
Lumen is a carbonaceous asteroid from the intermediate asteroid belt, approximately 130 kilometers in diameter. It is an identified Eunomian interloper.

Circe, minor planet designation 34 Circe, is a large, very dark main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by French astronomer J. Chacornac on April 6, 1855, and named after Circe, the bewitching queen of Aeaea island in Greek mythology.
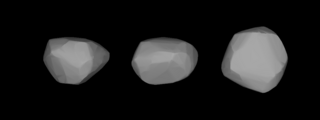
Kalypso is a large and very dark main belt asteroid that was discovered by German astronomer Robert Luther on April 4, 1858, at Düsseldorf. It is named after Calypso, a sea nymph in Greek mythology, a name it shares with Calypso, a moon of Saturn.

137 Meliboea is a large, dark main-belt asteroid that was discovered by Austrian astronomer J. Palisa at the Austrian Naval Observatory on 21 April 1874, the second of his many asteroid discoveries. It was later named after Meliboea, the daughter of Oceanus and Tethys in Greek mythology. The largest body in the Meliboea family of asteroids that share similar orbital elements, only 791 Ani approaches its size. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and may be composed of carbonaceous materials. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration.

165 Loreley is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by C. H. F. Peters on August 9, 1876, in Clinton, New York and named after the Lorelei, a figure in German folklore.

Eos is a large main-belt asteroid that was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on January 18, 1882, in Vienna. In 1884, it was named after Eos, the Greek goddess of the dawn, to honour the opening of a new observatory that was hoped to bring about a new dawn for Viennese astronomy.
Aletheia is a very large main-belt asteroid that was discovered by German–American astronomer Christian Peters on June 28, 1886, at Litchfield Observatory, Clinton, New York. The dark and heterogeneously composed X-type asteroid contains primitive carbonaceous materials, responsible for its low albedo of 0.04. Aletheia measures about 185 kilometers in diameter and belongs to the largest asteroids of the main-belt. It has a semi-major axis of 3.1 AU and an orbit inclined by 11 degrees with a period of 5.55 years.

Phaeo is an asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 70 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 27 November 1891, by French astronomer Alphonse Borrelly at the Marseille Observatory in southern France. The presumably metallic X-type asteroid is the principal body of the Phaeo family and has a rotation period of 17.6 hours. It was named for the Greek mythological figure Phaeo, one of the Hyades or nymphs. Several other asteroids were named for other of the Hyades – 106 Dione, 158 Koronis, 217 Eudora, and 308 Polyxo.

Gudrun is a main-belt asteroid.

Siegena is a very large main-belt asteroid. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of primitive carbonaceous material.
Thia is a very large main-belt asteroid. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material. This object was discovered by Auguste Charlois on July 23, 1895, in Nice, and was named after Theia, a Titaness in Greek mythology.
Aurelia is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by German astronomer Max Wolf on September 7, 1896, in Heidelberg. It is classified as an F-type asteroid.
Eichsfeldia is a large main belt asteroid that was discovered by German astronomers Max Wolf and A. Schwassmann on 15 February 1899 in Heidelberg. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of primitive carbonaceous material.

2002 Euler is a stony background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 17 kilometers (11 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 29 August 1973, by Russian astronomer Tamara Smirnova at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory in Nauchnyj, and assigned the prov. designation 1973 QQ1. It was named after Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler.
Patientia is approximately the 15th-largest asteroid in the asteroid belt with a diameter of 225 km. It was discovered by French astronomer Auguste Charlois on 4 December 1899, and assigned a provisional designation 1899 EY.
Evelyn is a main belt asteroid discovered by Raymond Smith Dugan on 19 January 1903. The asteroid was named after Evelyn Smith Dugan, mother of the discoverer.

Sylvania is a minor planet orbiting the Sun in the main belt. It was discovered on 20 October 1903 by American astronomer R. S. Dugan at the Heidelberg observatory. The name is Latin for forest lands. 519 Sylvania is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.79 AU with an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.186 and a period of 4.66 yr. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 11.0° to the ecliptic. This S-type (stony) asteroid has an estimated diameter of 48 km and is revolving with a period of 17.962 h.

747 Winchester is an asteroid, a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered in 1913, and is named after the town in which it was discovered, Winchester, Massachusetts, in the USA.

776 Berbericia is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. A main-belt C-type asteroid, it was discovered on 24 January 1914 by astronomer Adam Massinger at Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany. It was named by Max Wolf in honor of Adolf Berberich (1861–1920), a German astronomer. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration.
804 Hispania is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered from Barcelona (Spain) on 20 March 1915 by Josep Comas Solá (1868–1937), the first asteroid to be discovered by a Spaniard.













