In mathematics, a finite field or Galois field is a field that contains a finite number of elements. As with any field, a finite field is a set on which the operations of multiplication, addition, subtraction and division are defined and satisfy certain basic rules. The most common examples of finite fields are given by the integers mod p when p is a prime number.
In geometry, a Platonic solid is a convex, regular polyhedron in three-dimensional Euclidean space. Being a regular polyhedron means that the faces are congruent regular polygons, and the same number of faces meet at each vertex. There are only five such polyhedra:

Q, or q, is the seventeenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is pronounced, most commonly spelled cue, but also kew, kue and que.
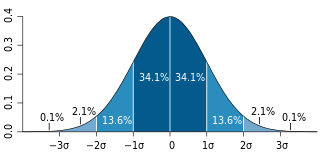
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of a random variable expected about its mean. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. The standard deviation is commonly used in the determination of what constitutes an outlier and what does not.

An electric field is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles. Charged particles exert attractive forces on each other when their charges are opposite, and repulse each other when their charges are the same. Because these forces are exerted mutually, two charges must be present for the forces to take place. The electric field of a single charge describes their capacity to exert such forces on another charged object. These forces are described by Coulomb's law, which says that the greater the magnitude of the charges, the greater the force, and the greater the distance between them, the weaker the force. Thus, we may informally say that the greater the charge of an object, the stronger its electric field. Similarly, an electric field is stronger nearer charged objects and weaker further away. Electric fields originate from electric charges and time-varying electric currents. Electric fields and magnetic fields are both manifestations of the electromagnetic field, Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions of nature.

In mathematics, the quaternion number system extends the complex numbers. Quaternions were first described by the Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton in 1843 and applied to mechanics in three-dimensional space. The algebra of quaternions is often denoted by H, or in blackboard bold by Quaternions are not a field, because multiplication of quaternions is not, in general, commutative. Quaternions provide a definition of the quotient of two vectors in a three-dimensional space. Quaternions are generally represented in the form

In mathematics, the Euclidean distance between two points in Euclidean space is the length of the line segment between them. It can be calculated from the Cartesian coordinates of the points using the Pythagorean theorem, and therefore is occasionally called the Pythagorean distance.

Capacitance is the capability of a material object or device to store electric charge. It is measured by the charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related notions of capacitance: self capacitance and mutual capacitance. An object that can be electrically charged exhibits self capacitance, for which the electric potential is measured between the object and ground. Mutual capacitance is measured between two components, and is particularly important in the operation of the capacitor, an elementary linear electronic component designed to add capacitance to an electric circuit.

In mathematics, a binary operation is commutative if changing the order of the operands does not change the result. It is a fundamental property of many binary operations, and many mathematical proofs depend on it. Perhaps most familiar as a property of arithmetic, e.g. "3 + 4 = 4 + 3" or "2 × 5 = 5 × 2", the property can also be used in more advanced settings. The name is needed because there are operations, such as division and subtraction, that do not have it ; such operations are not commutative, and so are referred to as noncommutative operations. The idea that simple operations, such as the multiplication and addition of numbers, are commutative was for many years implicitly assumed. Thus, this property was not named until the 19th century, when mathematics started to become formalized. A similar property exists for binary relations; a binary relation is said to be symmetric if the relation applies regardless of the order of its operands; for example, equality is symmetric as two equal mathematical objects are equal regardless of their order.

Kamaal Ibn John Fareed, better known by his stage name Q-Tip, is an American rapper, record producer, singer, and DJ. Nicknamed the Abstract, he is noted for his innovative jazz-influenced style of hip hop production and his philosophical, esoteric and introspective lyrical themes. He embarked on his music career in the late 1980s, as an MC and main producer of the influential alternative hip hop group A Tribe Called Quest. In the mid-1990s, he co-founded the production team The Ummah, followed by the release of his gold-certified solo debut Amplified in 1999. In the following decade, he released the Grammy Award-nominated album The Renaissance (2008) and the experimental album Kamaal the Abstract (2009).

In mathematics, E7 is the name of several closely related Lie groups, linear algebraic groups or their Lie algebras e7, all of which have dimension 133; the same notation E7 is used for the corresponding root lattice, which has rank 7. The designation E7 comes from the Cartan–Killing classification of the complex simple Lie algebras, which fall into four infinite series labeled An, Bn, Cn, Dn, and five exceptional cases labeled E6, E7, E8, F4, and G2. The E7 algebra is thus one of the five exceptional cases.

QAnon is a far-right American political conspiracy theory and political movement that originated in 2017. QAnon centers on fabricated claims made by an anonymous individual or individuals known as "Q". Those claims have been relayed and developed by online communities and influencers. Their core belief is that a cabal of Satanic, cannibalistic child molesters is operating a global child sex trafficking ring that conspired against president Donald Trump. QAnon has direct roots in Pizzagate, an Internet conspiracy theory that appeared one year earlier, but also incorporates elements of many other theories. QAnon has been described as a cult.

Margaret Denise Quigley, professionally known as Maggie Q, is an American actress.

The Toyota iQ is a city car manufactured by Toyota and marketed in a single generation for Japan (2008–2016); Europe (2008–2015); and North America (2012–2015), where it was marketed as the Scion iQ. A rebadged variant was marketed in Europe as the Aston Martin Cygnet (2011–2013).

In mathematics, a rational number is a number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, a numerator p and a non-zero denominator q. For example, is a rational number, as is every integer. The set of all rational numbers, also referred to as "the rationals", the field of rationals or the field of rational numbers is usually denoted by boldface Q, or blackboard bold
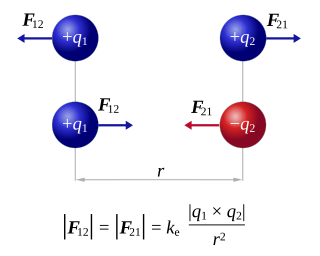
Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law of physics that calculates the amount of force between two electrically charged particles at rest. This electric force is conventionally called the electrostatic force or Coulomb force. Although the law was known earlier, it was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. Coulomb's law was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism and maybe even its starting point, as it allowed meaningful discussions of the amount of electric charge in a particle.

The Q source (also called The Sayings Gospel, Q Gospel, Q document(s), or Q; from German: Quelle, meaning "source") is an alleged written collection of primarily Jesus' sayings (λόγια, logia). Q is part of the common material found in the Gospels of Matthew and Luke but not in the Gospel of Mark. According to this hypothesis, this material was drawn from the early Church's oral gospel traditions.

Quincy Matthew Hanley, better known by his stage name Schoolboy Q, is an American rapper from South Los Angeles, California. He began recording in 2007, and released his first two mixtapes, ScHoolboy Turned Hustla (2008) and Gangsta & Soul (2009) to local success. After signing with the Carson-based record label Top Dawg Entertainment, Hanley's debut studio album, Setbacks (2011) and its follow-up, Habits & Contradictions (2012) were both released to positive critical response; both also performed moderately on the US Billboard 200 chart as digital exclusives.

Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises due to the structure of arguments alone, independent of their topic and content. Informal logic is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. Informal logic examines arguments expressed in natural language while formal logic uses formal language. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Logic plays a central role in many fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics.


















