
A carcinogen is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and biologic agents such as viruses and bacteria. Most carcinogens act by creating mutations in DNA that disrupt a cell's normal processes for regulating growth, leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation. This occurs when the cell's DNA repair processes fail to identify DNA damage allowing the defect to be passed down to daughter cells. The damage accumulates over time. This is typically a multi-step process during which the regulatory mechanisms within the cell are gradually dismantled allowing for unchecked cellular division.
Mutagenesis is a process by which the genetic information of an organism is changed by the production of a mutation. It may occur spontaneously in nature, or as a result of exposure to mutagens. It can also be achieved experimentally using laboratory procedures. A mutagen is a mutation-causing agent, be it chemical or physical, which results in an increased rate of mutations in an organism's genetic code. In nature mutagenesis can lead to cancer and various heritable diseases, and it is also a driving force of evolution. Mutagenesis as a science was developed based on work done by Hermann Muller, Charlotte Auerbach and J. M. Robson in the first half of the 20th century.

In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that permanently changes genetic material, usually DNA, in an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer in animals, such mutagens can therefore be carcinogens, although not all necessarily are. All mutagens have characteristic mutational signatures with some chemicals becoming mutagenic through cellular processes.

Benzo[a]pyrene (BaP or B[a]P) is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and the result of incomplete combustion of organic matter at temperatures between 300 °C (572 °F) and 600 °C (1,112 °F). The ubiquitous compound can be found in coal tar, tobacco smoke and many foods, especially grilled meats. The substance with the formula C20H12 is one of the benzopyrenes, formed by a benzene ring fused to pyrene. Its diol epoxide metabolites, more commonly known as BPDE, react with and bind to DNA, resulting in mutations and eventually cancer. It is listed as a Group 1 carcinogen by the IARC. In the 18th century a scrotal cancer of chimney sweepers, the chimney sweeps' carcinoma, was already known to be connected to soot.

Methylcholanthrene is a highly carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon produced by burning organic compounds at very high temperatures. Methylcholanthrene is also known as 3-methylcholanthrene, 20-methylcholanthrene or the IUPAC name 3-methyl-1,2-dyhydrobenzo[j]aceanthrylene. The short notation often used is 3-MC or MCA. This compound forms pale yellow solid crystals when crystallized from benzene and ether. It has a melting point around 180 °C and its boiling point is around 280 °C at a pressure of 80 mmHg. Methylcholanthrene is used in laboratory studies of chemical carcinogenesis. It is an alkylated derivative of benz[a]anthracene and has a similar UV spectrum. The most common isomer is 3-methylcholanthrene, although the methyl group can occur in other places.

Sudan I is an organic compound typically classified as an azo dye. It is an orange-red solid, used to color waxes, oils, petrol, solvents, and polishes. Historically, Sudan I used to serve as a food coloring agent, notably for curry powder and chili powder. However, along with its derivatives Sudan III and Sudan IV, the compound has been banned in many countries due to its classification as a category 3 carcinogenic hazard by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Nevertheless, Sudan I remains valuable as a coloring reagent for non-food-related uses, such as in the formulation of orange-colored smoke.
Glucuronidation is often involved in drug metabolism of substances such as drugs, pollutants, bilirubin, androgens, estrogens, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, fatty acid derivatives, retinoids, and bile acids. These linkages involve glycosidic bonds.

Glucuronic acid is a uronic acid that was first isolated from urine. It is found in many gums such as gum arabic, xanthan, and kombucha tea and is important for the metabolism of microorganisms, plants and animals.

In molecular genetics, a DNA adduct is a segment of DNA bound to a cancer-causing chemical. This process could lead to the development of cancerous cells, or carcinogenesis. DNA adducts in scientific experiments are used as biomarkers of exposure. They are especially useful in quantifying an organism's exposure to a carcinogen. The presence of such an adduct indicates prior exposure to a potential carcinogen, but it does not necessarily indicate the presence of cancer in the subject animal.

o-Toluidine (ortho-toluidine) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3C6H4NH2. It is the most important of the three isomeric toluidines. It is a colorless liquid although commercial samples are often yellowish. It is a precursor to the herbicides metolachlor and acetochlor.

UDP glucuronosyltransferase 2 family, polypeptide B4, also known as UGT2B4, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the UGT2B4 gene.

2-Acetylaminofluorene is a carcinogenic and mutagenic derivative of fluorene. It is used as a biochemical tool in the study of carcinogenesis. It induces tumors in a number of species in the liver, bladder and kidney. The metabolism of this compound in the body by means of biotransformation reactions is the key to its carcinogenicity. 2-AAF is a substrate for cytochrome P-450 (CYP) enzyme, which is a part of a super family found in almost all organisms. This reaction results in the formation of hydroxyacetylaminofluorene which is a proximal carcinogen and is more potent than the parent molecule. The N-hydroxy metabolite undergoes several enzymatic and non-enzymatic rearrangements. It can be O-acetylated by cytosolic N-acetyltransferase enzyme to yield N-acetyl-N-acetoxyaminofluorene. This intermediate can spontaneously rearrange to form the arylamidonium ion and a carbonium ion which can interact directly with DNA to produce DNA adducts. In addition to esterification by acetylation, the N-hydroxy derivative can be O-sulfated by cytosolic sulfur transferase enzyme giving rise to the N-acetyl-N-sulfoxy product.

Benzo[j]fluoranthene (BjF) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C20H12. Classified as a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH), it is a colourless solid that is poorly soluble in most solvents. Impure samples can appear off white. Closely related isomeric compounds include benzo[a]fluoranthene (BaF), benzo[b]fluoranthene (BbF), benzo[e]fluoranthene (BeF), and benzo[k]fluoranthene (BkF). BjF is present in fossil fuels and is released during incomplete combustion of organic matter. It has been traced in the smoke of cigarettes, exhaust from gasoline engines, emissions from the combustion of various types of coal and emissions from oil heating, as well as an impurity in some oils such as soybean oil.
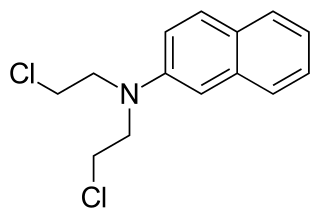
Chlornaphazine, a derivative of 2-naphthylamine, is a nitrogen mustard that was developed in the 1950s for the treatment of polycythemia and Hodgkin's disease. However, a high incidence of bladder cancers in patients receiving treatment with chlornaphthazine led to use of the drug being discontinued.

2-Amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine is one of the most abundant heterocyclic amines (HCAs) found in cooked meat. PhIP is formed at high temperatures from the reaction between creatine or creatinine, amino acids, and sugar. PhIP formation increases with the temperature and duration of cooking and also depends on the method of cooking and the variety of meat being cooked. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Toxicology Program has declared PhIP as "reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen". International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), part of World Health Organization, has classified PhIP as IARC Group 2B carcinogen. There is sufficient evidence in experimental animals, as well as in vitro models, for the carcinogenicity of PhIP.

2-Aminofluorene (2-AF) is a synthetic arylamine. It is a white to tan solid with a melting point of 125-132 °C. 2-AF has only been tested in controlled laboratory settings thus far. There is no indication that it will be tested in industrialized settings. There is evidence that 2-aminofluorene is a carcinogen and an intercalating agent that is extremely dangerous to genomic DNA that potentially can lead to mutation if not death. Furthermore, it has been suggested that 2-aminofluorene can undergo acetylation reactions that causes these reactive species to undergo such reactions in cells. Several experiments have been conducted that have suggested 2-aminofluorene be treated with care and with an overall awareness of the toxicity of this compound.
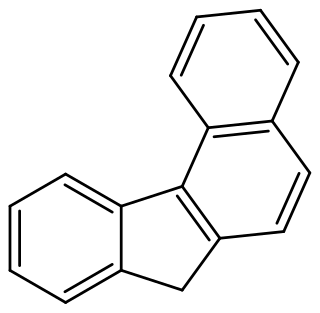
Benzo[c]fluorene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) with mutagenic activity. It is a component of coal tar, cigarette smoke and smog and thought to be a major contributor to its carcinogenic properties. The mutagenicity of benzo[c]fluorene is mainly attributed to formation of metabolites that are reactive and capable of forming DNA adducts. According to the KEGG it is a group 3 carcinogen. Other names for benzo[c]fluorene are 7H-benzo[c]fluorene, 3,4-benzofluorene, and NSC 89264.
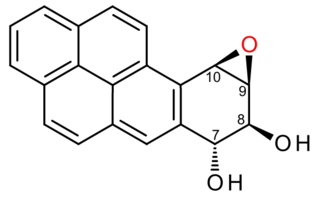
(+)-Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide is an organic compound with molecular formula C20H14O3. It is a metabolite and derivative of benzo[a]pyrene (found in tobacco smoke) as a result of oxidation to include hydroxyl and epoxide functionalities. (+)-Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide binds to the N2 atom of a guanine nucleobase in DNA, distorting the double helix structure by intercalation of the pyrene moiety between base pairs through π-stacking. The carcinogenic properties of tobacco smoking are attributed in part to this compound binding and inactivating the tumor suppression ability of certain genes, leading to genetic mutations and potentially to cancer.

4-Ipomeanol (4-IPO) is a pulmonary pre-toxin isolated from sweet potatoes infected with the fungus Fusarium solani. One of the 4-IPO metabolites is toxic to the lungs, liver and kidney in humans and animals. This metabolite can covalently bind to proteins, thereby interfering with normal cell processes.

The hydroxylation of estradiol is one of the major routes of metabolism of the estrogen steroid hormone estradiol. It is hydroxylated into the catechol estrogens 2-hydroxyestradiol and 4-hydroxyestradiol and into estriol (16α-hydroxyestradiol), reactions which are catalyzed by cytochrome P450 enzymes predominantly in the liver, but also in various other tissues.





















