Related Research Articles

511 Davida is a large C-type asteroid in the asteroid belt. It is one of the largest asteroids; approximately tied for 7th place, to within measurement uncertainties, and the 5th or 6th most massive. It was discovered by R. S. Dugan in 1903. Davida is named after David Peck Todd, an astronomy professor at Amherst College.
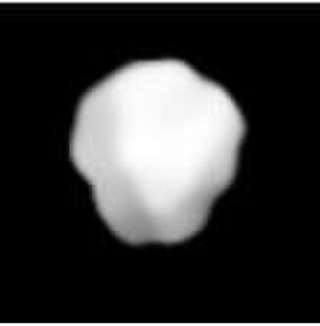
11 Parthenope is a large, bright main-belt asteroid.

13 Egeria is a large main-belt G-type asteroid. It was discovered by Annibale de Gasparis on November 2, 1850. Egeria was named by Urbain Le Verrier, whose computations led to the discovery of Neptune, after the mythological nymph Egeria of Aricia, Italy, the wife of Numa Pompilius, second king of Rome.

17 Thetis is a stony asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 90 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 17 April 1852, by German astronomer Robert Luther at Bilk Observatory in Düsseldorf, Germany who deferred to Friedrich Wilhelm August Argelander the naming his first asteroid discovery after Thetis from Greek mythology. Its historical symbol was a dolphin and a star; it is in the pipeline for Unicode 17.0 as U+1CECA .

160 Una is a fairly large and dark, primitive Main belt asteroid that was discovered by German-American astronomer C. H. F. Peters on February 20, 1876, in Clinton, New York. It is named after a character in Edmund Spenser's epic poem The Faerie Queene (1590).

167 Urda is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by German-American astronomer Christian Heinrich Friedrich Peters on August 28, 1876, in Clinton, New York, and named after Urd, one of the Norns in Norse mythology. In 1905, Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa showed that the asteroid varied in brightness.

170 Maria is a Main belt asteroid that was discovered by French astronomer Henri Joseph Perrotin on January 10, 1877. Its orbit was computed by Antonio Abetti, and the asteroid was named after his sister, Maria. This is the namesake of the Maria asteroid family; one of the first asteroid families to be identified by Japanese astronomer Kiyotsugu Hirayama in 1918.

176 Iduna is a large main-belt asteroid that was discovered by German-American astronomer Christian Heinrich Friedrich Peters on October 14, 1877, in Clinton, New York. It is named after Sällskapet Idun, a club in Stockholm that hosted an astronomical conference; Idun is also a Norse goddess. A G-type asteroid, it has a composition similar to that of the largest main-belt asteroid, 1 Ceres.

190 Ismene is a very large main belt asteroid. It was discovered by German-American astronomer C. H. F. Peters on September 22, 1878, in Clinton, New York, and named after Ismene, the sister of Antigone in Greek mythology.
275 Sapientia is a very large Main belt asteroid that was discovered by Johann Palisa on 15 April 1888 in Vienna. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material. It is named for the Roman personification of wisdom, Sapientia.

348 May is a large Main belt asteroid. It was discovered by Auguste Charlois on 28 November 1892 in Nice, and was named for the German author Karl May. This asteroid is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.97 AU with a period of 5.12 years and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.067. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 9.7° to the plane of the ecliptic. During its orbit, this asteroid has made close approaches to the dwarf planet Ceres. For example, in September 1984 the two were separated by 6.3 Gm (0.042 AU).
412 Elisabetha is a large main belt asteroid that was discovered by German astronomer Max Wolf on 7 January 1896 in Heidelberg. It may have been named after his mother, Elise Wolf. This minor planet is orbiting at a distance of 2.76 AU from the Sun with a period of 4.59 years and an orbital eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.044. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 13.8° to the plane of the ecliptic.
421 Zähringia, provisional designation 1896 CZ, is a stony asteroid from the intermediate asteroid belt, approximately 14 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 7 September 1896, by astronomer Max Wolf at Heidelberg Observatory in Germany. The asteroid was named for the House of Zähringen, a medieval noble family that ruled parts of Swabia and Switzerland.

19521 Chaos is a cubewano, a Kuiper-belt object not in resonance with any planet. Chaos was discovered in 1998 by the Deep Ecliptic Survey with Kitt Peak's 4 m telescope. Its albedo is 0.050+0.030
−0.016, making it, with its absolute magnitude (H) of 4.8, equivalent to a single spherical body 600+140
−130 km in diameter.

578 Happelia is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. On 24 February 2017 a possible small 3-kilometer moon was found orbiting the asteroid, based on occultation observations.
618 Elfriede is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. On July 24, 2013, it occulted the magnitude 12.8 star 2UCAC 23949304, over parts of Mexico and southwestern United States.

683 Lanzia is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered July 23, 1909, by Max Wolf at the Landessternwarte Heidelberg-Königstuhl observatory and was named in honor of Lanz, founder of the Heidelberg Academy of Sciences. Photometric observations made in 2003 at the Santana Observatory in Rancho Cucamonga, California, give a synodic rotation period of 8.63 ± 0.005 hours. The light curve shows a brightness variation of 0.15 ± 0.04 in magnitude.

705 Erminia is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. Its name derives from the comic opera Erminie. An occultation on 8 December 2014 gave 3 chords, with one measurement suggesting a small moon 6-10 kilometers wide at a distance of 400 kilometers to the primary.
(85633) 1998 KR65 (provisional designation 1998 KR65) is a trans-Neptunian object from the classical Kuiper belt, located in the outermost region of the Solar System. The cubewano belongs to the cold population. It has a perihelion (closest approach to the Sun) at 42.385 AU and an aphelion (farthest approach from the Sun) at 44.859 AU. It is about 192 km in diameter. It was discovered on 29 May 1998, by Gary M. Bernstein.
23135 Pheidas (provisional designation 2000 AN146) is a large Jupiter trojan from the Greek camp, approximately 66 kilometers (41 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 7 January 2000, by astronomers with the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States. The dark Jovian asteroid belongs to the 50 largest Jupiter trojans and has a rotation period of 8.7 hours. It was named after the Athenian warrior Pheidas from Greek mythology.
References
- 1 2 "693 Zerbinetta (1909 HN)". JPL Small-Body Database . NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory . Retrieved 11 April 2016.
- ↑ "Discovery Circumstances: Numbered Minor Planets". Minor Planet Center . Retrieved 18 May 2015.