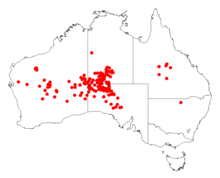
Acacia papyrocarpa, commonly known as western myall, is a tree in the family Fabaceae native to arid areas of central and western Australia.
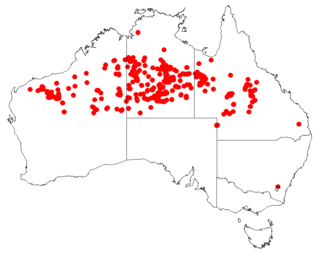
Acacia adsurgens is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to the northern areas of Australia.

Acacia catenulata, commonly known as bendee, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to some arid areas in Australia.

Acacia clelandii, also known as umbrella mulga, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to arid parts of central Australia.

Acacia intorta is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to arid parts of central Western Australia.

Acacia lirellata is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia paraneura, commonly known as weeping mulga, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to arid regions of Australia. The Indigenous Kurrama peoples know the tree as warlun.

Acacia rhodophloia, commonly known as minni ritchi or western red mulga, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to a large area of arid central western Australia. The Indigenous group the Kurrama peoples know the plant as mantaru.

Acacia stipuligera is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to arid and tropical parts of northern Australia.

Acacia symonii, also known commonly as Symon's wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to parts of arid central Australia.

Acacia thomsonii, commonly known as Thomson's wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that native to parts of northern Australia.

Acacia trachycarpa, commonly known as minni ritchi, curly-bark tree, sweet-scented minni ritchi or Pilbara minni ritchi, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to arid and semi-arid areas of Western Australia.

Acacia basedowii, commonly known as Basedow's wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae endemic to arid parts of central Australia.
Acacia blaxellii, also known as Blaxell's wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae endemic to Western Australia.

Acacia concolorans is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to Western Australia.

Acacia cuneifolia is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae endemic to south western parts of Australia.

Acacia laricina is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia trulliformis is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia lateriticola is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Pulchellae that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia alleniana is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae endemic to northern parts of Australia.