
Melete is a large and dark main belt asteroid. It is a rather unusual P-type asteroid, probably composed of organic rich silicates, carbon and anhydrous silicates, with possible internal water ice. The asteroid orbits the Sun with a period of 4.18 years.

Bertha is a main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by the French brothers Paul Henry and Prosper Henry on 4 November 1875, but the credit for the discovery was given to Prosper. It is probably named after Berthe Martin-Flammarion, sister of the astronomer Camille Flammarion.

164 Eva is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by the French brothers Paul Henry and Prosper Henry on July 12, 1876, in Paris. The reason the name Eva was chosen remains unknown. The orbital elements for 164 Eva were published in 1877 by American astronomer Winslow Upton. It is categorized as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of primitive carbonaceous chondritic materials.

Atropos is a typical Main belt asteroid that was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on 8 March 1888 in Vienna.
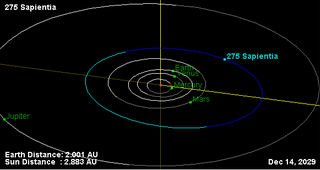
Sapientia is a very large Main belt asteroid that was discovered by Johann Palisa on 15 April 1888 in Vienna. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material. It is named for the Roman personification of wisdom, Sapientia.

Corduba is a very large main-belt asteroid that was discovered by the French astronomer Auguste Charlois on 21 March 1893 from Nice. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material.

Ducrosa is a typical Main belt asteroid. It was discovered by Auguste Charlois on 15 March 1895 in Nice.

Aspasia is a large main-belt asteroid that was discovered by French astronomer Auguste Charlois on 9 December 1895 in Nice. It is classified as a CX-type asteroid.
Cheruskia is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt that was discovered by German astronomer Paul Götz on 26 July 1905 from Heidelberg.

Rebekka is a minor planet orbiting the Sun, which was discovered on September 19, 1905, by a German astronomer Paul Götz in Heidelberg. It was named after a young lady from Heidelberg, and may have been inspired by the asteroid's provisional designation 1905 RB.
Bilkis is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt. It was discovered by German astronomer August Kopff in 1906 February and was given the Koran name for the Queen of Sheba. Photometric observations at the Palmer Divide Observatory in Colorado Springs, Colorado in 2006–7 were used to build a light curve for this object. The asteroid displayed a rotation period of 8.5742 ± 0.0005 hours and a brightness variation of 0.40 ± 0.02 in magnitude.

Juvisia is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt that was discovered 27 August 1906 in Heidelberg by German astronomer Max Wolf. It was named after the commune Juvisy-sur-Orge, France, where French astronomer Camille Flammarion had his observatory.
607 Jenny is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt that was discovered by German astronomer August Kopff on September 18, 1906.
620 Drakonia is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt. It was discovered October 26, 1906, in Taunton, Massachusetts, by American astronomer Joel Hastings Metcalf and given the preliminary designation 1906 WE. It may have been named for Drake University.
639 Latona is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt. It was discovered by German astronomer Karl Lohnert on July 19, 1907, at Heidelberg.
687 Tinette is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting primarily in the asteroid belt. It was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on 16 August 1909 from Vienna and was given the preliminary designation 1909 HG.

708 Raphaela is a minor planet orbiting the Sun.
793 Arizona is a minor planet orbiting the Sun that was discovered April 9, 1907 by American businessman Percival Lowell at Flagstaff. It was named for the state of Arizona. The object was independently discovered on April 17, 1907, by J. H. Metcalf at Taunton. This is a main belt asteroid orbiting 2.8 AU from the Sun with a period of 4.675 yr and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.13. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 15.8° to the plane of the ecliptic.
840 Zenobia is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered by German astronomer Max Wolf at Heidelberg on September 25, 1916. The origin of the name is uncertain, but it may be named after the Slavic god of the hunt.
947 Monterosa is a minor planet orbiting the Sun.











