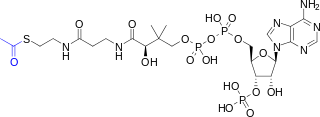
Acetyl-CoA is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production. Coenzyme A consists of a β-mercaptoethylamine group linked to the vitamin pantothenic acid (B5) through an amide linkage and 3'-phosphorylated ADP. The acetyl group of acetyl-CoA is linked to the sulfhydryl substituent of the β-mercaptoethylamine group. This thioester linkage is a "high energy" bond, which is particularly reactive. Hydrolysis of the thioester bond is exergonic (−31.5 kJ/mol).
Carboxy-lyases, also known as decarboxylases, are carbon–carbon lyases that add or remove a carboxyl group from organic compounds. These enzymes catalyze the decarboxylation of amino acids, beta-keto acids and alpha-keto acids.

In enzymology, a pyruvate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of pyruvate and acetyl-CoA. It is also called pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR).
The enzyme (2R)-sulfolactate sulfo-lyase catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a methylmalonyl-CoA carboxytransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-L-pentonate aldolase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate aldolase catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme 4-hydroxy-2-oxovalerate aldolase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 4-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-oxoglutarate aldolase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme citramalate lyase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme citramalyl-CoA lyase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme indolepyruvate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.74) catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme methylisocitrate lyase catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme N-acetylneuraminate lyase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 2-methylcitrate dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.79) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme acetylenecarboxylate hydratase (EC 4.2.1.27) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme dimethylmaleate hydratase (EC 4.2.1.85) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-methylcitrate synthase (EC 2.3.3.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, formate C-acetyltransferase is an enzyme. Pyruvate formate lyase is found in Escherichia coli and other organisms. It helps regulate anaerobic glucose metabolism. Using radical non-redox chemistry, it catalyzes the reversible conversion of pyruvate and coenzyme-A into formate and acetyl-CoA. The reaction occurs as follows:

In enzymology, a malate synthase (EC 2.3.3.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction







