near Calama, Chile in the Atacama Desert on December 9. The event had a hypocenter depth of 113.9 km, beneath the Caichinque volcanic complex. It measured magnitude Mw 8.2 on the moment magnitude scale, making it the largest intermediate depth earthquake ever recorded on Chilean soil. One person was killed and an unspecified number of people were injured in Calama.
The 1657 Concepción earthquake occurred on March 15 at 20:00 local time off the coast of Concepción, Biobío Region in the Spanish Empire. The earthquake caused severe damage along the coast, and generated a large tsunami in the Bay of Concepción. At least 40 people were killed, the majority due to drowning from the tsunami. The town of Concepción was the hardest hit, with the earthquake and tsunami totally destroying it.
The 2012 Constitución earthquake was recorded on March 25, 2012, at 7:37 pm local time. It had a moment magnitude of 7.1 and its epicenter was located 23 km (14 mi) northeast of the city of Constitución, in the Maule Region, Chile. According to experts, it was a strong and late aftershock of the Great Chile earthquake of February 27, 2010.







