2063 Bacchus, provisional designation 1977 HB, is a stony asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 1 kilometer in diameter. The contact binary was discovered on 24 April 1977, by American astronomer Charles Kowal at the Palomar Observatory in California, United States. It was named after Bacchus from Roman mythology.

1862 Apollo is a stony asteroid, approximately 1.5 kilometers in diameter, classified as a near-Earth object (NEO). It was discovered by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at Heidelberg Observatory on 24 April 1932, but lost and not recovered until 1973.

4660 Nereus, provisional designation 1982 DB, is a small asteroid. It was discovered by Eleanor F. Helin on 28 February 1982, approximately a month after it passed 4.1 million km (11 LD) from Earth.
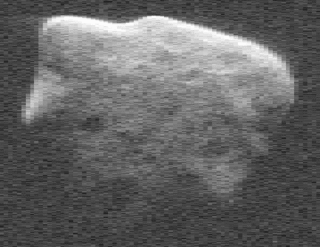
(53319) 1999 JM8 is an asteroid, slow rotator and tumbler, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid (PHA) of the Apollo group, approximately 7 kilometers (4 miles) in diameter, making it the largest PHA known to exist. It was discovered on 13 May 1999, by astronomers of the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico.

1981 Midas, provisional designation 1973 EA, is a vestoid asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid, approximately 2 kilometers in diameter.

(153591) 2001 SN263 is a carbonaceous trinary asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and former potentially hazardous asteroid of the Amor group, approximately 2.6 kilometers (1.6 miles) in diameter. It was discovered by the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research project at Lincoln Lab's Experimental Test Site in Socorro, New Mexico, on 20 September 2001. The two synchronous minor-planet moons measure approximately 770 and 430 meters and have an orbital period of 16.46 and 150 hours, respectively.
(6037) 1988 EG, is an eccentric, stony asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid. It belongs to the group of Apollo asteroids and measures approximately half a kilometer in diameter. It was discovered by American astronomer Jeff T. Alu at the U.S. Palomar Observatory, California, on 12 March 1988.
(7025) 1993 QA is a sub-kilometer asteroid classified as near-Earth object of the Apollo and Amor group, respectively. It was discovered on 16 August 1993, by astronomers of the Spacewatch program at the Kitt Peak National Observatory near Tucson, Arizona, United States. The asteroid measures approximately half a kilometer in diameter and has a short rotation period of 2.5057 hours.

(7482) 1994 PC1 is a stony asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 1.1 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 9 August 1994, by astronomer Robert McNaught at the Siding Spring Observatory in Coonabarabran, Australia. With an observation arc of 47 years it has a very well known orbit and was observed by Goldstone radar in January 1997. The 2022 approach has been observed every month since August 2021.
(152680) 1998 KJ9 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. Based on absolute magnitude, it is the third largest asteroid known to have passed closer than the Moon.
2012 XE133 is an asteroid, classified as near-Earth object of the Aten group that is a temporary co-orbital of Venus.
(31345) 1998 PG is an eccentric, stony asteroid and binary system, classified as near-Earth object of the Amor group of asteroids, approximately 900 meters in diameter. It minor-planet moon, S/2001 (31345) 1, has an estimated diameter of 270 meters.
(163132) 2002 CU11, provisional designation 2002 CU11, is a bright, sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. Based on absolute magnitude, it is the second largest asteroid known to have passed closer than the Moon.

(66063) 1998 RO1 is a stony near-Earth object of the Aten group on a highly-eccentric orbit. The synchronous binary system measures approximately 800 meters (0.50 miles) in diameter. It was discovered by astronomers of the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, on 14 September 1998.
2013 ND15 (also written 2013 ND15) is an asteroid that is a temporary trojan of Venus, the first known Venus trojan.

(192642) 1999 RD32, provisional designation: 1999 RD32, is an asteroid and suspected contact binary on an eccentric orbit, classified as a large near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 5 kilometers (3 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 8 September 1999, at a magnitude of 18, by astronomers of the LINEAR program using its 1-meter telescope at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, United States. The asteroid is likely of carbonaceous composition and has a rotation period of 17.08 hours.
2014 OL339 (also written 2014 OL339) is an Aten asteroid that is a temporary quasi-satellite of Earth, the fourth known Earth quasi-satellite.
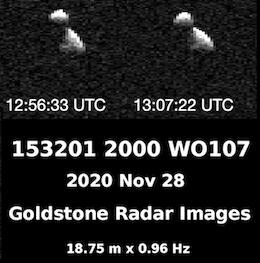
(153201) 2000 WO107 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Aten group with a very well determined orbit. It was discovered on 29 November 2000, by astronomers of the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR) at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States. It is a contact binary.

2015 TB145 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 650 meters (2,000 feet) in diameter. It safely passed 1.27 lunar distances from Earth on 31 October 2015 at 17:01 UTC, and passed by Earth again in November 2018.

(164121) 2003 YT1, provisional designation 2003 YT1, is a bright asteroid and synchronous binary system on a highly eccentric orbit, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 2 kilometers (1.2 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 18 December 2003, by astronomers with the Catalina Sky Survey at the Catalina Station near Tucson, Arizona, in the United States. The V-type asteroid has a short rotation period of 2.3 hours. Its 210-meter sized minor-planet moon was discovered at Arecibo Observatory in May 2004.












