
Acacia harpophylla, commonly known as brigalow, brigalow spearwood or orkor, is an endemic tree of Australia. The Aboriginal Australian group the Gamilaraay peoples know the tree as Barranbaa or Burrii. It is found in central and coastal Queensland to northern New South Wales. It can reach up to 25 m (82 ft) tall and forms extensive open-forest communities on clay soils.
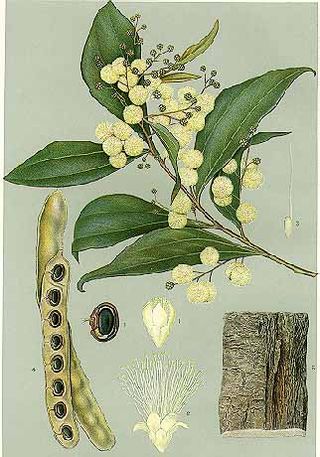
Acacia binervata, commonly known as two-veined hickory, is a shrub or tree that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia concurrens, commonly known as curracabah or black wattle, is a shrub native to Queensland in eastern Australia.

Acacia calcicola is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is native to parts of central Australia. Common names for this species include; shrubby wattle, shrubby mulga, myall-gidgee, northern myall and grey myall. Indigenous Australians the Pitjantjatjara peoples know the tree as ikatuka, the Warlpiri know it as jirlarti and the Arrernte know it as irrakwetye.

Acacia eremaea is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area in western Australia.

Acacia crassa, commonly known as the curracabah, is a species of Acacia native to eastern Australia.

Acacia subtilinervis, also known as the net-veined wattle, is a rare wattle in the Juliflorae subgenus found in eastern Australia.

Acacia burbidgeae, commonly known as Burbidge's wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to parts of New South Wales and Queensland.

Acacia conferta, commonly known as crowded-leaf wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia costiniana, commonly known as Costin's wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia ensifolia is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to Queensland.

Acacia falciformis, also commonly known as broad-leaved hickory, hickory wattle, mountain hickory, large-leaf wattle, tanning wattle and black wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to eastern Australia

Acacia pilligaensis, commonly known as Pillaga wattle or pinbush wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.

Acacia sertiformis, commonly known as curly-leaved wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia leichhardtii, commonly known as Leichhardt's wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to north eastern Australia.

Acacia blakei, commonly known as Blake's wattle or Wollomombi wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia cretata is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia mariae, commonly known as golden-top wattle or crowned wattle, is a species of wattle native to central New South Wales.

Acacia baeuerlenii is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in eastern Australia.

Acacia microsperma, commonly known as bowyakka, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of eastern Australia]. It is rated as least concern according to the Nature Conservation Act 1992.




















