The 2006 Tonga earthquake occurred on 4 May at with a moment magnitude of 8.0 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. One injury occurred and a non-destructive tsunami was observed.

The 1356 Basel earthquake is the most significant seismological event to have occurred in Central Europe in recorded history and had a moment magnitude in the range of 6.0–7.1. This earthquake, which occurred on 18 October 1356, is also known as the Sankt-Lukas-Tag Erdbeben, as 18 October is the feast day of Saint Luke the Evangelist.
The 1927 Crimean earthquakes occurred in the month of June and again in September in the waters of the Black Sea near the Crimean Peninsula. Each of the submarine earthquakes in the sequence triggered tsunami. The June event was moderate relative to the large September 11 event, which had at least one aftershock that also generated a tsunami. Following the large September event, natural gas that was released from the sea floor created flames that were visible along the coastline, and was accompanied by bright flashes and explosions.
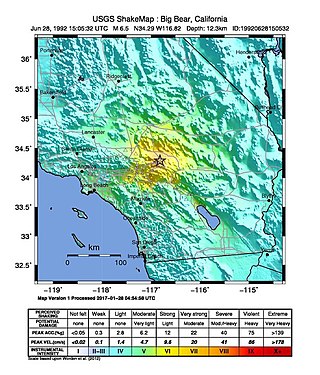
The 1992 Big Bear earthquake occurred at on June 28 in Big Bear Lake, California, with a moment magnitude of 6.5 and a maximum perceived intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Mercalli intensity scale. The earthquake occurred at a relatively shallow depth of 5 kilometers (3.1 mi).
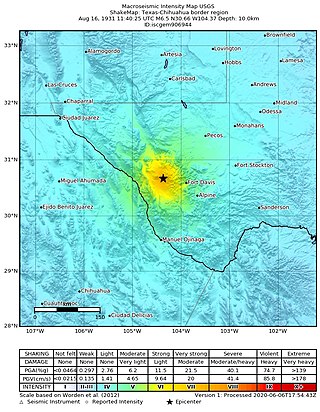
In the early morning hours of August 16, 1931, a powerful earthquake occurred in West Texas with a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). Estimates of its magnitude range between 5.8 and 6.4 mb, making it the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Texas history. Its epicenter was near the town of Valentine, Texas; there, the earthquake caused damage to many homes and buildings. The earthquake may have been caused by movement along oblique-slip faulting in West Texas, the most seismically active region in the state. Shaking from the earthquake was perceptible within a 400 mi (640 km) radius of the epicenter, affecting four U.S. states and northern Mexico. Several foreshocks and aftershocks accompanied the primary temblor, with the aftershocks continuing until at least November 3, 1931. The main earthquake caused no fatalities, though several people sustained minor injuries; the damage in Valentine amounted to $50,000–$75,000.

The Swiss Seismological Service at ETH Zurich is the federal agency responsible for monitoring earthquakes in Switzerland and its neighboring countries and for assessing Switzerland's seismic hazard. When an earthquake happens, the SED informs the public, authorities, and the media about the earthquake's location, magnitude, and possible consequences. The activities of the SED are integrated in the federal action plan for earthquake precaution.
Striking southern Italy on 8 September, the 1905 Calabria earthquake had a moment magnitude of 7.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme). The first major earthquake of the 20th century, it severely damaged parts of Lipari, Messina Province and a large area between Cosenza and Nicotera and killed between 557 and 2,500 people.
The 1982 North Yemen earthquake hit near the city of Dhamar, North Yemen on December 13. Measuring 6.2 on the moment magnitude scale, with a maximum perceived intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Mercalli intensity scale, as many as 2,800 people were killed and another 1,500 injured. The shock occurred within several hundred kilometers of a plate boundary in a geologically complex region that includes active volcanoes and seafloor spreading ridges. Yemen has a history of destructive earthquakes, though this was the first instrumentally recorded event to be detected on global seismograph networks.
The 1967 Mudurnu earthquake or more correctly, the 1967 Mudurnu Valley earthquake occurred at about 18:57 local time on 22 July near Mudurnu, Bolu Province, north-western Turkey. The magnitude 7.4 earthquake was one of a series of major and intermediate quakes that have occurred in modern times along the North Anatolian Fault since 1939.
The 1971 Bingöl earthquake was a 6.6–6.7 earthquake that occurred at on 22 May. It had a surface-wave magnitude of 6.9 and a maximum intensity of IX (Violent) on the Mercalli intensity scale, killing 755–1,000 people. Bingöl was largely destroyed, as well as many houses in the nearby Bingöl plain. Surface displacement of 38 km (24 mi) and various other surficial effects were directly caused by the earthquake.

The 2011 Lorca earthquake was a moderate 5.1 earthquake that occurred 6:47 p.m. CEST on 11 May 2011, near the town of Lorca, causing significant localized damage in the Region of Murcia, Spain, and panic among locals, and displacing many from their homes. The quake was preceded by a magnitude 4.4 foreshock at 17:05, that inflicted substantial damage to many older structures in the area, including the historical Espolón Tower of Lorca Castle, the Hermitage of San Clemente and the Convent of Virgen de Las Huertas. Three people were killed by a falling cornice. A total of nine deaths have been confirmed, while dozens are reported injured. The earthquake was the worst to hit the region since a 5.0 Mw tremor struck west of Albolote, Granada in 1956.

The 1918 San Jacinto earthquake occurred in extreme eastern San Diego County in Southern California on April 21 at . The shock had a moment magnitude of 6.7 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). Several injuries and one death occurred with total losses estimated to be $200,000.
On November 2 of 1946, west Kyrgyzstan was struck by a magnitude 7.5–7.6 earthquake, the largest in the republic since 1911. The earthquake's hypocenter is probably located beneath the Tian Shan Mountains, near the border with Uzbekistan and north of Namangan.
On April 13, 1923 at 15:31 UTC, an earthquake occurred off the northern coast of the Kamchatka Peninsula in the USSR, present-day Russia. The earthquake had a surface-wave magnitude (Ms ) of 6.8–7.3 and an estimated moment magnitude (Mw ) of 7.0–8.2. This event came just two months after a slightly larger earthquake with an epicenter struck south of the April event. Both earthquakes were tsunamigenic although the latter generated wave heights far exceeding that of the one in February. After two foreshocks of "moderate force", the main event caused considerable damage. Most of the 36 casualties were the result of the tsunami inundation rather than the earthquake.
The 1941 Sa'dah earthquake or the Jabal Razih earthquake occurred on January 11 in Razih District of the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen. The earthquake had a surface-wave magnitude of 5.8–6.5 and a shallow focal depth. Despite the moderate size of this earthquake, an estimated 1,200 people perished and at least 200 injured. With a maximum MSK-64 intensity assigned at VIII, it destroyed many villages and collapsed homes in the region of North Yemen.
The 1925 Montana earthquake occurred at 17:21:12 MDT on 27 June in Montana, with the epicenter being located near Townsend. The earthquake had a magnitude of 6.9 in the surface-wave magnitude scale. A maximum intensity of IX (Violent) was observed. Serious damage was reported near the epicenter. 3 hours after the mainshock, a strong aftershock was recorded with an unknown magnitude that also caused damage.
The 1997 Bojnurd earthquake occurred on 4 February at 14:07 IRST in Iran. The epicenter of the 6.5 earthquake was in the Kopet Dag mountains of North Khorasan, near the Iran–Turkmenistan border, about 579 km (360 mi) northeast of Tehran. The earthquake is characterized by shallow strike-slip faulting in a zone of active faults. Seismic activity is present as the Kopet Dag is actively accommodating tectonics through faulting. The earthquake left 88 dead, 1,948 injured, and affected 173 villages, including four which were destroyed. Damage also occurred in Shirvan and Bojnord counties. The total cost of damage was estimated to be over US$ 30 million.
On 22 April 2022 at 23:07 local time, a magnitude 5.7 earthquake struck southern Bosnia and Herzegovina. The epicentre was in the Herzegovinian village of Strupići, roughly 10 km (6.2 mi) east of Stolac or 14 km (8.7 mi) from Ljubinje or Nevesinje. It is the country's fifth largest earthquake, as well as its most significant since the 1969 Banja Luka earthquake.
The 1584 Aigle earthquake occurred on 11 March at 23:00–23:30 local time in Switzerland. The earthquake had a moment magnitude of 5.9–6.4 and maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The shock generated a tsunami in Lake Geneva. It was followed by 25 aftershocks in the following days. An aftershock on 14 March triggered a large rockslide that killed 320 people.







