Related Research Articles

Leda is a large, dark main-belt asteroid that was discovered by French astronomer J. Chacornac on January 12, 1856, and named after Leda, the mother of Helen of Troy in Greek mythology. In the Tholen classification system, it is categorized as a carbonaceous C-type asteroid, while the Bus asteroid taxonomy system lists it as a Cgh asteroid. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration.
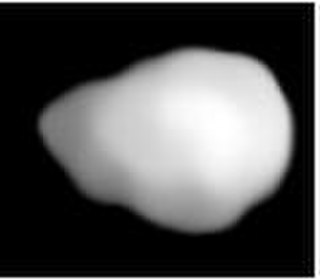
Daphne is a large asteroid from the asteroid belt. It is a dark-surfaced body 174 km in diameter is probably composed of primitive carbonaceous chondrites. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration. It was discovered by H. Goldschmidt on May 22, 1856, and named after Daphne, the nymph in Greek mythology who was turned into a laurel tree. Incorrect orbital calculations initially resulted in 56 Melete being mistaken for a second sighting of Daphne. Daphne was not sighted again until August 31, 1862.

Artemis is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by J. C. Watson on September 16, 1868, at Ann Arbor, Michigan. It was named after Artemis, the goddess of the hunt, Moon, and crossways in Greek Mythology.

Felicitas is a dark and fairly large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by German-American astronomer C. H. F. Peters on October 9, 1869, and named after Felicitas, the Roman goddess of success. The only observed stellar occultation by Felicitas is one from Japan.

Ate is a main-belt asteroid discovered by the German-American astronomer C. H. F. Peters on August 14, 1870, and named after Ate, the goddess of mischief and destruction in Greek mythology. In the Tholen classification system, it is categorized as a carbonaceous C-type asteroid, while the Bus asteroid taxonomy system lists it as an Ch asteroid.

Kassandra is a large and dark main-belt asteroid. It belongs to the rare class T. It was discovered by C. H. F. Peters on July 23, 1871, and is named after Cassandra, the prophetess in the tales of the Trojan War. The asteroid is featured in the 2009 film Meteor, in which it is split in two by a comet, and set on a collision course with Earth.

Johanna is a large, dark main-belt asteroid that was discovered by French astronomers Paul Henry and Prosper Henry on 5 November 1872, and is believed to be named after Joan of Arc. It is classified as a CX-type asteroid, indicating the spectrum shows properties of both a carbonaceous C-type asteroid and a metallic X-type asteroid.

137 Meliboea is a large, dark main-belt asteroid that was discovered by Austrian astronomer J. Palisa at the Austrian Naval Observatory on 21 April 1874, the second of his many asteroid discoveries. It was later named after Meliboea, the daughter of Oceanus and Tethys in Greek mythology. The largest body in the Meliboea family of asteroids that share similar orbital elements, only 791 Ani approaches its size. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and may be composed of carbonaceous materials. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration.
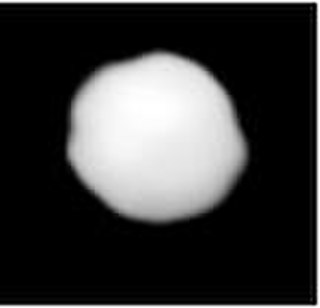
Adeona is a large asteroid from the intermediate asteroid belt, approximately 150 kilometers in diameter. Its surface is very dark, and, based upon its classification as a C-type asteroid, is probably composed of primitive carbonaceous material. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration. The Adeona family of asteroids is named after it.
Isolda is a very large, dark main-belt asteroid. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of primitive carbonaceous material. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration.

225 Henrietta is a very large outer main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on April 19, 1882, in Vienna and named after Henrietta, wife of astronomer Pierre J. C. Janssen. The asteroid is orbiting at a distance of 3.39 AU from the Sun with a period of 6.24 years and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.26. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 20.9° to the plane of the ecliptic. 225 Henrietta belongs to Cybele group of asteroids and is probably in a 4:7 orbital resonance with the planet Jupiter.

Eukrate is a rather large main-belt asteroid. It is dark and probably a primitive carbonaceous body. The asteroid was discovered by Robert Luther on March 14, 1885, in Düsseldorf. It was named after Eucrate, a Nereid in Greek mythology.

Aline is a fairly large main belt asteroid that was discovered by Johann Palisa on 17 May 1887 in Vienna and is thought to have been named after the daughter of astronomer Edmund Weiss. It is a dark C-type asteroid and is probably composed of primitive carbonaceous material. 266 Aline is orbiting close to a 5:2 mean motion resonance with Jupiter, which is located at 2.824 AU.

Chaldaea is a large Main belt asteroid. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on 30 August 1891 in Vienna. It was named in honor of the Chaldeans, considered the founders of astrology.

Lacadiera is a large Main belt asteroid. It is classified as a D-type asteroid and is probably composed of organic rich silicates, carbon and anhydrous silicates. The asteroid was discovered by Auguste Charlois on 19 September 1892 in Nice.
Thia is a very large main-belt asteroid. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material. This object was discovered by Auguste Charlois on July 23, 1895, in Nice, and was named after Theia, a Titaness in Greek mythology.
Lotis is a large Main belt asteroid. It is classified as a probable C-type asteroid and is likely composed of primitive carbonaceous materials. This object was discovered by Auguste Charlois on 23 November 1897 in Nice.
Gyptis, minor planet designation: 444 Gyptis, is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by J. Coggia on March 31, 1899, in Marseilles. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration.

Cava is a minor planet orbiting the Sun.
712 Boliviana is a C-type asteroid from the asteroid belt, with the type indicating the surface has a low albedo with high carbonaceous content. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration. It is named after Simón Bolívar.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "488 Kreusa (1902 JG)". JPL Small-Body Database . NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory . Retrieved 6 May 2016.
- ↑ "Creüsa". Dictionary.com Unabridged (Online). n.d.
- ↑ AstDys-2 on (488) Kreusa Retrieved 2012-01-03
- 1 2 3 Carry, B. (December 2012), "Density of asteroids", Planetary and Space Science, 73 (1): 98–118, arXiv: 1203.4336 , Bibcode:2012P&SS...73...98C, doi:10.1016/j.pss.2012.03.009.See Table 1.
- ↑ Fornasier, S.; et al. (February 1999), "Spectroscopic comparison of aqueous altered asteroids with CM2 carbonaceous chondrite meteorites", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement, 135: 65−73, Bibcode:1999A&AS..135...65F, doi: 10.1051/aas:1999161 .
- ↑ Magri, Christopher; et al. (January 2007), "A radar survey of main-belt asteroids: Arecibo observations of 55 objects during 1999 2003" (PDF), Icarus, 186 (1): 126–151, Bibcode:2007Icar..186..126M, doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2006.08.018 , retrieved 14 April 2015.