
Acacia melanoxylon, commonly known as the Australian blackwood, is an Acacia species native to south-eastern Australia. The species is also known as blackwood, hickory, mudgerabah, Tasmanian blackwood, or blackwood acacia. The tree belongs to the Plurinerves section of Acacia and is one of the most wide-ranging tree species in eastern Australia and is quite variable mostly in the size and shape of the phyllodes.

Acacia salicina is a thornless species of Acacia native to Australia. It is a large shrub or small evergreen tree growing up to 13.7 m tall. It is a fast grower, dropping lots of leaf litter, with a life span of about 10–50 years. In its native range, A. salicina flowers from February to June. In the Northern Hemisphere, A. salicina flowers primarily from October to January and the seed pods are often visible from April to July. The tree's seeds are shiny, black and have a crimson appendage-like aril. A. salicina is "closely related" to Acacia ligulata and Acacia bivenosa.

Acacia meiantha is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to a small area in eastern Australia. It was listed as Endangered in 2018 according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.

Acacia neriifolia, also known as the oleander wattle, silver wattle or pechy wattle, is a tree in the genus Acacia native to north eastern Australia. It is common in the Moonbi Ranges.

Acacia bakeri, known as the marblewood, white marblewood, Baker's wattle or scrub wattle, is one of the largest of all acacias, growing to 40 m (130 ft) tall. It is a long-lived climax rainforest tree from eastern Australia. Unlike most acacias, fire is not required for seed germination. This tree is considered vulnerable to extinction. Its former habitat is lowland subtropical rainforest, which has been mostly cleared in the 19th and 20th centuries.

Acacia effusifolia is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to an area in the Mid West and the Wheatbelt regions of Western Australia.

Acacia orthocarpa, also commonly known as Pilbara weeping wattle, needle-leaf wattle or straight-podded wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to tropical parts of northern Australia. The indigenous Nyangumarta peoples know it as yartupu.
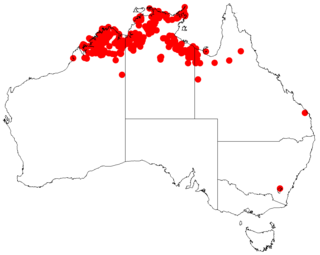
Acacia plectocarpa is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemism to north western Australia.
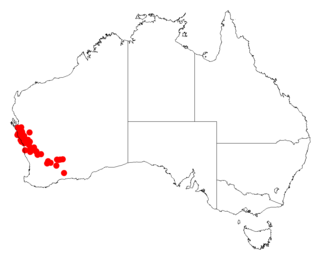
Acacia signata is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia umbraculiformis, commonly known as western umbrella wattle, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae native to western Australia.

Acacia eremaea is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area in western Australia.

Acacia trineura, known colloquially as three-nerve wattle or three nerved wattle or green wattle, is a species of Acacia native to south eastern Australia.

Acacia pilligaensis, commonly known as Pillaga wattle or pinbush wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.

Acacia torringtonensis is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and is endemic to a small area in northern New South Wales in Australia. It is an erect or spreading shrub with crowded, linear to narrowly elliptic phyllodes and spherical head of yellow to bright yellow flowers.

Acacia doratoxylon, commonly known as currawang, lancewood, spearwood or coast myall, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to eastern and south eastern Australia.

Acacia multistipulosa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to northern Australia.

Acacia spania, also known as western rosewood, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to north eastern Australia.

Acacia rhodoxylon, also known as rosewood, ringy rosewood or spear wattle, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia excelsa, also known as ironwood, rosewood, bunkerman and doodlallie is a tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to inland parts of north-eastern Australia. In the Gamilaraay language it is known as dhan, gayan or gan.

Acacia melvillei, commonly known as yarran, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to south eastern Australia.





















